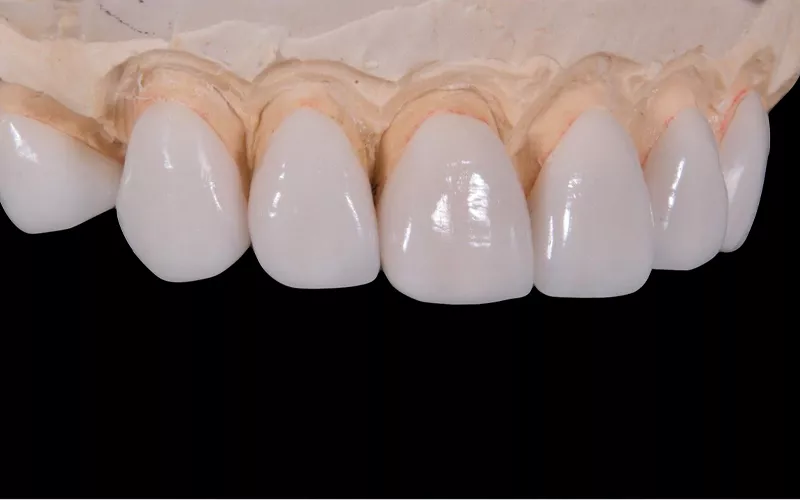
Surprisingly, there are 17 different types of zirconia. That’s way more than 6 or 7! These types are categorized according to certain characteristics. Every one of them is beneficial because it has a specific property, which is strength, does not rust, stands heat, and remains stable at challenges.
Now it is time to know more about zirconia. So, keep reading!
What is zirconia and how many different classes it has?
What is zirconia and how many types does it have?
Zirconia/Zirconium oxide (ZrO2) is a high-performance ceramic material that can withstand high temperatures. It comes from minerals. A German scientist, Martin Heinrich Klaproth identified zirconia in 1789 while working with zircon (ZrSiO₄). He obtained oxides from zircon and he gave them the name zirconia. Afterward in 1824, a swede chemist called Jöns Jakob Berzelius isolated zirconium from Zircon for the first time.
Zirconia is a fine white powder. It is very strong and does not tend to break when exposed to quick temperature changes. It is also resistant to strong chemicals.
Due to these wonderful characteristics, zirconia finds its application in many fields. It is used in the manufacturing of ceramic knives, medical instruments, industrial machines, aerospace parts and electric insulators.
It’s also applied in the development of other technologically enhanced materials such as coatings that protect against heat, car exhaust converters, oxygen sensors, and fuel cell membranes. Due to its compatibility with the human body, it can be used in the manufacturing of dental crowns and medical implants.
At ordinary temperature, zirconia is in monoclinic form. But when the temperature increases then zirconia undergoes a phase transformation and thus changes its shape. The melting point of this material is very high. In fact, it melts at 2716 degrees Celsius.
Here’s how it transforms:
-
At 1170°C, it becomes tetragonal zirconia.
-
At 2370°C, it shifts to a cubic shape. This cubic form is often used to make jewelry that looks like diamonds.
-
Above 2370°C, and just before it melts, zirconia takes on a fluorite structure.
These changes affect how stable zirconia is and change some of its properties.
Zirconia is grouped into types based on different features:
-
Stabilization methods, like adding minerals such as yttria or calcium.
-
Composite structures.
-
Special mixtures and uses.
-
Processing and physical traits.
-
Unique applications in industries.
17 types of zirconia explained
There are 17 types of zirconia widely applied in manufacturing, for instance, in the production of dental implants and orthopedic instruments.
Types of zirconia based on stabilization methods
-
Monoclinic Zirconia
This is the purest form of zirconia and the most stable one at normal temperature conditions. It is also very brittle and not very strong. It is still relatively weak to increase its strength it has to be converted to tetragonal zirconia polycrystals (TZP).
-
Tetragonal Zirconia
This type is stable at high temperatures. It is stronger and more durable and thus suitable for dental tools and high-performance ceramics.
-
Partially Stabilized Zirconia (PSZ)
This type has both the monoclinic and tetragonal zirconia present in the same type. It is stabilized by using yttria or calcia which means calcium. The stabilizer used alters the properties of the PSZ. In general, it is more difficult and durable.
-
Fully Stabilized Zirconia (FSZ)
FSZ is a stable form of cubic zirconia. It has good high temperature and chemical stability. Due to the above mentioned characteristics, it is applied in thermal barrier coatings as well as sensors.
-
Ceria Stabilized Zirconia (CSZ)
CSZ is prepared when zirconia is doped with CeO2. It is highly stable, almost unbreakable and also performs well in low temperatures. All these make CSZ suitable for medical and industrial applications.
Types of zirconia based on composite structures
-
Zirconia Toughened Alumina (ZTA)
ZTA is a combination of Zirconia and Alumina. These materials when incorporated into ZTA result to an even harder and more durable material. Due to these characteristics, ZTA finds application in dental work, joint replacements, cutting tools, engine parts and mining equipment etc.
-
NanoZR
NanoZR combines tiny zirconia particles with alumina. It is an improved version of ZTA with extra toughness and stability in high heat. These qualities make NanoZR perfect for medical tools, high-temperature uses, and dental implants.
-
Multilayer Zirconia (M3Y, M4Y, M5Y, M6Y, and hybrid variants like M3Y-5Y, M3Y-4Y, etc).
