Zirconia is an advanced ceramic material, and many products on the market are made of it. Zirconia has superior performance and is one of the toughest ceramic materials. From medical dentistry and prostheses to industrial bearings and knives in daily life, zirconia has been involved in many professional fields. If you want to know more about the uses and characteristics of zirconia, please read on, I believe you will gain a lot.
Quick Links
- What is Zirconium Oxide?
- Market Size
- Zirconium Oxide Pricing
- Critical Properties of Zirconium Oxide
- Common Uses of Zirconium Oxide
What is Zirconium Oxide?

Zirconia is a white crystalline form of zirconium oxide composed of zirconium (Zr) and oxygen (O), with the chemical formula ZrO2.
This material boasts excellent physical and chemical properties, primarily known for its high strength, toughness, and outstanding corrosion resistance.
Market Size
The global zirconium dioxide market was USD 79.99 million in 2023. It is expected to grow at a CAGR of 3.8% from 2024 to 2032, reaching a value of USD 110.32 million.
Zirconium Oxide Pricing
Zirconium oxide products can vary in price, depending on the purity, size, and application. High-quality Zirconia for dental or electronic applications is priced higher due to the level of refinement required, while industrial-grade Zirconia is affordable.
You will see Zirconium Oxide raw powder, ZrO2 Pellets, Yttria stabilized Zirconium powder, industrial grade Zirconium, and other types online, with prices ranging from $10 to $2,000, depending on your order and type.
As technology advances and industries adopt Zirconia, the market prospects for this material are strong. Growth is expected particularly in dental, electronics, and aerospace applications.
Critical Properties of Zirconium Oxide
Physical Properties
Zirconium oxide is known for its high melting point (2,715°C) and density (5.68 g/cm³), which give it outstanding thermal stability. It’s also physically hard, contributing to its durability and abrasion resistance. Cubic Zirconia, which is the cubic crystalline form of ZrO2. It is a man-made and colorless stone that looks like a diamond, which is why it is also a popular choice in jewelry.
Chemical Properties
Zirconium oxide is well-known for its impressive chemical stability. It is highly resistant to strong acids, alkalis, and other corrosive substances, which makes it extremely useful in environments where it may be exposed to harsh chemicals or extreme heat.
This material remains stable even in oxidizing (where it gains oxygen) and reducing (where it loses oxygen) conditions, giving it great versatility.
Zirconia is extremely stable and excels in industries that must withstand high temperatures, such as industrial furnaces and other high-temperature applications
Mechanical Properties
One of the major qualities of zirconium oxide is its toughness. Due to its high ‘fracture toughness,’ it doesn’t crack under regular pressure. This is why dentists use it for dental crowns, and the automotive industry uses it for engine parts where such tough material is required.
Electrical Properties
Zirconium oxide is an electrical insulator, which doesn’t let electricity pass through it quickly. But in the case of special electronics, you can make it conduct ions (charged particles). It is highly useful in fuel cells and sensors where proper ion movement is necessary.
Common Uses of Zirconium Oxide
Dental Industry
Dentists commonly use three types of zirconia: zirconia-toughened alumina (ZTA), magnesium-stabilized zirconia, and tetragonal zirconia. These materials are made into crowns, implants, abutments, ceramic brackets, and more.
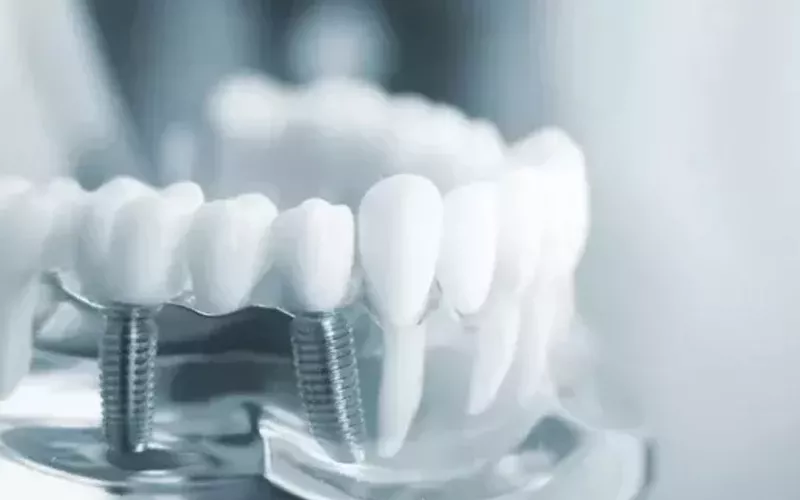

