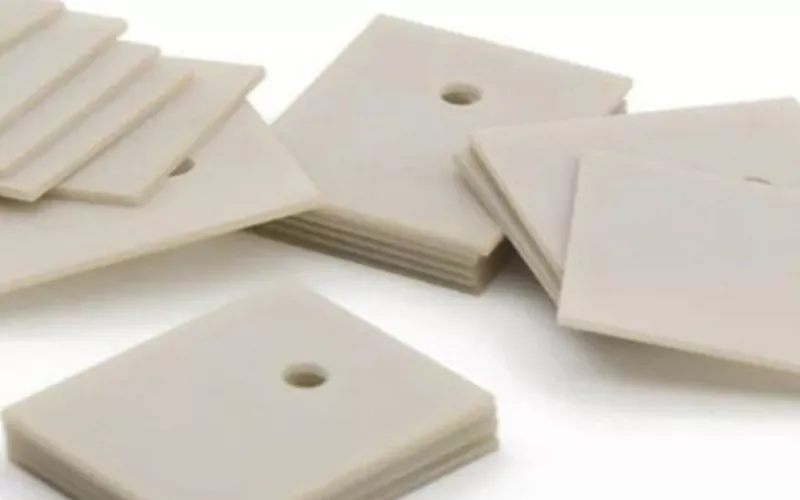
Ceramic substrates have been gaining popularity with the advancements in engineering, science and technology. The usefulness of ceramic substrates is matchless in sectors such as automobiles, electronics and renewable energy. Ceramic substrate differs from materials in terms of durability, lifespan, conductivity and thermal stability which contribute to the overall functionality.
Ceramic substrate: a detailed overview
Substrates provide a robust and durable foundation for equipment in industries such as electronics, industrial, and automotive. Their surfaces are typically smooth and uniform, and most are rectangular in shape.

Properties of Ceramic substrates
As mentioned, ceramic substrates have superior properties while comparing with any competitive counterparts.
|
Properties |
Description |
|
Durability |
The higher compressive strength of ceramic substrate makes them suitable for application that requires structural stability . |
|
Thermal Stability |
Ceramic substrates can withstand high temperature that makes them suitable for applications of automotive, industrial and electronic. |
|
Electrical Conductivity |
Ceramic substrate is an insulator material, they can be used to retard the flow of current. |
|
Stability |
Ceramic substrate material offers good dimensional stability. This property finds its application in microelectronics |
|
Corrosion resistance |
Ceramic substrates are inert materials which makes them ideal choice for Ceramic substrate catalytic convertor |
Types of Ceramic Substrates and their uses
Ceramic substrates are of different types depending on the material constitution. The advantageous properties of distinct material help the engineers use the required ceramic substrate for the desired application. Different ceramic substrates are listed here:
Alumina Ceramic Substrate
Alumina ceramic is a multipurpose ceramic. They are widely used in applications that require good thermal stability .Alumina ceramics are perfect insulators. They also offer greater corrosion resistance which makes them an ideal fit for ceramic substrate catalytic convertors.

Alumina ceramic are good sensor materials. The ability to thrive in harsh environments, heat resistance and less weight makes them ideal material for sensors. The sensors made of Alumina ceramic offer wear resistance and holds higher lifespan. They are also used in microelectronics for their structural stability.
Alumina ceramic by now has conquered automotive sectors also. Alumina Ceramics when used in engine body are said to increase the efficiency up to 46 %. Their heat insulating ability and resistance contains energy inside the system. This has benefited the end user in terms of minimising the usage of fuel.

Alumina ceramics is also used as shock absorbers in cars. In smart cars if used , they reduce the vibrations caused while travelling in non-uniform surfaces or terrains.
Aluminum Nitride Ceramic Substrate (ALN Ceramic)
Aln ceramic materials are known for their superior thermal conductivity. They also offer higher electrical insulation which makes them an ideal fit for electronic substrate. As the name suggests Aluminium Nitride substrate is made up of majorly alumina around 65% and 34% Nitrogen.
The thermal conductivity of ALN substrate is well above Alumina ceramic. Aln Ceramic has a thermal conductivity value around 170 W/mK. They offer good mechanical properties around 450 MPa and are often deployed in industrial applications. They are corrosion resistant and offer lesser dielectric constant.
The thermal expansion of Aln ceramic is lesser when compared to Silicon that finds application in chips. They also come with extreme purity.
