Boron Nitride cbn is an advanced ceramic known for its superior properties. BN chemistry has Boron Nitrogen bonds that give rise to different structures. Of the structures of BN one such prominent structure of interest is Cubic Boron Nitride cbn. Let us try to understand c-bn and its relative aspects.
Table of Contents
Hexagonal Boron Nitride (h-BN)
- Structure of Hexagonal Boron Nitride
- Properties of Hexagonal Boron Nitride
- Applications of Hexagonal Boron Nitride
- What is cubic Boron Nitride?
- Structure of Cubic Boron Nitride
- Cubic Boron Nitride Properties
- Cubic Boron Nitride Vs Diamond
- Cubic Boron Nitride uses
- Super abrasive wheels – or diamond c-BN wheel
Boron Nitride: An Overview
Boron Nitride is indicated by chemical formula “BN.” As earlier mentioned, Boron Nitride exist in different forms. Generally, it is the location of Boron and Nitrogen in lattice that creates various Boron Nitride structures. Some of them are quiet famous such as amorphous, hexagonal, cubic and Wurtzite.
When it comes to functionality, Boron Nitride ceramic is highly machinable. Once machined they does not really require any heat sintering or treatment for stabilization. In addition, Boron Nitride has higher heat capacity and is also a good electrical insulator.
For now, let’s try to understand derivatives of BN, Hexagonal Boron Nitride (h-BN) and another Cubic Boron Nitride (c-BN)
Hexagonal Boron Nitride (h-BN)
Structure of Hexagonal Boron Nitride
Hexagonal Boron Nitride is a constituent in many industrial products such as cosmetics. HBN has a structure controlled by covalent bonds. However, the layers in HBN obey wander Waals forces. The plate like geometry of HBN is the reason why it is ideal for lubrication.
Hexagonal Boron Nitride has elements of Boron and Nitrogen fixed to its lattice. The arrangement has three nitrogen atoms attached to a Boron Atom. The similarity in the honeycomb structure is the reason for its analogy with carbon. In addition to, properties of mechanical, chemical strength and electrical insulation are due to the planar triangular bonds
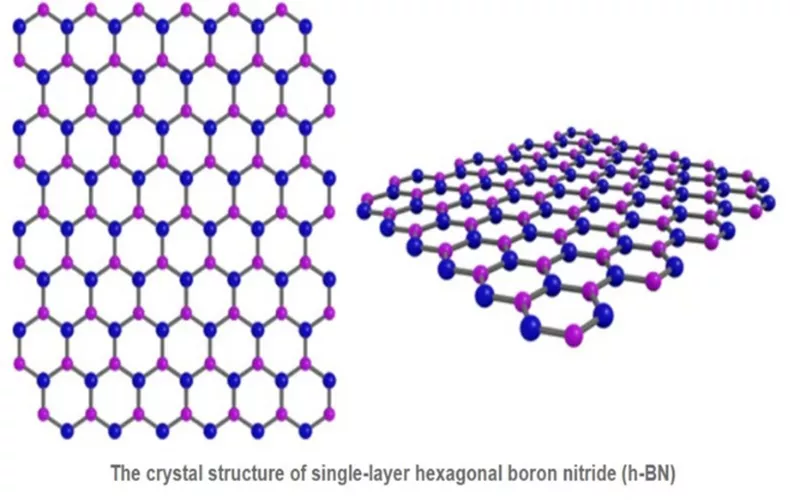
Properties of Hexagonal Boron Nitride
Hexagonal Boron Nitride is popularly manufactured through Boric Oxide nitridation at elevated temperatures. Since its stability is closer to graphene, Hexagonal Boron Nitride is often acclaimed as the most advanced technical ceramic. Some superior properties of Hexagonal Boron Nitride are its thermal conductivity, and low frictional coefficient.
Applications of Hexagonal Boron Nitride

- HBN is used on nanoelectronics devices as a substitute to graphene substrate
- Hexagonal Boron Nitride in its thin form is used as coatings that resists corrosion
- HBN is often used in the manufacture of sensor materials. It is also used in electron tunneling due to its low value of dielectric constant.
