According to reports, since 2024, there have been more than 385 mass shootings in the United States. As a result, gun violence in 2024 has caused approximately 11,600 deaths.
In modern society, security issues are becoming more and more worthy of our attention. Most people have turned their attention to bulletproof materials. So what are the bulletproof materials? Read this article in depth and you will have different gains!

Quick Navigation
- Ballistic Testing Standards And Protection Levels
- Common Bulletproof Materials for Armor and Personal Protection
- What is The Best Bulletproof Material?
- Characteristics Of Bulletproof Ceramics
If you don’t have time to read the article, we have prepared some quick questions for you. I believe you can find the answers you need from them.
Ballistic Testing Standards And Protection Levels
Before understanding bulletproof materials, you should first understand some knowledge about ballistic testing standards and protection levels, which will help you choose the most suitable bulletproof material!
UL Standards
UL (Underwriters Laboratories) has eight grades for bulletproof materials:
- UL 1-3: Mainly for pistol bullets, such as 9mm and .357 Magnum.
- UL 4-6: For rifle ammunition, such as .30-06 and 7.62mm.
- UL 7-8: Can defend against high-powered ammunition and multiple impacts.
NIJ Standards
NIJ (National Institute of Justice) has four main grades from I to IV:
- Grade I: Can defend against small-caliber bullets such as .22LR.
- Grade II and Grade IIIA: Suitable for light bulletproof equipment for daily use, such as bulletproof vests.
- Grade III and Grade IV: Higher-grade materials can defend against rifle bullets and high-penetration ammunition, suitable for military and special protection needs.
Common Bulletproof Materials for Armor and Personal Protection
With the improvement of people’s awareness of protection, various bulletproof materials have emerged, covering lightweight and simple protective equipment and high-strength building materials. It should be clear that no material can completely protect against bullets. Currently known bulletproof products will be penetrated by the critical value of impact. However, these bulletproof materials can still play a very important role and can protect people from bullets to the greatest extent.
We will fully analyze these common bulletproof materials for you to help you understand them in depth.
Steel
Steel is the most well-known traditional building bulletproof material. The advantages of this type of material are high strength and good durability. Its strong mechanical strength can resist a variety of mechanical attacks.
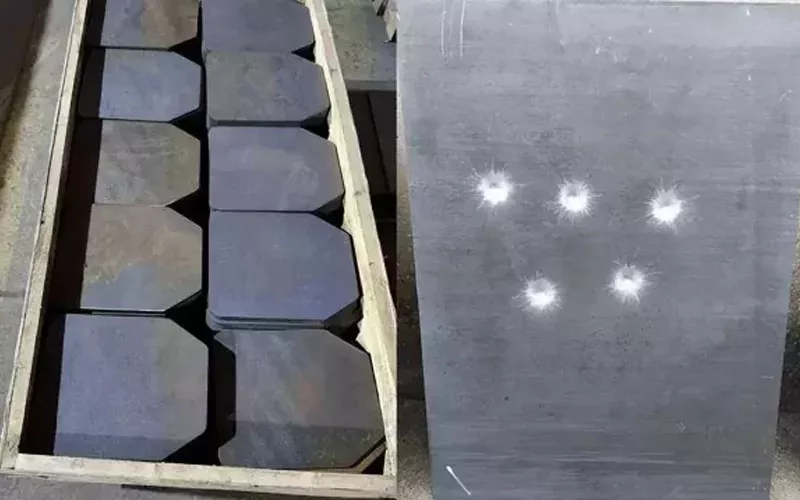
The bulletproof performance of steel is mainly determined by thickness and special surface treatment. The most common bulletproof steels on the market are wear-resistant (AR) steel, high-carbon alloy steel, etc. These steels can effectively resist the powerful impact of bullets and are the best type of steel for bulletproof effect.
Although steel has unparalleled bulletproof performance, its heavy weight and easy rust and corrosion are headaches, and additional protective treatment is required. In addition, steel is not beautiful, and it is obviously not an ideal material for buildings that require design and beauty.
Applicable scenarios: buildings, vehicles
Ceramics
Ceramic materials have become another common bulletproof material because of their extremely high hardness. Compared with steel, ceramics are harder and can more effectively disperse the energy of bullets, prevent bullet penetration, and are not easily corroded. Ceramics are about 37% lighter than steel, which makes them more convenient to install. At the same time, ceramics are cheaper than PE (polyethylene), making them a very cost-effective material.