Applications of Aluminum Nitride Ceramic Substrate
- Aln substrates are used in electronic sensors
- They are good furnace materials due to their higher thermal stability
- Since Aln ceramic are non-corrosive, they can be used as catalytic materials.
- Aluminum nitride sheets are used as semiconductor substrates. They offer good heat dissipation due to their higher thermal conductivity.
- Due to higher electrical resistivity, Aln Substrate are used as insulator materials in power applications.
- In microwave equipments Aln Ceramic are used as Ceramic packaging materials
Silicon Nitride (Si3N4) Substrates
Silicon nitride ceramic offers good thermal conductivity and superior mechanic strength. They are often used as electronic substrates. Unlike Aluminum nitride substrate and Alumina substrate, Si3N4 substrates excels in greater power output, compactness and being light weight.
Applications of Silicon nitride Ceramic Substrate
- Manufactured in the form of thin plates Silicon nitride Ceramic offer excellent thermal dissipation which is used in power electronics.
- High temperature semiconductor applications of today prefers Si3N4 ceramic due to their extreme stability at elevated temperatures.
- Modern sensor technology also uses Silicon Nitride (Si3N4) in the field of aerospace, medical and other industrial applications.
Comparison between different types of Ceramic substrates
Let’s have a look at the comparison chart given below. Different properties pertaining to the ceramic substrates are given for reference. The data helps you to chose the ideal ceramic substrate material for your desired application.
|
|
COMPARISON CHART OF DIFFERENT TYPE OF CERAMIC MATERIALS |
|||
|
Name of the Ceramic substrate |
Alumina Ceramic |
Aln Ceramic |
Silicon Nitride (Si3N4) |
|
|
General Properties |
Appearance |
White |
White |
White |
|
% composition |
96 - Al2O3 |
Aln |
Si3N4 |
|
|
Capability to absorb water (%) |
0 |
0 |
– |
|
|
Bulk Density (g/cm3) |
3.74 |
3.3 |
3.2 |
|
|
Reflectivity (%) |
94 |
30 |
– |
|
|
Mechanical Properties |
Bending Strength (MPA) - 3 point |
450 |
450 |
800 |
|
Surface roughness |
0.2-0.75 |
0.3-0.6 |
0.55 |
|
|
Fracture Toughness (MPam1/2) |
3 |
3 |
6.5 |
|
|
Hardness (GPa) |
14 |
11 |
15 |
|
|
Elasticity (GPa) |
330 |
320 |
310 |
|
|
Camber |
<2 |
|
|
|
|
Thermal Properties |
Thermal Expansion Coefficient (ppm/degC) |
6.5 – 7.5 |
2.5 – 3.5 |
3.3 |
|
Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) |
24 |
170 |
30-32 |
|
|
Specific Heat (Cp) |
750 |
720 |
680 |
|
|
Electrical Properties |
Dielectric Constant (1MHz) |
9.8 |
8.5 |
7.8 |
|
Dielectric strength (MV/m) |
>15 |
>17 |
>14 |
|
|
Dielectric Loss |
2 x 10-4 |
3 x 10-4 |
4 x 10-4 |
|
|
Volume Resistance |
>1014 |
>1014 |
>1010 (25 degc) |
|
Ceramic Substrate in Electronics
The advancements in material technology and the related inventions have made ceramic beneficial in different fields of engineering. They are termed to be incomparable offering numerous technical benefits. Since robust engineering and longevity is required for long term application ceramics are often used in various sectors.
What are substrate Electronics?
Substrate electronics are altogether an emerging field with immense potential. Gone the days of metal PCB’s and tedious designs. The introduction of ceramics into the PCB’s has opened the gateway to better functionality.
The printed circuit boards substrates are basically any rigid material to which the crucial circuits are incorporated. The design of the circuit boards requires greater precision. The popular materials used globally are fiber reinforced Epoxy because of their rigidity and other properties.
However, the modern advancements have found out that ceramics can be successfully deployed as PCB substrates. Let us have a look at electronics and what the modern material science did to the field.
