Structural ceramics are everywhere in our daily lives, from products such as smartphones and household items to aircraft and machinery. Advanced engineering ceramics have made our lives easier, faster, and more enjoyable.
Let’s explore the importance, differences, and applications of structural ceramics below.
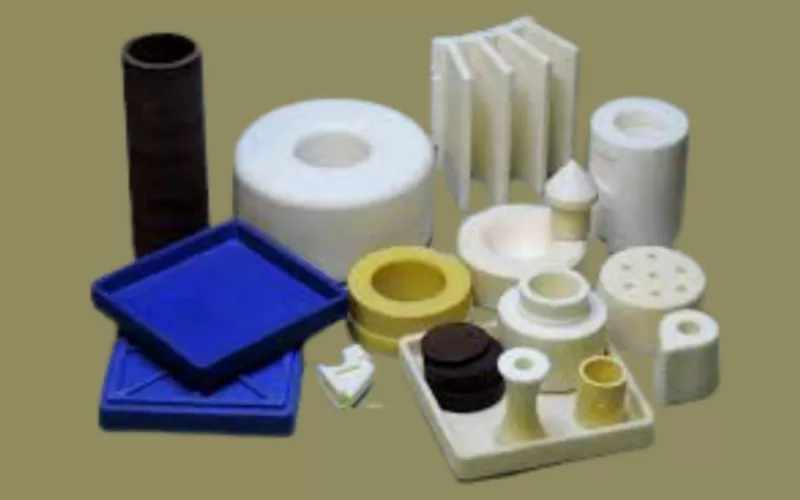

What are Structural Ceramics?
Structural ceramics are also known as advanced ceramics, engineered ceramics, fine ceramics, technical ceramics, and high-performance ceramics. High-technology-grade structural ceramics can resist high temperatures and stresses.
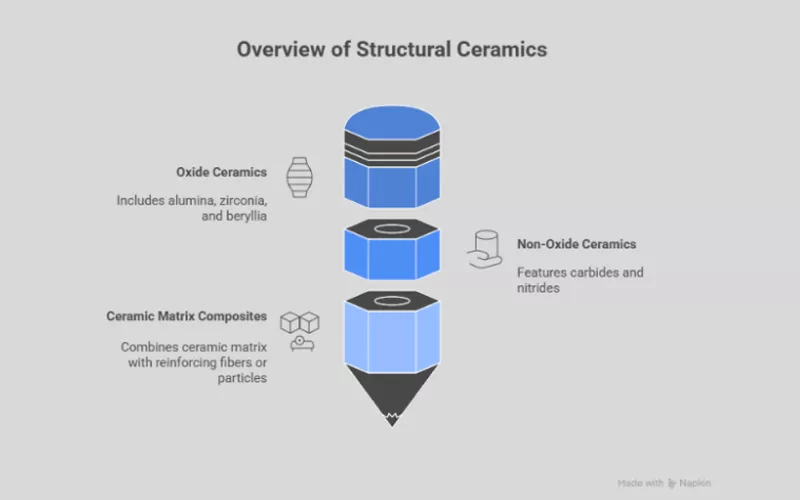
At an early stage, only oxides of some ceramics, such as alumina and zirconia, were popular. At present, you will find applications of borides, carbides, nitrides, and their composites as structural ceramics.
Usually, structural engineering ceramics exhibit outstanding performance and properties in adverse environments. However, you should also learn about their limitations. Structural ceramics are brittle and prone to cracks and flaws.
In recent years, some ceramics have been introduced with self-crack-healing properties, high bending strength, improved fracture toughness, and grain reinforcement. Examples of highly enduring crack-proof ceramics are nanocomposite ceramics, SiAlON, and Al₂O₃.
What Are the Three Main Categories of Structural Ceramics?
|
Name |
Examples |
|
Oxide Ceramics |
|
| Non-Oxide Ceramics | Carbides such as Silicon Carbide(Sic), Boron Carbide(B4C)
Nitrides such as Silicon Nitride(Si3N4), Aluminum Nitride(AlN) , Boron Nitride(BN) |
|
Ceramic Matrix Composites(CMCs) |
|
What Properties Have made Advanced Structural Ceramics Important?
