High-Performance, High-Reliability Ceramic Feedthroughs And Pain Point Solutions,Maintenance and Care Guide
Introduction
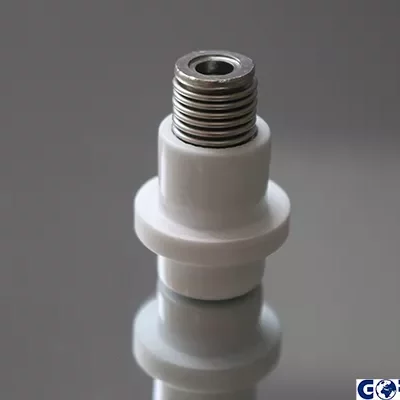
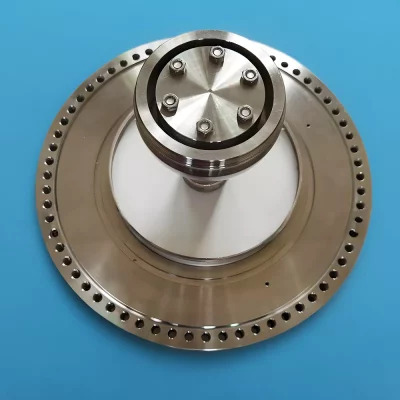
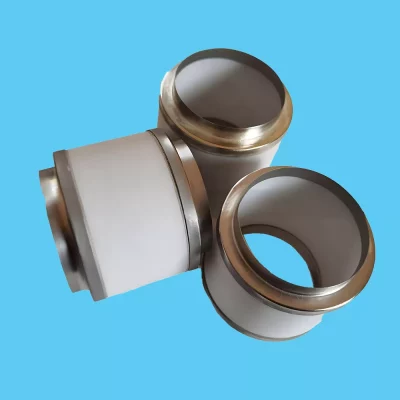
Ceramic feedthroughs are components used to pass wires or cables through sealed walls or partitions. They are made of ceramic materials and have the advantages of high strength, high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, and electrical insulation, making them widely used in electronics, medical devices, aerospace, and other fields.
Product Types
We produce the following main types of ceramic feedthroughs:
-
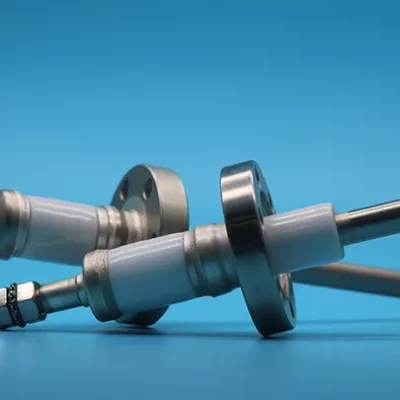
Vacuum Feedthroughs: Used to pass wires or cables through the sealed walls or partitions of vacuum environments.
 Vacuum Feedthroughs
Vacuum Feedthroughs
-
Electrical Feedthroughs: Used to pass wires or cables through sealed walls or partitions and provide electrical connections.
Power Feedthroughs: Used to pass high-voltage or high-current wires or cables through sealed walls or partitions.
Hermetic Feedthroughs: Used to pass wires or cables through sealed walls or partitions and ensure sealing.

-
Thermocouple Feedthroughs: Used to pass thermocouples through sealed walls or partitions and ensure their electrical isolation.
-
Ceramic Feedthroughs: Made of ceramic materials, they have the advantages of high strength, high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, and electrical insulation.
Product Applications
Ceramic feedthroughs are widely used in the following fields:
-
Electronic Devices: Used to pass wires or cables through circuit boards, chassis, etc.
-
Medical Devices: Used to pass wires or cables through medical instruments and equipment.
-
Aerospace: Used to pass wires or cables through aircraft, spacecraft, etc.
-
Industrial Control: Used to pass wires or cables through industrial control equipment.
-
Laboratory Instruments: Used to pass wires or cables through laboratory instruments and equipment.
Product Advantages
Ceramic feedthroughs have the following advantages:
-
High Strength: Can withstand high voltage, high current, and high vibration.
-
High Temperature Resistance: Can withstand high temperature environments.
-
Corrosion Resistance: Can withstand various corrosive media.
-
Electrical Insulation: Has good electrical insulation performance.
-
Good Sealing: Can ensure sealing.
Product Selection
When selecting ceramic feedthroughs, consider the following factors:
-
Application Environment: Choose the appropriate feedthrough type based on the application environment.
-
Performance Requirements: Choose the appropriate feedthrough specifications based on performance requirements.
-
Size: Choose the appropriate feedthrough size based on the installation space.
-
Price: Choose the appropriate feedthrough price based on your budget.
Ceramic Feedthroughs Pain Point Solutions and Maintenance and Care Guide
Pain Point Solutions
Ceramic feedthroughs may encounter the following problems during use:
-
Poor Sealing: Poor sealing of feedthroughs can lead to air or liquid ingress, affecting their performance or even damaging equipment.
-
Decreased Electrical Performance: Decreased electrical performance of feedthroughs can lead to unstable connections and even fire hazards.
-
Insufficient Mechanical Strength: Insufficient mechanical strength of feedthroughs can lead to their inability to withstand high voltage, high current, or high vibration, resulting in damage.
-
Short Service Life: Short service life of feedthroughs can lead to frequent replacements and increased maintenance costs.
To address these pain points, the following solutions can be taken:
-
Choose the Right Feedthrough: Choose the appropriate feedthrough type and specifications based on the application environment and performance requirements.
-
Proper Feedthrough Installation: Install the feedthrough correctly according to the installation instructions to ensure sealing.
-
Regular Inspection and Maintenance of Feedthroughs: Regularly inspect feedthroughs for damage or sealing problems and repair or replace them promptly.
-
Use Appropriate Cleaning Agents: Use appropriate cleaning agents to clean the surface of feedthroughs, avoiding the use of corrosive chemicals.
Maintenance and Care Guide
To extend the service life of ceramic feedthroughs, regular maintenance and care should be performed. Here are some maintenance and care guidelines:
-
Regularly Check the Appearance of Feedthroughs: Check for cracks, breaks, or other signs of damage on the feedthroughs.
Check the Sealing of Feedthroughs: Use a leak tester to check the sealing of feedthroughs to ensure there are no leaks.
-
Clean the Surface of Feedthroughs: Use a clean soft cloth and appropriate cleaning agent to clean the surface of feedthroughs, avoiding the use of corrosive chemicals.
-
Check the Electrical Performance of Feedthroughs: Use a multimeter to check the electrical performance of feedthroughs to ensure it meets requirements.
-
Regularly Replace Feedthroughs: Replace feedthroughs regularly based on their service life to avoid failures.
Precautions
-
Before performing maintenance and care, be sure to read the feedthrough user manual.
-
If you are unfamiliar with the maintenance and care of feedthroughs, please consult a professional technician.
-
When replacing feedthroughs, use original accessories.
By following these guidelines, you can extend the service life of your ceramic feedthroughs, improve their reliability and safety, and reduce maintenance costs.
Conclusion
Ceramic feedthroughs are high-performance, high-reliability components widely used in various industries. Understanding their pain point solutions and maintenance and care guidelines can help you extend their service life, improve their reliability and safety, and reduce maintenance costs.