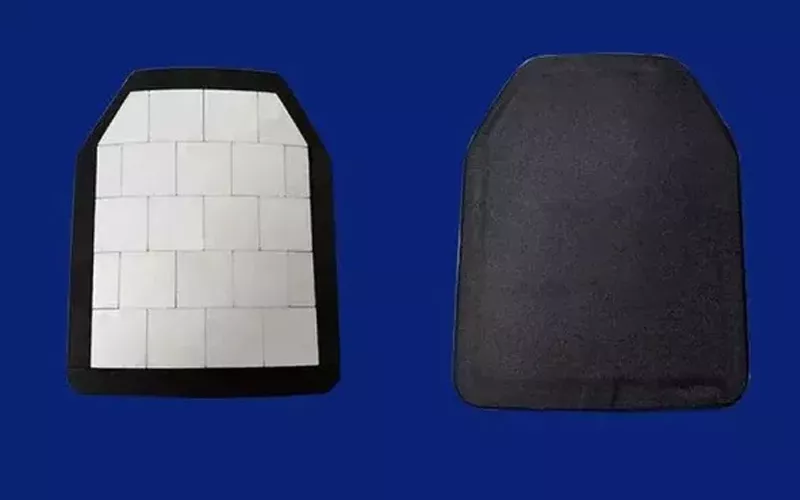

Common bulletproof ceramics include boron carbide, silicon nitride and silicon carbide, which are currently widely used in the military and security fields.
Of course, ceramic materials have more than just advantages. Bulletproof ceramics are brittle and prone to cracks. After multiple impacts, they are likely to break and lose their original protective capabilities. Therefore, in order to improve the protective capabilities of ceramics, they are usually used in combination with other materials (Kevlar and steel).
Applicable scenarios: personal equipment, armored vehicles
Fiber materials
Kevlar and Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) are two common fiber-based bulletproof materials, which are characterized by lightness and high strength.
Kevlar is often used to make protective equipment such as bulletproof vests and helmets, which can effectively absorb the kinetic energy of bullets and reduce the damage caused by impact to the human body.
Applicable scenarios: bulletproof vests, helmets
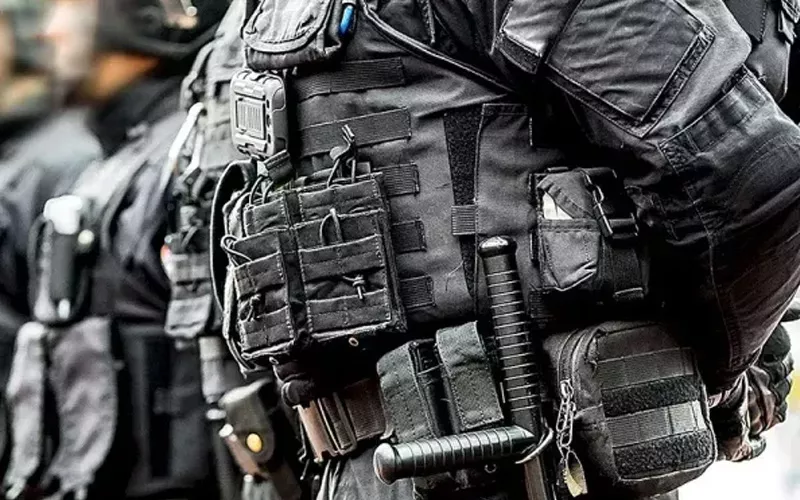

Polyethylene, referred to as PE, is a lightweight material with excellent impact resistance. Compared with Kevlar, it has better bullet resistance and can be used to make bulletproof shields, car windows and other building protection.
Applicable scenarios: bulletproof vests, shields
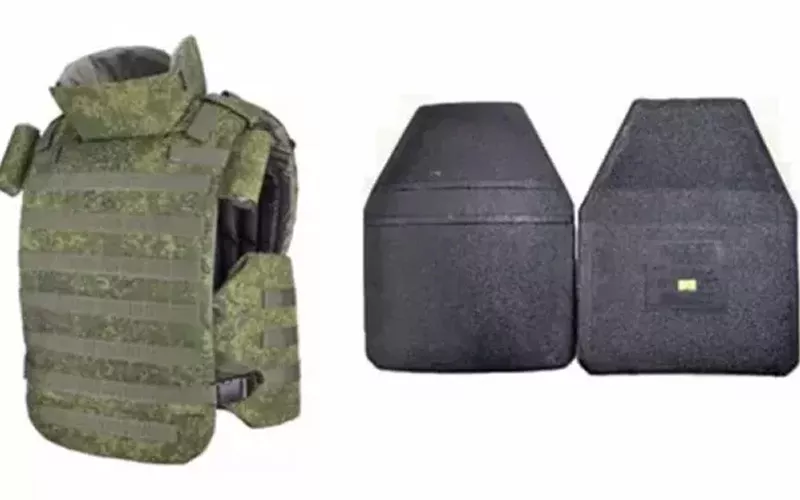

The lightness and portability of fiber materials are the main advantages, but their protective ability is relatively weak in the face of high-powered bullets.
