
A ceramic heater element is a heating component that converts electrical energy into heat in a process called Joule heating.
Ceramic heater plates, therefore, are a flat application or assembly that uses a ceramic heater element to provide uniform heat distribution.
A laboratory hot plate, one of its industrial applications, is a source of regulated heat for clinical, production, and research labs. These heater plates come with many far-fetched benefits like precise temperature setting, even heat distribution, and excellent heat resistance.
Let’s unravel this industrial heating technology and how the use of a ceramic heater element prevents scalding accidents!
How Does a Ceramic Heating Element Work?
In Joule heating, electric current flows through a conductor that generates resistance. The conductor in this case is the ceramic heater element embedded inside the ceramic hot plate. The element’s atoms collide with the electrons of the current flowing through it. More collision causes more vibration and hence more heat.
The generated heat amount is subject to the magnitude of the electric current and the resistance of the heating element.
How to Choose a Good Ceramic Heater
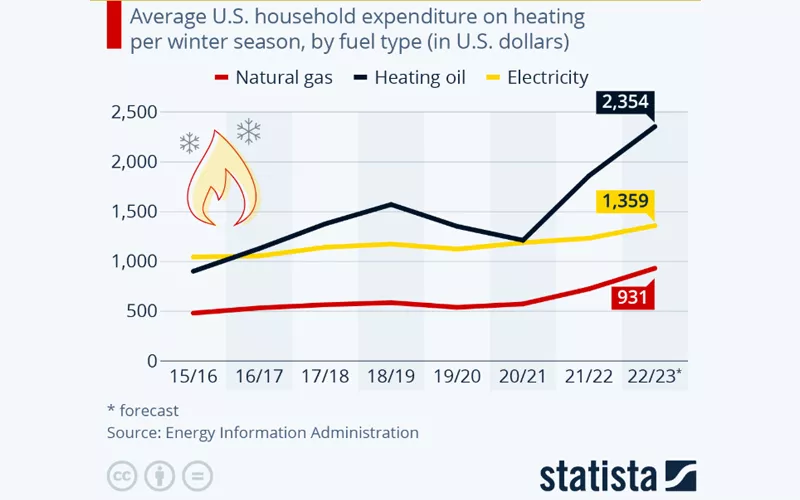
Source: Statista
Statista predicts that this year’s winter will be colder than average, thereby increasing the average US household energy expenses.
However, that doesn’t have to happen when you have a powerful, energy-efficient ceramic heater. Here’s how to choose one:
High electrical resistance: This generates the right amount of heat needed by the ceramic plate. Note that very high electrical resistance will inhibit the flow of currents through the heater element, making it an insulator.
Oxidation resistance: Typically, heater elements are coated with silicon oxide or aluminum oxide to prevent oxidation. Otherwise, an oxide layer susceptible to cracking and wrinkling would form on the element’s surface, eventually leading to equipment failure.

Temperature resilience: A good ceramic heater should be tailored for high performance at specific temperatures, depending on its industrial application.
Ductility: Ceramic heating elements are designed to be manipulated into different forms and shapes without major changes in efficiency.
High melting point: Ceramics are widely preferred to metallic heating elements. This is mainly because ceramics can generate high heat amounts without compromising their mechanical structure or state.
How Ceramic Heating Plates Prevent Scalding

Modern technology facilitates the manufacture of state-of-the-art ceramic heating plates without compromising safety. If well capitalized, this could help solve a problem that the World Health Organization says is a leading cause of injury and disability.
Burns are among the leading causes of disability-adjusted life-years lost in low- and middle-income countries, World Health Organization.
Below are some of the scalding-proof features that manufacturers incorporate in contemporary heating plates:
1Automatic Power-off Feature
You’ll notice that your silicon nitride heating element shuts down in case of overheating. This feature also prevents fire accidents by going off when the equipment is knocked over or left running without being used.
2Cool-to-touch Surface
Unlike traditional hot plates, you can touch the surface of your ceramic heating plate without burns. The ceramic heater element is superimposed with a top-tier coating that prevents the surface from overheating.
3Inbuilt Thermostat
This facilitates precise temperature control and reduces energy wastage.
4No Need for Cooling Products
Modern ceramic heating plates won’t need products like asbestos to help with cooling, thanks to their powerful insulation.
Ceramic Heating Plates Vs. Metallic Heating Plates
The table below shows direct differences between ceramic and metallic heating plates.
|
Feature |
Ceramic Heating Plate |
Metallic Heating Plate |
|
Heating core |
Hard and not easy to break |
Easy to break |
|
Scalding accidents |
Rare |
More likely to happen |
|
Heating speed |
Fast and more efficient |
Slow, causing energy wastage |
|
Temperature control |
Precise and customizable |
Not precise |
|
Heat distribution |
Even, hence no hot spots |
Uneven with hot spots |
|
Oxidation resistance |
High, hence more durable |
Low, hence, more chances of equipment failure |
|
Pressure resistance |
Low |
High |
|
Initial cost |
High |
Low |
|
Versatile? |
Yes |
Some applications may cause a fire |
Hazards of Ceramic Heating Elements
According to the World Health Organization, millions of people globally die each year from burn injuries. The organization stated that many of these accidents, happening from home or at work, were caused by appliances.
While ceramic hot plates are subject to safety standards, they can still cause serious accidents:
Scalding or burns: Research lab hot plates are curated to heat up to over 500 °C and take time to cool down. This could result in serious burns if one accidentally touches the hot ceramic plate.
Fire: This happens when the plates heat too much and don’t cool down, leading to an explosion. Heating flammable substances at high temperatures poses a significant fire threat. Besides, a ceramic hot plate may catch fire if you activate the wrong setting.
Electrocution: Many things can cause the power cord’s insulation to wear out, like accidentally leaving it on the ceramic plate. An electric shock may happen if you accidentally hold the naked wire with your bare hands.
Frequently Asked Questions
1How Do You Safely Use Ceramic Heater Plates?
For research laboratories, ensure that a Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory endorses the ceramic heater plate. For home use, exercise caution when boiling fluids to prevent spills. Keep the ceramic heater plate on a stable surface and always turn it off when not using it.
2Why Does my Ceramic Heater Plate Take so Long to Heat?
If your ceramic heater plate heats so slowly, you need to check the heater element. The power supply could also be insufficient, or the thermostat could be faulty.
3Should I Use a Grill Brush to Clean my Cooker’s Heat Plate?
No. Ceramic hot plates are self-cleaning. To remove the black surface color, set the heat plate to high temperatures for 15 minutes for a burn off. After the skunk is gone, turn the burner off and remember to set it back to cook mode.
How do I Find a Trustworthy Ceramic Heater Plate Manufacturer?
A good example of a trustworthy ceramic heater manufacturer is Gorgeous Ceramics. The company manufactures industry-standard ceramic heaters using aluminum oxide, silicon carbide, etc. Its sophisticated manufacturing process makes the ceramic heater elements durable and highly versatile.
Talk to Us Today!
Gorgeous’ solid international presence gives you a smooth onboarding process, regardless of your location. The company’s all-around website gives a glance at all your ceramics needs. Talking to our professional customer service is as easy as a click of a button.