
Your silicon carbide bearing offers wear & corrosion resistance, hardness, and stability, ensuring durability and efficiency in your harsh, high-temperature environments. Silicon nitride ceramic bearings deliver high fracture toughness and resistance, providing precision in your high-speed applications.
2. What Is a Ceramic Bearing?
-
Ceramic bearings are high-performance bearings made from advanced Keramik materials like silicon carbide (SiC) and silicon nitride (Si3N4).
2.1 Types of Ceramic Ball Bearings
2.1.1 Hybrid Ceramic Bearings
-
Your bearing ceramic hybrid uses ceramic balls with an inner and outer steel cage. They provide lower friction and weight and also electrical insulation and wear resistance. Your bearing ceramic hybrid performs reliably in your high-speed machinery and electronics.
2.1.2 Full Ceramic Bearings
-
Your bearing full ceramic uses a ceramic material in both the balls and the rings. They offer high temperature, corrosion and chemical resistance. Your bearing full ceramic is ideal for your chemical processing, medical and aerospace applications.
2.2 Ceramic Bearings Vs Steel Bearings
-
When comparing a ceramic vs steel bearing bike, ceramic offers competitive performance. Most of your ceramic bearings deliver wear rate <0.01%, resist temperatures >1700°C, higher speeds, and are lightweight. Steel bearings offer better shock absorption and durability under loads at lower costs.
3. Why Are Ceramic Bearings Preferred In Your Industry
-
Your ceramic bearings are chosen over traditional steel due to their superior properties and advantages. They provide higher speeds, increased stiffness, insulation, and resistance to corrosion. This improves performance and efficiency and extends service lifespan in your demanding applications.
4. Comparison Between Silicon Carbide Bearings and Other Ceramic Bearings
4.1 Silicon Carbide Bearings: Properties & Advantages

Your silicon carbide bearings are made through a high precision process from >99% purity Siliziumkarbid (SiC) powder.
4.1.1 Extreme Hardness
-
Your silicon carbide sliding bearings offer a Mohshärte of 9.2-9.5 (harder than Si3N4, alumina and zirconia). This near-diamond hardness reduce wear and abrasion and ensure the durability of your high-speed spindles.
4.1.2 High Temperature Stability
-
Your silicon carbide sleeve bearings withstand 1750°C temperatures. This ensures reliability in your high-temperature furnaces and kilns.
4.1.3 Corrosion Resistance
-
Due to silicon carbide’s excellent resistance to chemicals, your SiC bearings perform under chemical, base and acidic environments.
4.1.4 High Thermal Conductivity
-
With a thermal conductivity of 270±20 W/(m·K), your silicon carbide bearing excellently dissipates heat. This provides efficiency in your high speed systems.
4.1.5 Lightweight
-
Due to a low density of 3.21 g/ gcm³, your SiC ceramic bearings reduces weight in your aerospace and high speed applications.
4.1.6 Electrical Insulation
-
Silicon carbide is an excellent electrical insulator. This makes your silicon carbide ceramic bearing ideal for your electronics.
“We’ve been using silicon carbide bearings in our electric spindles for over 3 years now. They’ve been providing very high speeds with no wear.” — Jakob G., Engineer, Spindsales
4.2 Silicon Nitride Ceramic Ball Bearings

4.2.1 High Hardness
-
Dein Siliziumnitrid (Si3N4) is extremely hard, ranking slightly lower than SiC on the Mohs scale. This hardness provides excellent wear resistance and extends your ceramic bearing life.
4.2.2 Fracture Toughness
-
Your silicon nitride offers a toughness of 5-12 MPa·m¹ᐟ²; higher than SiC and alumina. While Si3N4 is more brittle than steel, it effectively absorbs shock and withstands impact in your gas turbine applications.
4.2.3 High Temperature Resistance
-
Your silicon nitride ceramic bearings maintain high hardness and strength under temperatures >1750°C.
4.2.4 Superior Corrosion Resistance
-
Because your silicon nitride bearings are made from an inert compound, they resist corrosion from salt water, acids and chemicals.