Glass materials
Bulletproof glass is a very important transparent protective material, which is widely used in banks, airports and other places. Bulletproof glass is composed of multiple layers of glass and plastic (such as polycarbonate) alternating layers, which makes bulletproof glass transparent and beautiful while also having superior bulletproof capabilities.
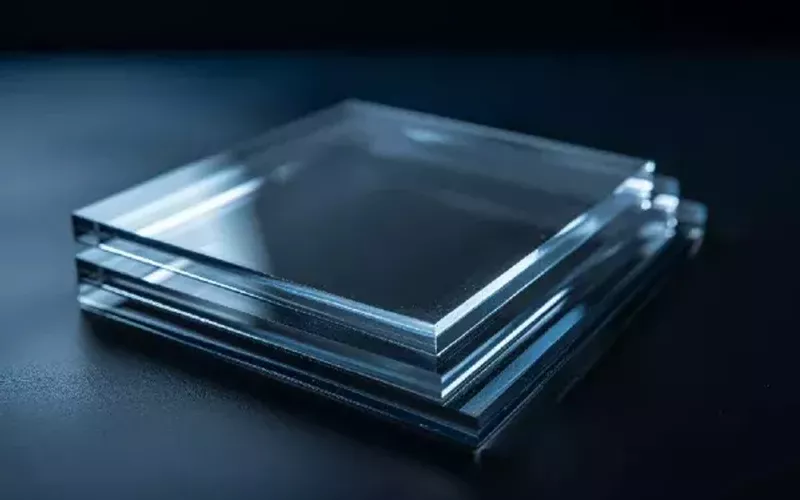

The bulletproof grade of bulletproof glass is determined by thickness and number of layers. High-grade bulletproof glass can resist high-powered firearm attacks. However, bulletproof glass also has the problems of heavy weight and high thickness, and the cost of installation and maintenance is high.
Applicable scenarios: banks, building windows
Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate is a transparent, high-strength plastic that is often used to make bulletproof windows and bulletproof panels.
Compared with ordinary glass, polycarbonate has better transparency and impact resistance, and is suitable for places where protection and transparency are required.
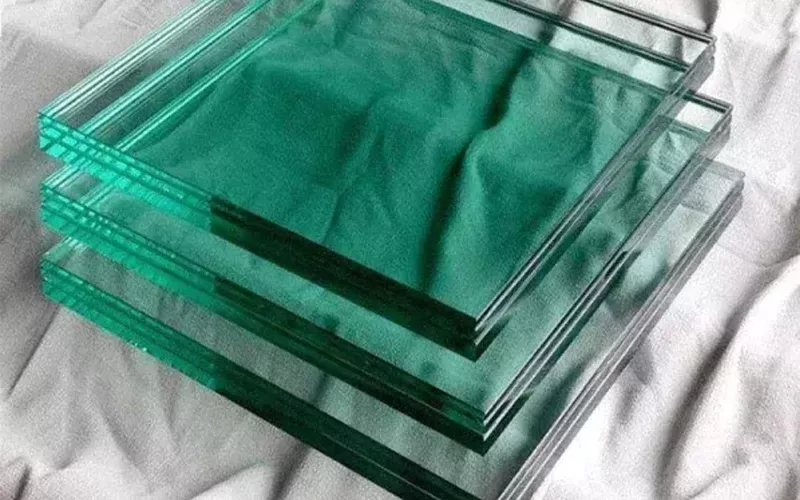

Of course, polycarbonate also has disadvantages. If exposed to ultraviolet rays for a long time, its surface will gradually turn yellow, seriously affecting its appearance and transparency.
Applicable scenarios: banks, building windows,HOLA’s LED display
Graphene - Future Trend
In the research and development of bulletproof materials, graphene has received attention. Some people wonder, is graphene bulletproof? Yes, as a new material, graphene is known as one of the “hardest materials in the world”. It has a tensile strength 200 times stronger than steel and can be very thin and light. It is an ideal bulletproof material and can be used as graphene bulletproof armor and graphene bulletproof vests.
In theory, graphene is expected to become the core material of the next generation of bulletproof technology, but at the current stage, due to the high cost and technology, graphene is still in the research stage. We believe that with the development of science and technology, graphene will soon become a new star in the new bulletproof material.
What is The Best Bulletproof Material?