These zirconia types have layers of different zirconia mixes. This layering gives them better translucency, strength, and compatibility with the body. The “Y” stands for yttria (Y₂O₃), and the number tells how many moles of yttria are in each type. For example, M3Y has 3 moles, while M5Y has 5 moles of yttria. These features make multilayer zirconia a top choice for dental implants.
-
Transformed Toughened Zirconia
This type is made from tetragonal zirconia by using stress to change its phase. It is extremely durable and resists wear, making it ideal for cutting tools and dental implants.
Types of zirconia based special compositions and applications
-
Yttria-Stabilized Tetragonal Zirconia Polycrystals (Y-TZP)
Y-TZP is a subtype of zirconia which is modified by adding yttria to make it strong and durable. This makes it one of the strongest forms of zirconia on the market. That is due to its high strength and stability, that’s why it is used for making different dental equipment and prosthetics, as well as surgical instruments. For these properties it is suitable for use in applications that require strength and durability.
-
Monolithic zirconia
Monolithic zirconia is a single-layer version of Y-TZP zirconia. It is one of the toughest materials and can stand lots of use and abuse. This means that it is ideal for incorporation in dental applications for instance crowns and bridges because of its stability. This makes it suitable for use in medical and dental operations because it can be used severally without getting tired.
-
Magnesia-Stabilized Zirconia (Mg-PSZ)
This type of zirconia is then stabilized by incorporating magnesium oxide and is characterized by high thermal and fracture toughness. Due to the possession of these properties, it is widely used in high temperature applications such as aerospace where materials are exposed to a high temperature. It is also employed in furnace linings and some other industrial applications where material with high thermal shock resistance is needed.
-
3Y-HA
This type of zirconia is yttria and hydroxyapatite partially stabilized zirconia which has 3 mol% yttria. It duplicates the hierarchical structure of bone tissue and that is why it is used for orthopedic implants. This zirconia is integrated with hydroxyapatite that improves the bonding between this material and bone and may also promote the formation of new bone tissue.
It also reduces bone density loss when implants are taken out, and may also have antibacterial effects. It is these properties that make 3Y-HA zirconia suitable for use in the production of bone screws, plates, artificial joint, and other components used in the fracture fixation of load bearing bones.
-
3Y
3Y zirconia is another type stabilized with 3 mol% yttria. It is known for its high mechanical strength and reduced translucency. This combination of properties makes it a popular choice for dental crowns and prosthetics. However, increasing the amount of yttria beyond this percentage can lead to a loss of strength, so the balance in its composition is crucial. This material is trusted for applications where both aesthetics and strength are important, such as in cosmetic dentistry and medical prosthetics.
Specialized zirconia types based on processing and properties
-
Low Temperature Degradation (LTD) Zirconia
LTD zirconia is made to resist damage caused by moisture. This makes it strong and long-lasting in wet conditions. It’s often used for dental implants that age over time and in industrial tools.
-
Hot Isostatic Press (HIP) Zirconia
HIP zirconia is created using high pressure and heat. This process makes it very dense and strong. It’s used in top-quality products like industrial blades, gap subrings, MWD sleeves, and waterjet plunger parts.
-
Ceramic Injection Molding Zirconia
For ceramic injection molding, types like Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia, Magnesium-Stabilized Zirconia, and Ceria-Stabilized Zirconia are used. During the process, the particle size is kept around 1μm. This improves the strength and durability of the final product.
Additional types based on specific applications
-
3Y-4Y, M3Y-5Y, and other multilayer variants like M4Y-5Y
Multilayer zirconia has three layers made from different yttria zirconias. These layers go from the core to the surface. It’s used in high-quality dental crowns, bridges, and implants. Multilayer zirconia looks natural, like real teeth, and is strong. Zirconia with more yttria is more see-through, like natural teeth, but it’s less flexible and less durable.
What types of zirconia are used in dentistry?
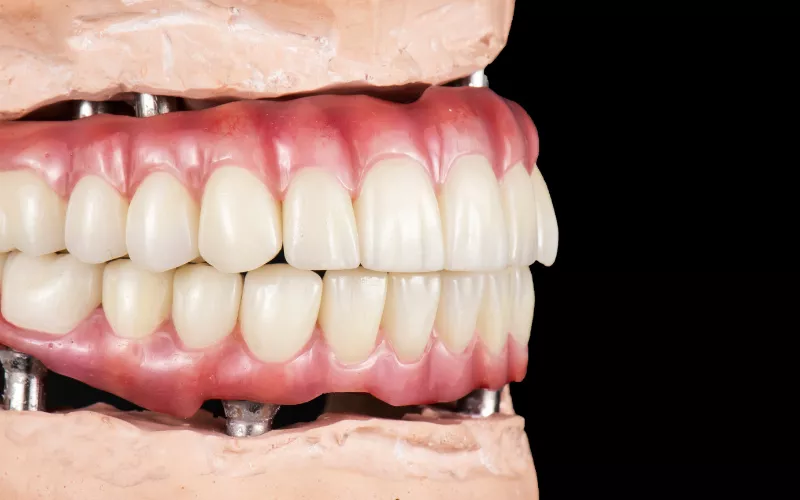
In dentistry, special types of zirconia are chosen because they are strong and safe for the body. The most common ones are Yttria Stabilized Tetragonal Zirconia Polycrystals (Y-TZP), magnesia-stabilized zirconia (Mg-PSZ), and Zirconia Toughened Alumina (ZTA). Dentists use these types by themselves or as part of layered zirconia.
Conclusion
These are the 17 main types of zirconia that keep improving over time. Picking the right type for your product can be tricky. That’s why ceramic makers help by understanding your needs and creating the perfect product for you.

