Material quality and process stability are crucial in modern industries. If you are a crystal growth operator, you already know how the purity of your crucible materials impacts your process.
Let’s explore how the performance, advantages, and uses of the silicon carbide crucible could benefit your manufacturing process.
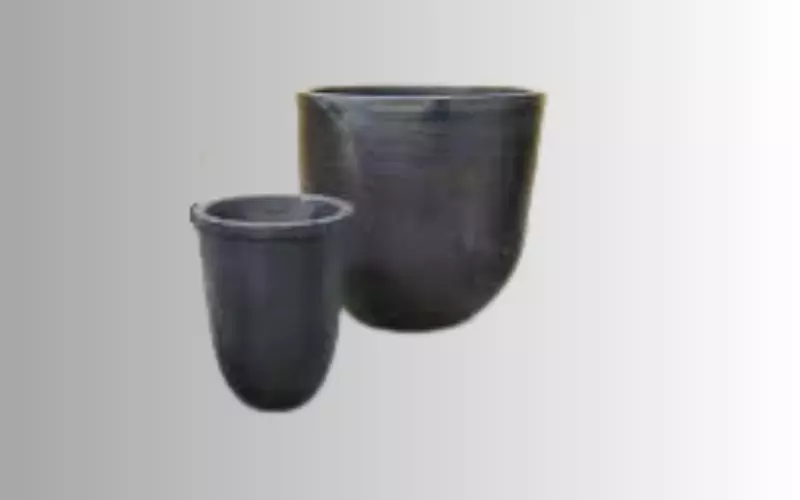

What Is a Silicon Carbide Crucible?
The silicon carbide crucible is a highly durable container you can use in advanced material melting and refining. It offers you an extremely pure and stable state at a high temperature above 1700 degrees Celsius. A silicon carbide crucible is actually a very hard ceramic compound.
You may also know a SiC crucible as a SiC graphite crucible, a type of graphite crucible. It is an ideal receptacle for high-temperature materials melting. You can employ this vessel to the composition of metals and compound materials.
Silicon carbide crucibles are excellent thermal conductors, which increases the efficiency of your melting process. They help you maintain even temperatures in material processing.
SiC crucibles are available in different sizes and shapes. Suppliers like Gorgeous Ceramics offer customized designs to meet your diverse needs.

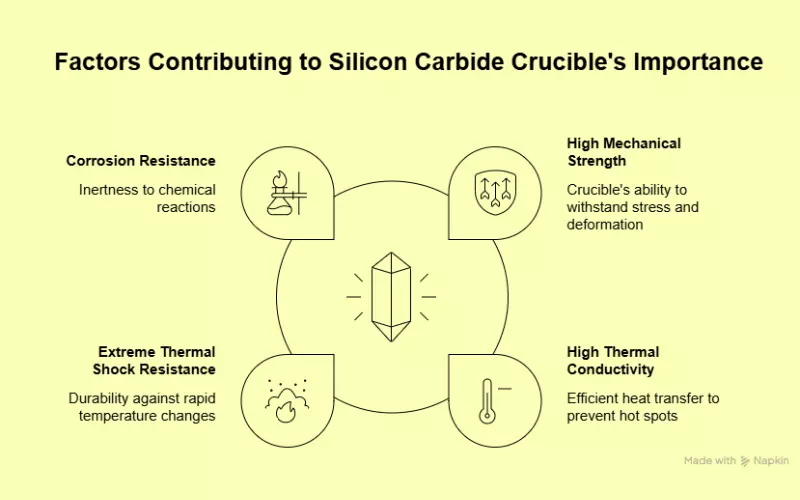
Why Is The Silicon Carbide Crucible Important in Crystal Growth?
Crystal growth for advanced semiconductors requires you to reach extremely high temperatures over 1400 degrees. Maintaining the purity of your materials in this high-temperature process is difficult. In such material processing, your crucible integrity is essential for crystal quality.
Silicon carbide crucibles are important for the crystal growth because of their:
High Mechanical Strength: Silicon carbide crucibles have high mechanical strength due to their unique compound structure. They are the complex compound of silicon (Si) and carbon (C) elements.
Silicon and carbon atoms in the SiC crucible create a strong covalent bond and a three-dimensional structure. These carbon-bonded silicon carbide crucibles offer you exceptional strength and hardness.
The Mohs hardness scale of silicon carbide is 9.5, which is the second highest after diamond. This indicates that your SiC crucible can remain stable under extreme mechanical stress and withstand deformation and cracking. Thus, it ensures your system’s success.
For these reasons, your SiC crucibles enhance purity, reduce deformation, and prevent cracking of advanced semiconductor and PV crystals.
High Thermal Conductivity: The excellent thermal conductivity of silicon carbide crucibles can prevent spot heating with their quick, even heat transfer capability. It improves the efficiency of crystal growth. They can also prevent heat loss and ensure process consistency.
Extreme Thermal Shock Resistance: Silicon carbide crucibles are extremely resistant to thermal shock due to high thermal conductivity and low thermal expansion.
Thermal shock resistance makes the crucibles durable and can prevent cracking in fast heating or cooling processes. So, the SiC crucibles improve crystal quality and enhance productivity and the components’ lifespan.
Corrosion Resistance: Silicon carbide crucibles are chemically inert and have high oxidation resistance. They are resistant to corrosion in a harsh chemical environment.
They can oppose most acids, salts, and bases by creating a protective layer of silicon dioxide (SiO₂) to avoid oxidation. They also can prevent metal oxide erosion and work against corrosive media.
However, the corrosion resistance of the silica carbide crucible resists high-temperature silicon vapor. It ensures a stable thermal field for pure, high-quality, defect-free crystals for the high-performance semiconductor and PVs.
Silicon Carbide vs Graphite Crucible: A Comparison Table
|
Features |
Silicon Carbide Crucible |
Graphite Crucible |
|
Thermal Shock Resistance |
SiC crucibles offers you excellent thermal shock resistance |
A graphite crucible offers moderate thermal shock resistance |
|
Chemical Inertness |
Silicon carbide crucibles are highly inert to the chemical reactions |
This crucible has lower inertness than SiC crucibles |
|
Mechanical Strength |
It has very high mechanical strength |
A graphite crucible has lower mechanical strength at extreme temperatures |
|
Carbon Contamination |
Silicon carbide crucible has minimal risk of contamination with carbon. |
A graphite crucible is comparatively prone to carbon contamination. |
|
Lifespan |
This crucible is popular for its longer lifespan and durability |
It has a shorter lifespan than the SiC Crucible. |
|
Price |
Silicon carbide crucible price is comparatively higher |
The graphite crucible price is lower. |