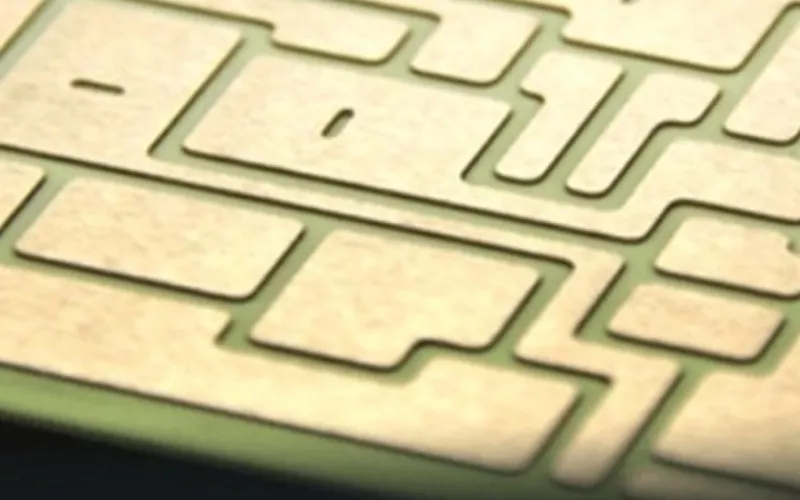
Ceramic substrate PCB
The new generation printed circuit board is popular due to its light weight and miniature form. Easy to work is another property that has made the product an ever-loving entity for PCB designers. Ceramic substrate PCB has lesser thermal expansion coefficient and higher thermal conductivity.
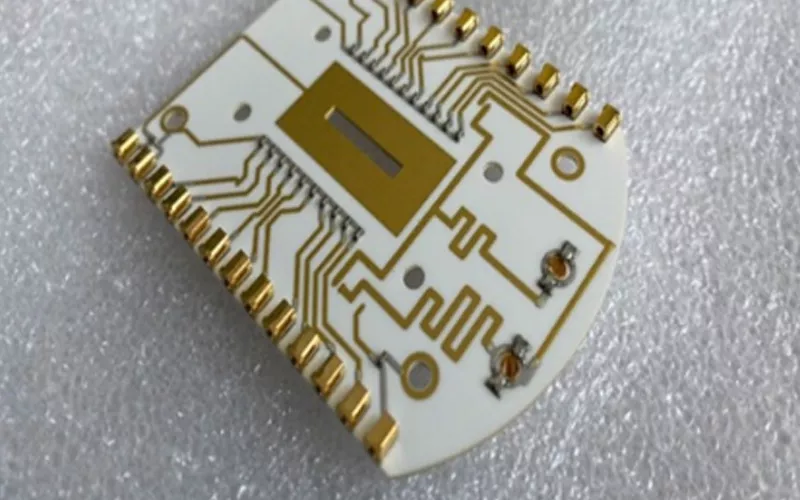
The average range of thermal conductivity of ceramic substrate PCB is around 9 – 20 W/mK. Ceramic substrate PCB are just printed circuit boards mounted on Ceramic substrate. The substrate material is chosen depending upon the type of application. The popular Substrate materials as discussed above are Alumina, Aln Ceramic and Si3N4
Advantages of Ceramic Substrate PCB
- Unlike metal clad PCB, ceramic substrate PCB offers greater heat dissipation properties. These Electronic substrate lets the heat pass through the board easily as there are no isolation layers
- Ceramic substrate PCB offers greater thermal compatibility due to its lesser coefficient of expansion and higher thermal stability. The stability is often observed to be above the working temperature of 350 deg C.
- Electronic substrate made of Ceramics are resistant to any chemical erosion to the contact of molten metals in the PCB.
- Dielectric property of the Ceramic PCB also ensures that the system once used in any electronic devices functions perfectly.
Direct Bonded Copper
These are made by bonding Copper onto a ceramic substrate under high temperature melting - diffusion process. The popular ceramic counterpart can either be Alumina or Aln substrate. The dbc substrates are useful in the field of DC power and the related electronic application.
Advantages of DBC substrates
- The amalgamation of the higher purity compounds to a substrate contributes in superior heat dissipation in DBC substrates.
- The thermally induced stress on the components is very well handled in DBC substrates.
- A soldering working temperature of around 170 – 800 degree is technically viable. The working temperature has no deteriorating impacts on the adjacent materials.
- As other ceramic substrates they offer corrosion resistance and higher mechanical stability
- The power cycling ability of DBC substrates matches with silicon which makes them useful in electronics.
- The conductive elements in the PCB are etched on to then copper layer in DBC substrates. The substrate makes sure to separate the system from adjacent sections and prevent short circuiting.
- Specific sections where Direct bonded Copper substrates are used include Solar Cells, Laser technology, Power supply and Aerospace
Conclusion
Modern world is gifted with technical inventions and their distinct benefits. Of course, Ceramic substrates hold a special place in material technology. The unparalleled benefits offered by the material makes it an ideal fit for applications in the field of electronics, Industry, renewable energy and many more.