High Thermal Stability: Structural ceramic materials exhibit high melting points and low thermal expansion, maintaining their stability in extreme heat conditions. High-technology ceramics can withstand temperatures from 1000°C to over 3000°C. You can use these fine ceramics where abrupt temperature changes occur.
Hardness and Compressive Strength: Structural ceramic materials are characterized by hardness and strength, which are attributed to a dense, crystalline ceramic structure. The hardness values of technical ceramics can exceed 1000 HV, which is higher than that of steel.
Corrosion Resistance: Advanced engineering ceramics exhibit excellent chemical resistance. Ceramics, such as alumina, silicon nitride, silicon carbide, and sapphire, can resist any chemical attack. Structural ceramics made components remain rust- and corrosion-free in any harsh chemical environment.
High Electric Insulation and Low Dielectric Strength: High electric insulation and low dielectric strength of ceramics protect against short circuits and leakage current. That is why ceramic components are popular in electric safety devices such as fuses, insulators, and circuit breakers.
Wear Resistance: Structural ceramics are strong and hence wear-resistant and abrasion-proof. You will find their application in mechanical cutting tools.
Lightweight: Engineering ceramics are lightweight, which reduces the overall weight of parts and structures.

Why Are Structural Ceramics Important?
The following are the key reasons why you find structural ceramics in most modern equipment.
Longevity: Structural engineering ceramics are resistant to wear and tear. Hence, the ceramic-made products are glowing and the longest-lasting.
Cost Effectiveness: You will get most of the structural ceramic-made components at a reasonable price. Some may be high-priced, but it minimizes with time due to low maintenance and high longevity.
Environment-Friendly: You have no worries about the environment when using ceramic-made products. Structural ceramics are environmentally friendly. The lightweight and longevity of high-tech ceramics contribute to energy savings in many ways.
Safety: You may find engineering ceramics in high-risk applications such as aerospace, kilns, furnaces, heat shields, and refractories. They are safe for critical engineering use, due to their high chemical imperviousness and thermal resistance.
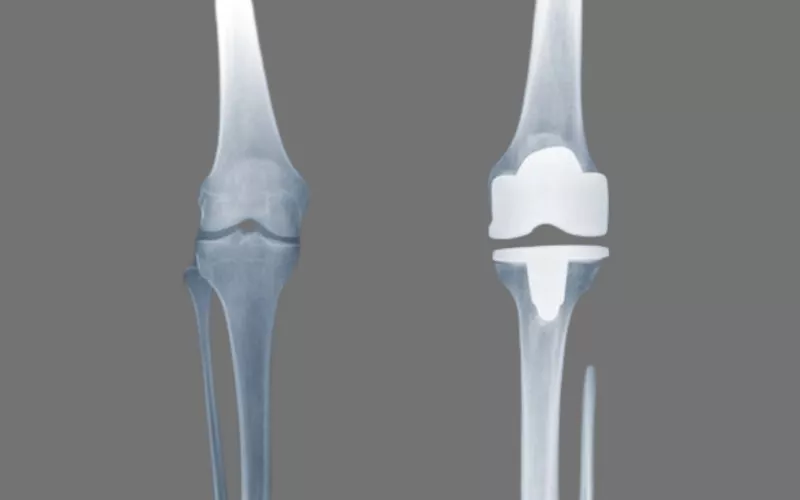
Biocompatibility: Structural ceramics such as alumina and zirconia are biocompatible and integrable with the human body. You will find applications of sustainable engineering ceramics in medical implants and dental healthcare.