Cubic Boron Nitride
What is cubic Boron Nitride?
c-BN is a derivative of Hexagonal Boron Nitride (h-BN) produced under high temperature and pressure.
The biggest specialty of c-BN is that it holds the place of second hardest material in the world. The mechanical strength of Cubic Boron nitride is popular and is in par with diamond. It is one among the most popular polymorph of Boron Nitride.
Structure of Cubic Boron Nitride
The basic structure of Cubic Boron Nitride is crystalline. It has density around 3.5 g/cm3 and appears in pale yellow or transparent complexion. C-BN follows alternate arrangement of Boron and Nitrogen atoms. Here, the Boron Nitrogen atoms follow covalent bonding which is the basic reason of its hardness and stability.
Cubic Boron Nitride Formula is given as c-BN. There are two popular types of c-Bn available today in the market. One is dense cubic boron nitride and the other polycrystalline cubic Boron Nitride.
Cubic Boron Nitride Properties
C-BN is a brilliant semiconductor whose bandgaps are susceptible to changes in applied pressure. These changes in bandgap helps them excel as electric insulators. Cubic Boron Nitride are generally inert and possesses low dielectric constant value. Their thermal conductivity is around 1300 KW/MK.
When it comes to reactivity, c-BN remains non-respondent even to ferrous materials. The optical range dealt by cubic boron nitride varies from Ultra violet to the visible spectrum.
Cubic Boron Nitride Vs Diamond

Although not harder than diamond, cubic Boron nitride has its place special when compared with diamond. Cubic boron Nitride hardness is 4500 Kg/mm2 whereas diamond has hardness around 600 Kg/mm2.The value of modulus both young’s and bulk are also in similar range of 800 – 1000 and 370 – 450.
Furthermore, when it comes to structure, like diamond, c-BN has its two base atoms that are different. The similarity of both diamond and c-BN is generally attributed to the lookalike structure they possess.
Cubic Boron Nitride uses
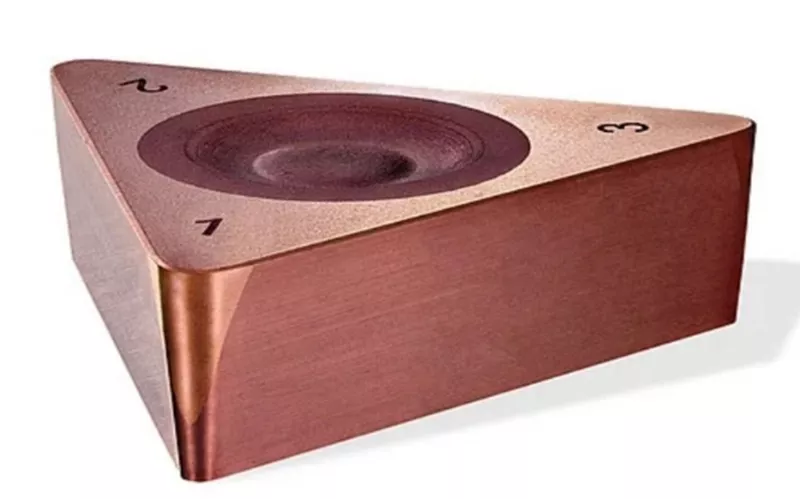

cbn cutting tool material
Cubic Boron Nitride exhibits both young’s and Bulk modulus greater than Boron Carbide and Silicon Carbide. This very reason strongly contributes to the hardness of cubic Boron Nitride. The hardness makes them suitable as abrasives and help them function as cbn cutting tool material. Generally Dense c-Bn is used for cutting application and porous type for grinding requirements.
The inert nature of Cubic Boron Nitride also helps them function as cutting and machining material. Unlike diamond it doesn’t react to iron. However, conventional c-Bn requires manipulation for utilising it in cutting application. This is generally done during the conversion of h-Bn to c-Bn while sintering.
cbn as electrical insulators
Apart from hardness Cubic boron Nitride also excels in electrical insulators. This is attributed to their wide bandgap.
cbn in semiconductor applications
By coating aluminium and Group 8 metals, C-BN functionality of becoming a sink is popular in electronic industry. C-BN is used as heat sink in lasers, microelectronic devices and LEDs.