What Are the Uses of a Silicon Carbide Crucible?
Silicon carbide crucibles have wide applications in metal smelting. They are popular in extracting zinc, aluminum, copper, carbon steel, metal alloys, and non-ferrous metals. Here are the common fields of silicon carbide crucible uses.
Foundry and Metallurgy: You will find SiC crucibles in the melting, refining, and casting of all ferrous and non-ferrous metals and alloys. They are popular in metal melting, metal holding, induction and fuel fired furnaces, foundry casting, powder metallurgy, and laboratory analysis.
Glass and Ceramic: Glass and ceramic industries use SiC crucibles in melting, refining, and firing materials.
Some exceptional properties of the crucible help to produce high-quality dense ceramics. Excellent thermal shock resistance and durability of the container prevent cracking and ensure reliable performance in glassmaking and ceramic production.

Research and Chemistry Lab: The SiC crucible does not react with acids, bases, salts, or reactive substances. That is why you will find these crucible applications in most of the research and chemistry labs.
You can mix and process your research materials at high temperatures in the ceramic silicon carbide crucibles. The inertness of the crucible materials ensures contamination-free experiments.
Metal Casting and Jewelry: Jewelry metals (gold, silver, platinum) melting and casting is performed in silicon carbide crucibles. These vessels can dissipate heat evenly and prevent contamination of the precious metals.
The thermal insulation of the SiC vessel helps in cooling the molten metals. Thus, it contributes to making your jewelry piece a precisely cast, complex, and designed ornament.

Frequently Asked Questions:
1.What Is Crystal Growth?
Crystal growth is a process of growing crystals from a solution into a solid or crystalline lattice through molecular transition. The crystals formed on an existing “seed” crystal by supersaturation or supercooling.
2.What Are The Advantages of a Silicon Carbide Crucible?
Silicon carbide crucibles offer many advantages such as:
-
faster heating,
-
even heating,
-
break and leak prevention,
-
increased durability,
-
and contamination risk reduction.
3.What Is The Melting Point of Silicon Carbide?
The melting point refers to the temperature where a solid substance changes its state to the liquid. Silicon carbide does not melt at normal pressure. It transforms from the solid to the gas directly by a process called sublimation at around 2730 °C. So, the correct term for the silicon carbide is the sublimation point instead of the melting point.
4.Why Is Silicon Carbide Used in Semiconductors?
Silicon carbide (SiC) used in advanced semiconductor chips for its wide bandwidth. You will notice many uses of SiC semiconductor chips in modern electric vehicles (EVs) and data centers. These chips offer lighter weight, easy cooling, and high performance.
5.What Is Another Name for Silicon Carbide?
Carborundum is another name for silicon carbide. It is a compound material consisting of silicon and carbon with a density of around 3.21 g/cm³.
6.Is Silicon a Conductor or a Semiconductor?
Silicon is a semiconductor material in its pure form which acts in between insulators and conductors. Modified silicon is used in transistors by increasing its conductivity, and pure silicon is used as an insulator for sealing.
Conclusions
Learning the performance, advantages, and application of silicon carbide crucible helps you understand the impacts of them in advanced material processing. The SiC container performs high where other materials fail for its exceptional mechanical strength and extreme thermal shock resistance.
Selecting the SiC vessel ensures your success in material processing.