Dentists often use zirconia crowns for restoration after root canal treatment. As a restoration, zirconia crowns can effectively restore the structure and function of teeth and prevent further damage to your teeth. In addition, it is also used to bridge the gap between two teeth or as an implant to replace other teeth under treatment when necessary.
Zirconia shines in dentistry because it is hard, natural-looking, biocompatible with the human body, and resists wear over time.
Industrial Ceramics
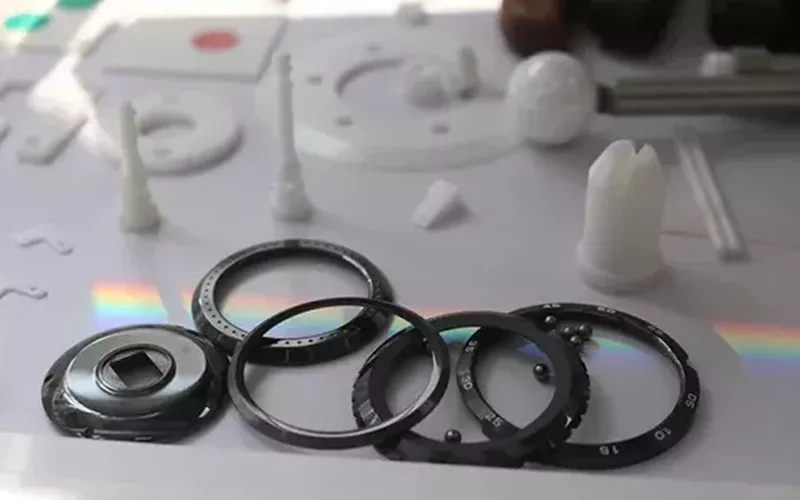

Zirconia is used extensively in industrial ceramics, including furnaces, molds, and cutting tools. Its hardness, heat resistance, and resistance to wear and tear make it ideal for abrasive materials and protective coatings. ZrO2 is also used in the manufacturing of pump seals, precision ball valves, impellors, titanium dioxide coatings, and bushings.
In the nuclear industry, Zirconium dioxide (ZrO2) makes neutron-absorbing ceramics for control rods.
Aerospace and Automotive Industries
Zirconia plays a vital role in the aerospace and automotive industries due to its excellent heat resistance and toughness.
These industries require high-performance materials to operate properly in harsh environments, and many manufacturers use zirconium oxide to make turbocharger rotors, oxygen sensors and brake pads.
Jewelry
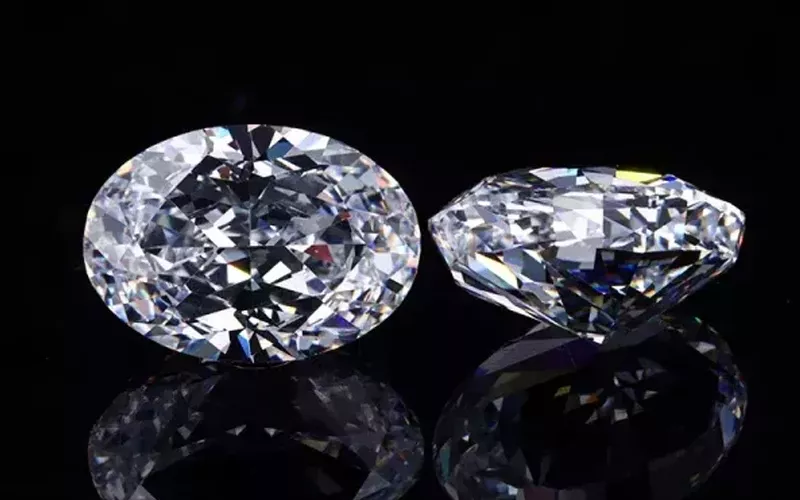

Zirconia is a popular diamond substitute in the jewelry world. Cubic zirconia is a type of zirconium oxide crystal that is brighter, more durable, and much cheaper than real diamonds. Therefore, cubic zirconia is an affordable substitute for diamonds, and people can get jewelry that is as durable, long-lasting, and beautiful as diamonds at a fraction of the price.
Electronics Industry
Zirconium oxide plays a huge role in the electronics industry, too. It can act as an insulator but can also help with ionic conductivity with some special arrangements.
ZrO2 is widely used in optical devices such as wafer-level optics, diffractive optical elements, and micro-lens arrays. It also has many uses in display technologies. It is used in organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), mini and micro light-emitting diodes (LEDs), and quantum dots.
Other uses of ZrO2 in the electronics industry include thermal barrier coatings, Fuel Cell technology, Solid-state electrolytes, Electro-optical materials, Catalyst or catalyst support, Ceramic biomaterial, and thermoluminescence UV dosimeters.
Zirconium has many other uses, including:
Paper and printing
Zirconium coatings are used to make paper stronger and more water-resistant.
Paints and inks
Zirconium chemicals improve adhesion and increase resistance to heat, scrubbing, water, and solvents.
Cosmetics
Zirconium oxide (ZrO2) serves as an additive and waterproofing agent in cosmetics.
Orthopedic Implants
Zirconia ceramics also serve as replacement parts for hip and knee joints.
Watch Components
Zirconia is a popular material in watchmaking due to its aesthetic appeal and scratch-resistant properties.
Ceramic Knives
Zirconium oxide can be made into ceramic knives for daily use, which are very convenient for cutting soft ingredients such as vegetables and fruits.
Conclusion
Zirconium oxide (ZrO₂) is durable, corrosion-resistive, and possesses thermal abilities, making it useful in many work areas and industries. Due to its electrical, mechanical, physical, and chemical properties, it has many uses in the dental, industrial ceramics, aerospace, automotive, jewelry, and electronics industries.
Researchers are exploring new properties of Zirconium oxide and finding new ways to use it in even more industries, which tells us how versatile and valuable this material is.