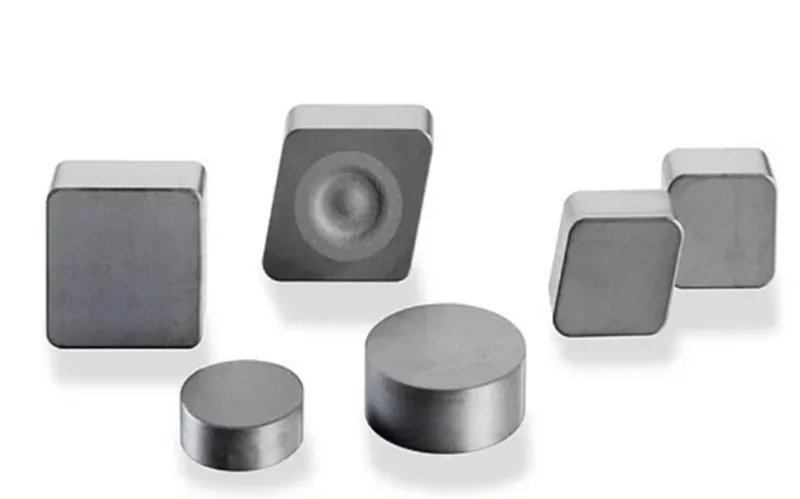

Cubic Boron Nitride also adds value during semiconductor synthesis to obtain p and N type by proper doping. The common materials used for doping are Silicon or Beryllium. These semiconductors work at high temperature and are used in UV sensors.
c-BN grinding wheels
The invention of c-BN grinding wheels merited precision manufacturing due to the increased efficiency. wheels made up of c-BN contributed to industries such as aerospace, machines, tool production and automobile. c-BN grinding wheels also offer high hardness and good performance on comparison with SiC and Alumina. They ensure structural integrity at higher temperature and undergo no degradation.
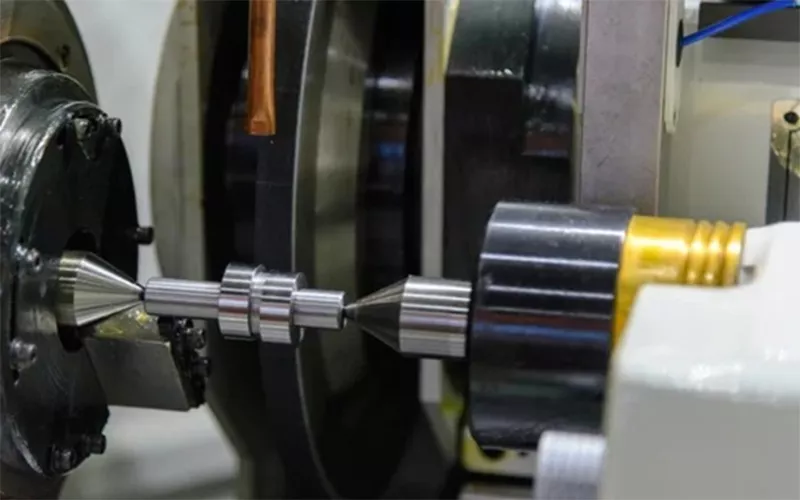
The wheels of c-BN can withstand high temperature and deals with the amount of heat generated during the process. The resistance to wear and tear is also economically beneficial while considering c-BN grinding wheels. c-BN grinding wheels offer excellent surface finish and keeps away the work piece wastage. It also ensures lesser cycle time as the tasks are done quickly and precisely.
Super abrasive wheels – or diamond c-BN wheel
The super abrasive wheels are the ones differ from conventional wheel of Sic and Alumina. They are made from combining c-Bn and diamond. The super abrasive wheel offers better thermal conductivity limiting the rise in temperature of the workpiece. The diamond c-Bn wheel also offer high accuracy and precision cutting that contribute to better lifespan.
Conclusion
Cubic Boron Nitride is desirable in modern science and material manufacturing. They are competitive when compared to materials such as diamond. They excel in properties such as hardness, strength, and electrical insulation. The wide band gap, inert nature, low dielectric constant and optical specialities are the other factors of merit.
