
Source: Unsplash.com
Boron nitride nanosheets are an emerging technology that combats corrosion from the atomic level. A one-atom-thick material, approximately 10,000 times thinner than human hair, that effectively protects your equipment surfaces from corrosion!
The boron nitride nanomaterial comes with strong thermal conductivity, electrical insulation, and high temperature resistance. BNNs won’t break at extreme mechanical stresses, have high thermal integrity, and chemical inertness.
In this guide, we’ll unravel the properties of BNNs and explain why the nanomaterial should be part of your anti-corrosion arsenal. We also analyze a case study of BNNs when deposited on mild steel. Later on, we will reflect on the future perspectives of boron nitride nanosheets.
Let’s get started!
Boron Nitride Nanosheets for Metal Protection
Source: Unsplash.com
Boron nitride nanosheets are single layers of boron nitride that are arranged in a hexagonal structure. They are a type of two-dimensional nano material with excellent mechanical and chemical properties that come from boron nitride.
The 2D materials are effective anti-corrosion coatings for copper[1], steel, and other metals. They act as either fillers in composite materials or are used as coatings.
Some industries apply the binder-free BNNs coating directly on the metal surface. Others add BNNs into their binder-based coatings.
1. How Boron Nitride Nanosheets Prevent Corrosion
Typically, multi-layered boron nitride nanosheets with a thickness of up to 10nm have superior barrier characteristics, including a large surface area. A feature that most traditional corrosion remedies lack.
Its 2D structure presents exceptional dimensionality for use as a filler or as a nanocomposite coating.
Boron nitride nanosheets demonstrate top-tier mechanical properties, including ~32GPa bending modulus and thermal conductivity of up to 2,000 W/m.K. Such features make it efficient for extreme thermal environments.
Due to their impermeability, a BN nanosheet barrier layer is chemically stable and strong for its robust sigma bonds. The lack of dangling bonds in BN nanosheets contributes to its tenacity and endurance even in harsh working conditions.
Source: Unsplash.com
2. Advantages of Boron Nitride Nanosheets
-
High impermeability: BN nano material provides an invincible coating that won’t allow external substances or particles to permeate through
-
Electrical insulation: They do not cause galvanic corrosion
-
Thermal stability: BNNs do not undergo phase transformations or degradation in extreme thermal conditions, boosting the longevity of the underlying metal
-
Chemical stability: They exhibit oxidation resistance of over 800 degrees Celsius, making them ideal for use in chemical and high-temperature working conditions.
-
Wide bandgap (5-6 eV): Diversifies the application of metal equipment, including industries with high-voltage and high-temperature conditions.
-
Non-toxic: BNNs are an environmentally safe material compared to toxic materials like chromium
Case Study of Hexagonal Boron Nitride (h-BN) Nanosheets for Mild Steel Surface Protection
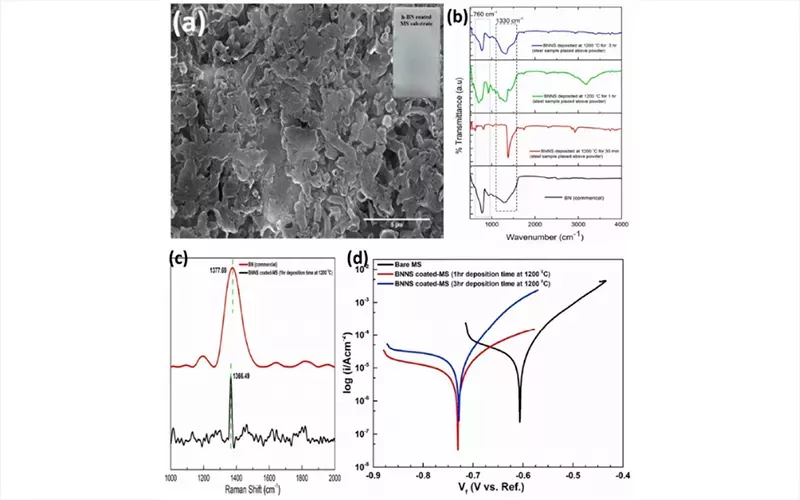
In this study, boron nitride nanosheets are successfully deposited on mild steel using chemical vapor deposition (CVD). The coating, consisting of 80% BNNs, is subjected to deposition at 1,200°C. Mild steel strips were cleaned with 5% HCl and cleaned with NaOH.
Observations:
Source: researchgate.net
Figure (a) shows Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) images of the mild steel substrates coated with BN nanosheets.
Figure (b): FTIR spectroscopy of mild steel samples coated with BNNs shows two characteristic peaks at 1330cm-1 and 760cm-1.
In Figure (c), the Raman Spectroscopy of BNNs-coated mild steel shows two transmission peaks at 1377.69 cm−1 (commercial BN) and 1366.49 cm−1.
Figure (d) reveals a characteristic shift in corrosion potential toward the negative values.
Conclusion:
The shift in corrosion density of BNNs-coated mild steel causes a characteristic reduction of corrosion density (Icorr). This demonstrates the efficacy of the BNNs coating in inhibiting ion oxidation and enhancing oxygen reduction.
The negative shift in corrosion potential implies that the BNNs coating was efficient in providing electrical insulation, acted as a cathodic coating, and prevented galvanic corrosion.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Which Metals are Efficiently Used with Boron Nitride Nanosheet Coatings?
Copper and steel are the metals that research has found to work well with BNNs coatings.
2. Are Boron Nitride Nanosheets Better than Graphene Alternatives?
Yes, boron nitride sheets are better than graphene for their outstanding chemical and thermal integrity. They are great electrical insulators, ensuring they do not react with the underlying metal. Graphene, however, causes galvanic corrosion with the underlying metal.
3. What are the Disadvantages of Boron Nitride Nanosheets?
BN nanosheets have a higher price tag than traditional methods of preventing corrosion. Besides, you need to be sure of the metal you want to coat.
4. Are Boron Nitride Nanosheets Better than Traditional Methods of Preventing Corrosion?
Yes, BNNs are better because of their exceptional thermal stability, wide bandgap, chemical stability, and mechanical strength. They also exhibit low electrical conductivity, impressive thermal shock resistance, and have a high dielectric constant.
The Corrosion Problem
Corrosion is the gradual degradation of the chemical and electrochemical properties of a metal when exposed to corrosive agents like water, oxygen, and chloride ions. Eventually, a metal loses its luster, mechanical strength, and integrity.
Source: Unsplash.com
Traditional corrosion protection methods don’t seem to improve corrosion, whose yearly losses worldwide account for approximately 3% of the global GDP [2] (gross domestic product).
The Future Perspectives of Boron Nitride Nanosheets
This article debunks the long-held belief that companies must always incur losses due to corrosion. Nanomaterials are changing that narrative.
Boron nitride nanosheets are an emerging technology whose research is at its primary stages. Yet, physicists have found immense capabilities in nanomaterials for metal corrosion and other industrial uses like medicine, energy, and environmental protection.
In materials science [3], nanoparticles or nanomaterials have a promising future in nano-scale engineering. This is where nanoparticles will create self-healing and self-assembling materials. Engineers will leverage nanomechanics to create bridges and infrastructure.
Nanomedicine [4] is quite advanced now, as physicians seem to find an intricate way to treat chronic diseases like cancers and tumors.
Talk to Us!
Visit our website to learn more about boron nitride nanosheets and other advanced industrial materials. Alternatively, you may talk to us today and start your anti-corrosion plan with a futuristic nanomaterial!