The best bulletproof material often needs to be determined by specific application scenarios and needs. Below I will recommend some of the best bulletproof material options for common scenarios.
Personal protective equipment
Best material: polyethylene(Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene, UHMWPE)
Polyethylene is very light, which can reduce your wearing fatigue, and it has excellent impact resistance, but the obvious disadvantage is that you cannot use it in extremely hot environments.
Building protection
Best material: bulletproof glass + ceramic composite layer
Bulletproof glass can provide a good observation area for your residence, and the ceramic composite material can improve the hardness, which means that it retains the beauty and has good performance improvement. The disadvantage is that it is expensive and heavy.
Vehicle armor
Best material: ceramic (such as silicon boride or silicon carbide) + backing steel
Ceramics can effectively disperse the kinetic energy of bullets and cause them to break apart, while backing steel can provide better toughness support. The disadvantage is that ceramics are fragile and require maintenance.
Aerospace protection
Best material: graphene composite material
Graphene is very light and has a very high hardness, which can improve the overall efficiency. It is very suitable for the shell of space capsules and drone armor. The disadvantage is that it is expensive and has not been commercialized on a large scale.
Economical choice
Best material: Steel
Compared with other materials, steel is very cheap, very easy to process and maintain, and it can withstand high-powered bullets, making it a very economical choice! The disadvantage is that it is heavy and not easy to install and move.
Common materials comparison table
|
Material |
Protection level |
Advantages |
limitation |
|
Steel |
UL 1-8 |
High strength, high durability, easy processing |
Heavy and difficult to install |
|
Ceramics |
UL 4-8 |
High hardness, destroy bullets |
Fragile, heavy |
|
Kairav |
UL 2-3 |
Lightweight and easy to process |
High temperature sensitivity |
|
Polyethylene |
UL 2-4 |
Ultralight, impact-resistant |
Not resistant to high temperatures |
|
Bulletproof glass |
UL 3-8 |
Transparent and observable |
Heavy and difficult to install |
|
Polycarbonate |
UL 2-4 |
Transparent and light weight |
The protection performance is not as good as bulletproof glass |
|
Material |
Density(g/cm3 ) |
Protection level |
Relative Cost($/m2) |
|
Steel |
7.85 |
NIJ III-IV |
50-200 |
|
Ceramics(B4C) |
2.5-2.7 |
NIJ IV |
300-600 |
|
Kairav |
1.44 |
NIJ IIIA or below |
100-300 |
|
Polyethylene |
0.94 |
NIJ III or below |
200-500 |
|
Bulletproof glass |
2.5-2.8 |
NIJ IIA-III (depending on thickness) |
500-1000 |
*Please note that the protection rating is based on UL (Underwriters Laboratories) or NIJ (National Institute of Justice) standards, which indicate the protection against different types of bullets.The cost price is for reference only.
Characteristics Of Bulletproof Ceramics
Ceramic materials have been applied to all aspects of our lives and occupy an indispensable position. My police friend praised bulletproof ceramics. He shared his story with us. Because of the superior bulletproof performance of bulletproof ceramics, he survived the terrible bullet by chance… Yes, not only as bulletproof vests, ceramic materials have been widely used in military, police, security equipment and other fields. Bulletproof ceramics have gradually become an important part of modern protection systems.

Next, we will take you to understand the various bulletproof ceramics.
Excellent hardness and impact resistance
The core performance of bulletproof ceramics is hardness. Many ceramic materials have a hardness comparable to that of diamond. Among the many ceramic materials, compounds such as silicon carbide (SiC), boron nitride (BN) or silicon nitride (Si3N4) are commonly used for bulletproofing. These materials have excellent impact resistance, far exceeding that of steel.

In the face of high-speed bullet impacts, ceramics can be very effective and can disperse the energy of bullets to the greatest extent. After being hit by bullets at high speeds for many times, the surface of the ceramics will crack or break. This fragmentation phenomenon absorbs most of the energy. Even if the ceramics break, they can still effectively block bullets due to their hard structure and hardness. Therefore, some people often regard ceramics as the “first line of defense”. Hard ceramics can destroy the integrity of bullets, slow down the speed of bullets in flight, and protect humans from harm.
Lightweight and high performance
Ceramics are much lighter than traditional steel concrete, which makes them the first choice for military bulletproof materials. Even for heavy protective facilities that need to withstand a lot of impact, ceramics can provide superior impact resistance.
If lighter ceramics are combined with fiber materials such as Kevlar, they can be made into bulletproof vests, which not only ensures lightweight efficiency but also improves protective performance.