How Are Structural Ceramics Different From Traditional Ceramics?
|
Differences in |
Structural Ceramics |
Traditional Ceramics |
|
Materials Used |
Technical ceramics consist of highly refined raw materials such as alumina, zirconia, silicon carbide, silicon, and nitride. |
Traditional ceramics use natural raw materials with little refinement. Clay, silica, and feldspar are the raw materials used in conventional ceramics. |
|
Products |
Common structural ceramic products are engine parts, bearings, cutting tools, seals, heavy machinery, molds, solar panels, substrates, semiconductors, and sensors. |
Various everyday items, including pottery, bricks, and tiles, are traditional ceramic products. |
|
Manufacturing Process |
Advanced structural ceramics manufacturing processes are complex and precise. It includes primary methods such as powder processing, sintering, and hot pressing. Chemical vapor deposition (CVD), physical vapor deposition (PVD), and sol-gel processing are also required in the advanced ceramics manufacturing process. |
The manufacturing process of traditional ceramic materials is simple. It requires molding, firing, and traditional techniques such as hand building, wheel throwing, and slip casting. |
|
Properties |
Structural ceramics have properties, such as high strength, extreme hardness, excellent wear resistance, high thermal stability, and low thermal expansion. |
Traditional ceramics are brittle and porous, and have moderate thermal stability and high electrical resistivity. |
|
Applications |
They have applications in many high-tech industries such as aerospace, automotive, electronics, energy systems, industrial equipment, and semiconductors. |
They are commonly used in household items like dishes, pottery, vases and construction materials like cement, bricks, and tiles. |
|
Cost and Availability |
Structural ceramics are costlier than traditional ceramics due to their material purity, manufacturing complexity, and limited availability. |
Traditional ceramics are cheaper than structural ceramics due to their raw materials and production process. |
|
Environmental Impact |
Advanced ceramics have less adverse effect on the environment due to their recyclability, eco-friendly manufacturing process, longevity, and energy efficiency. |
Conventional ceramics production requires raw materials extraction from nature, which results in land degradation and resource consumption. |
Application of Structural Ceramics:
Aerospace Industry: The improvements in aerospace you see have become possible due to engineering ceramics. Advanced ceramics are essential for modern spacecraft and aircraft heat shields, turbine blades, and engine components.
Automotive: The automotive brake systems and engine parts are made of high-tech ceramics.
Energy Sector: Many energy-generating components, such as turbines, solar panels, and nuclear reactor insulators, are made of structural ceramics.
Medical Implants: Structural ceramics have various applications in healthcare and dental care. You will find their use as bone implants, joint replacements, and bone scaffolds.
Industrial Applications: Industrial tools such as cutting tools, grinding tools, bearings, wear plates, and hubs are common industrial ceramic components. Other manufacturing industries, such as, oil mining and gas mining fields, also use ceramics to increase productivity.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What Makes Ceramics Great for Structural Uses?
The exceptional properties of structural ceramics have made them a great choice for structural applications. The extreme hardness, lower density, and high temperature tolerability are key reasons for their greatness.
What Are Structural and Functional Ceramics?
Structural and functional ceramics are two advanced ceramic categories that have some differences in their properties and applications. Heat resistance, mechanical strength, and durability are the key characteristics of structural ceramics. They are used in equipment where physical resilience is important.
On the other hand, functional ceramics are characterized by their electrical, magnetic, and optical properties and are used in manufacturing electronic items, sensors, and displays.
What Type of Structure Do Ceramics Have?
The structure of ceramics can vary from simple to complex, depending on the manufacturing process. Their structure can be crystalline, glassy, or a blend of these. Ceramics have strong covalent and ionic bonds and have characteristics between the metallic and non-metallic elements.
What are Engineering Ceramics?
Engineering ceramics are advanced ceramic materials having excellent characteristics. They are strong, lightweight, wear-resistant, and corrosion-resistant. They can survive in harsh acidic, alkaline, and corrosive conditions.
Conclusion: Structural ceramics are essential materials for our modern world. Some cutting-edge technologies have become possible with the advancement of structural ceramics. Future advancements in material science and technology will make engineering ceramics more valuable for modern industries.