“After switching to silicon nitride bearings in our pumps, corrosion reduced by more than 99% and speeds increased.” — Jia C., Design engineer, Flowvalves Solutions
4.3 Zirconia Ceramic Bearings

4.3.1 High Hardness
-
With a Moh’s hardness of 8-8.5, your Zirkonoxid (ZrO2) ceramic balls resist wear and pressure.
4.3.2 High Toughness
-
Your zirconia is tougher than SiC, silicon nitride, and alumina. Zirconia undergoes a unique transformation toughening process, achieving 9-17 MPam¹/² fracture toughness.
4.3.3 Low Friction
-
Due to zirconia’s low friction coefficient, your ceramic bearing achieves 20-40% higher efficiency than steel at high speeds.
4.3.4 Electrical Insulation
-
Since zirconia is non-magnetic and also insulating, it’s ideal for your electronic applications.
4.4 Alumina Ceramic Bearing

4.4.1 High Hardness and Strength
-
Your alumina ceramic bearing balls deliver a Mohs hardness of 9 and compressive strength of 2300-3000 MPa. Despite their low fracture toughness, your alumina bearings sustains significant mechanical load. They also offer a wear rate <0.01%, extending service life.
4.4.2 High Temperature Resistance
-
Your alumina ceramic bearings withstand temperatures >1750°C, ensuring stability in your demanding processes.
4.4.3 Corrosion Resistance
-
Your alumina offers excellent resistance to chemicals. This makes your ceramic bearings ideal for use in chemical and corrosive environments.
4.4.4 Electrical Insulation
With a purity of >=99.99%, your alumina delivers high electrical resistivity. Combined with insulation properties, alumina bearings are ideal for your semiconductors and electronics.
4.5 Hybrid Ceramic Bearings
-
Your bearing ceramic hybrid delivers properties of ceramics, such as high temperature and corrosion resistance, and high speeds. Combined with steel’s stability under loads and reduced brittleness, your bearings perform reliably and efficiently in demanding applications.
5. Applications of Ceramic Ball Bearings
5.1 Pumps and Valves
-
Steel bearings would corrode if used in your pumps and valve processes. Ceramic bearings’ chemical resistance, stability, and wear rate of <0.01% ensure your systems run with fewer failures.
4.2 Electronic Vehicle (EV) Components
-
For your EV drivetrains, ceramic ball bearings provide less weight than steel, reduced friction, and electrical insulation. This improves efficiency and extends battery range in your high-performance electric vehicles.
4.3 Aerospace & Defense
-
Your aerospace industry uses silicon carbide sleeve bearings in turbines and engines. With their high temperature resistance, they ensure safety and durability in extreme flight conditions.
4.4 Furnaces and Kilns
-
Your silicon carbide sliding bearings’ stability under 1700°C temperatures facilitates optimal performance in continuous high-heat cycles.
4.5 Machine Tool Spindles
-
Your spindles demand precision at very high speeds. Your silicon nitride ceramic ball bearings reduce vibration. Your silicon carbide bearings resist thermal stress during extended machining runs.
4.6 Semiconductor Manufacturing
-
Ceramic materials provide cleanroom compatibility in your semiconductor tools. Being a non-magnetic and insulator, alumina boosts accuracy in your microelectronics fabrication.
5. Comparison Between Silicon Carbide Bearings and Other Ceramic Bearings Table
CeramicBearings_Table1.png
|
EIGENTUM |
SILICON CARBIDE |
SILICON NITRIDE |
ALUMINA |
ZIRCONIA |
|
Hardness (Mohs hardness) |
9-9.5 |
8.5-9 |
9 |
8-8.5 |
|
Temperature Resistance (°C) |
1750 |
>1750 |
>1750 |
>1600 |
|
Verschleißrate |
Excellent (Best) |
Very good |
Gut |
Gut |
|
Dichte (g/cm³) |
3.21 |
3.24 |
3.99 |
5.6-6.1 |
|
Dielektrizitätskonstante |
9.7 |
8.0 |
9.8 |
10-25 |
|
Biegefestigkeit (MPa) |
450 ± 15 |
800-1000 |
386 ±12 |
600-1200+ |
|
Fracture toughness (MPa·m¹ᐟ²) |
4-6 |
8.5 |
8-10 |
10-17 |
|
Korrosionsbeständigkeit |
Exzellent |
Very good |
Good (lower than SiC) |
Gut |
|
Thermal conductivity (W/(m·K)) |
120 |
70 |
24-27 |
2-4 |
|
Relative Cost |
Hoch |
Hoch |
Niedrig |
Medium |
Table: Comparison of the performance of silicon carbide vs other ceramic bearings
Data source: Mater. Sci. Eng. 2025; 109(2): 021004; IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol., vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 21004–21012, Feb. 2025
Ceramic Bearings Cost
-
Your ceramic bearings cost more than steel bearings, especially for SiC and Si3N4, due to complex, energy-intensive manufacturing.