With reasonable matching materials, bulletproof ceramics can not only reduce the burden on equipment, but also achieve optimal energy absorption in multi-layer protection. This is why bulletproof ceramics are loved by so many people.
Multilayer structure and enhanced performance
I mentioned in the previous section that ceramics can be combined with other materials to improve performance. Yes, the protective performance of bulletproof ceramics is enhanced by multilayer design. The brittleness of a single layer of ceramics loses its protective ability after being subjected to multi-layer impact. Therefore, if ceramics are combined with polyethylene, steel plates or Kevlar, a multilayer composite structure is formed. Using ceramics as the first layer or core layer can play a key role in absorbing the bullet by relying on hardness and brittleness, while the second layer can use more flexible materials to absorb the remaining impact energy.
This not only enhances the overall protective ability, but also extends the service life of bulletproof equipment.
High temperature resistance and durability
Ceramic materials have excellent high temperature resistance, which allows them to maintain excellent protection in extreme high temperatures, especially the high temperatures generated by bullet impact. Many bulletproof ceramic materials are more stable than metal materials in high temperatures, which is extremely important for battlefields in harsh environments. In the face of explosions or fires, ceramic materials can provide longer protection and stability.
At the same time, corrosion resistance is also a very prominent feature of ceramic materials. This property prevents bulletproof ceramics from being easily affected by weather, humidity, and salt spray, and has a longer service life, reducing the frequency of maintenance and replacement.
Cost
Although ceramics have outstanding performance, they are expensive, especially high-end ceramic materials such as silicon carbide and silicon nitride. The processing technology of ceramics requires precise instruments and high-temperature firing. At the same time, ceramic materials are not easy to install. The high brittleness means that if they are not installed properly, large-scale damage may occur after impact.
But the good news is that with the advancement of technology and the improvement of production technology, the production cost of ceramic materials has gradually decreased, and more and more fields can use ceramics as the preferred option for protection.
Conclusion
As the global security needs grow, bulletproof materials play an increasingly important role in protecting individuals and facilities from impact damage. From traditional steel to modern composite materials, bulletproof technology is constantly improving to meet increasingly complex security challenges.
If you need high-quality bulletproof ceramic materials, choose GORGEOUS!
FAQs About Bulletproof Materials and Their Applications
1.Bulletproof Meaning?
“Ballistic resistance” refers to the ability of materials or products to resist penetration or damage by bullets or shrapnel, providing effective protection against ballistic threats.
2.Bulletproof Means?
“Ballistic protection” generally refers to the use of various methods and materials to prevent bullet penetration, such as some reinforced armor, ballistic fabrics, and shock-absorbing composite materials.
3.What Are the Common Bulletproof Materials?
We’ve quickly compiled some of the more common bulletproof materials for you: steel, ceramic, Kevlar, polyethylene, fiberglass, polycarbonate, and bulletproof glass.
4.What are the Lightweight Bulletproof Materials?
If you are looking for lightweight bulletproof materials, we can tell you with certainty that Kevlar fiber and ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) are the most popular lightweight bulletproof materials. They are not only light in weight but also very strong, making them ideal materials for your bulletproof vests and helmets.
5.What is the Best Bulletproof Material?
The best bulletproof material depends on your specific needs. For personal protection, we recommend Kevlar and polyethylene. For armored vehicles, ceramics are obviously the best due to their excellent bulletproof performance. In order to achieve the best performance, a single material is obviously difficult to meet. The best bulletproof material is usually a combination of multiple materials.
6.What are Some Cheap Bulletproof Materials?
If you are looking for a low price, fiberglass and polycarbonate are relatively cheap bulletproof materials.
7.What are Bulletproof Metals?
Bulletproof steel is the most commonly used bulletproof metal. Although steel is heavy, it can effectively stop bullets.
8.Applications of Bulletproof Materials
The range of applications for bulletproof materials is very wide, and we will give you some examples:
Personal protection: bulletproof vests, helmets and shields.
Vehicle armor: cars, military vehicles and aircraft.
Building security: bulletproof doors, windows and walls in banks, airports and government facilities.
Special uses: protective panels for industrial equipment and space exploration.
These are the most common uses for bulletproof materials.
9.How Much Does a Kevlar Vest Cost?
Basic Kevlar body armor typically costs between $300 and $600, but if you want a higher-end model with more protection, the price can exceed $1,000.
10.How Much Is Body Armor?
The price of a bulletproof vest depends on the type of material and the level of protection.We conducted relevant research based on the market. A lightweight vest made of materials such as Kevar usually costs between $300 and $800, while a hard vest made of ceramic usually costs between $600 and $2,000, or even higher.