-
However, since ceramics last longer, require lower maintenance, and perform better, they’re more economical long-term.
Select GGSCERAMIC® for ISO-certified solutions.
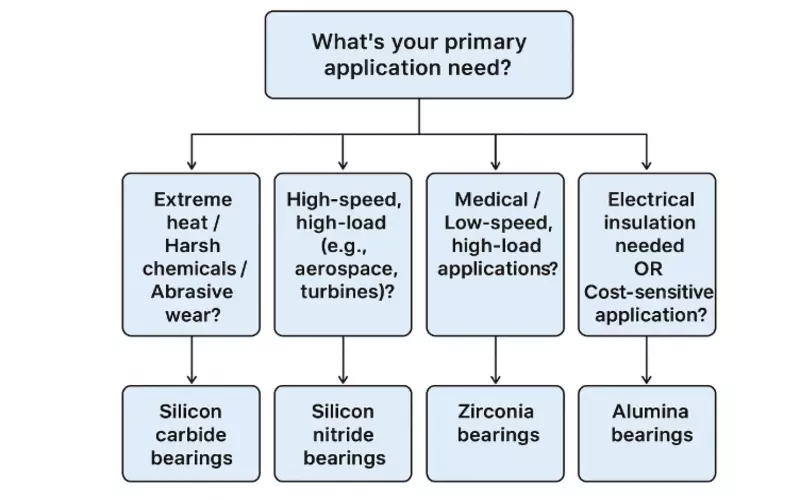
7. Ceramic Bearing Selection Criteria
7.1 Selection Flowchart
7.2 Certification Checks For Quality
-
Your best ceramic bearing must meet strict ASTM and ISO standards. Always verify supplier certification when selecting a SiC bearing manufacturer for your application.
7.3 Silicon Carbide Bearings Manufacturers and Suppliers
-
China ceramic bearing manufacturers produce high-quality ceramic bearings at competitive pricing. Select GGSCERAMIC® for ISO-certified solutions that guarantee consistency in your demanding industry operations.
FAQs About Ceramic Bearings
Q: When should your industry specify silicon carbide bearing or silicon nitride?
A: Where chemicals or high temperatures are involved, use silicon carbide. Choose silicon nitride where resistance to impact or toughness matters most.
Q: What are the differences between silicon carbide and zirconia bearings?
A: Your silicon carbide offers higher hardness and conductivity, while zirconia provides greater toughness and lower pricing.
Q: Why should your application specify alumina bearings?
A: If electrical insulation is the core of your process and mechanical loads remain moderate, alumina works best.
Q: What is the difference between a ceramic vs steel bearing bike?
A: Ceramics offer lighter weight, higher speed, and resists corrosion. Steel absorbs impact and costs less.
Q: How do a bearing ceramic hybrid compare with a bearing full ceramic?
A: Your bearing ceramic hybrid blends steel toughness with ceramic speed, while a bearing full ceramic excels in corrosion resistance and where temperatures > 1700 are involved.
Q: Which is the best ceramic bearing?
A: Good ceramic bearings are determined by your use. For extreme heat, silicon carbide leads. For high speed, silicon nitride performs better.
Abschluss
Your industrial process defines the best ceramic bearing. SiC excels in temperature stability and corrosion resistance. Your silicon nitride delivers toughness for high-speed spindles. Zirconia gives toughness, while alumina provides insulation.