Bornitrid cbn ist eine fortschrittliche Keramik, die für ihre hervorragenden Eigenschaften bekannt ist. BN-Chemie hat Bor-Stickstoff Bindungen, die zu unterschiedlichen Strukturen führen. Von den Strukturen von BN ist eine solche prominente Struktur von Interesse Kubisches Bornitrid cbn. Versuchen wir, c-bn und seine relativen Aspekte zu verstehen.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- Struktur von hexagonalem Bornitrid
- Eigenschaften von hexagonalem Bornitrid
- Anwendungen von hexagonalem Bornitrid
- Was ist kubisches Bornitrid?
- Struktur von kubischem Bornitrid
- Eigenschaften von kubischem Bornitrid
- Kubisches Bornitrid vs. Diamant
- Verwendung von kubischem Bornitrid
- Super-Schleifscheiben – oder Diamant-C-BN-Scheibe
Bornitrid: Ein Überblick
Bornitrid wird durch die chemische Formel „BN“ angegeben. Wie bereits erwähnt, Bornitrid existieren in verschiedenen Formen. Im Allgemeinen ist es die Position von Bor und Stickstoff im Gitter, die verschiedene Bornitridstrukturen. Einige davon sind recht bekannt, wie etwa amorphe, hexagonale, kubische und Wurtzit-Formen.
Wenn es um Funktionalität geht, Bornitrid-Keramik ist sehr gut bearbeitbar. Nach der Bearbeitung ist kein Wärmesintern oder eine Stabilisierungsbehandlung erforderlich. Darüber hinaus Bornitrid hat eine höhere Wärmekapazität und ist auch ein guter elektrischer Isolator.
Versuchen wir zunächst, die Ableitungen von BN zu verstehen. Hexagonales Bornitrid (h-BN) und noch eins Kubisches Bornitrid (c-BN)
Hexagonales Bornitrid (h-BN)
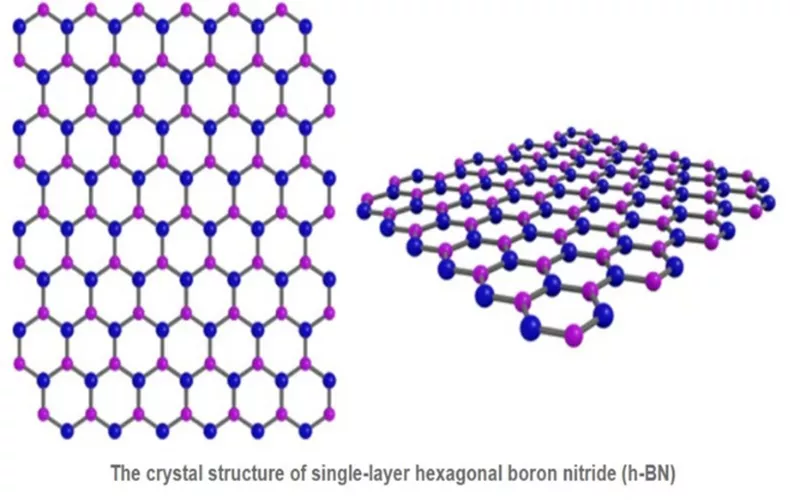
Struktur von hexagonalem Bornitrid
Hexagonales Bornitrid ist Bestandteil vieler Industrieprodukte wie Kosmetika. HBN hat eine Struktur, die kontrolliert wird durch kovalente Bindungen. Die Schichten in HBN gehorchen jedoch wandern Waalskräfte. Aufgrund seiner plattenartigen Geometrie eignet sich HBN ideal zur Schmierung.
Hexagonales Bornitrid hat Elemente aus Bor und Stickstoff, die an seinem Gitter fixiert sind. Die Anordnung besteht aus drei Stickstoffatomen, die an ein Boratom gebunden sind. Die Ähnlichkeit in der Wabenstruktur ist der Grund für die Analogie zu Kohlenstoff. Darüber hinaus sind die Eigenschaften der mechanischen, chemischen Festigkeit und elektrischen Isolierung auf die planaren Dreiecksbindungen zurückzuführen
Eigenschaften von hexagonalem Bornitrid
Hexagonales Bornitrid wird üblicherweise durch Boroxidnitrierung bei erhöhten Temperaturen hergestellt. Da seine Stabilität der von Graphen ähnelt, Hexagonales Bornitrid wird oft als die fortschrittlichste technische Keramik gepriesen. Einige überlegene Eigenschaften von Hexagonales Bornitrid sind seine Wärmeleitfähigkeit und sein niedriger Reibungskoeffizient.
Anwendungen von hexagonalem Bornitrid

- HBN wird in nanoelektronischen Geräten als Ersatz für Graphensubstrate verwendet
- Hexagonales Bornitrid in seiner dünnen Form wird als Beschichtung verwendet, die Korrosion widersteht
- HBN wird häufig bei der Herstellung von Sensormaterialien verwendet. Aufgrund seiner niedrigen Dielektrizitätskonstante wird es auch beim Elektronentunneln eingesetzt.
Kubisches Bornitrid
Was ist kubisches Bornitrid?
c-BN ist ein Derivat von Hexagonales Bornitrid (h-BN) unter hoher Temperatur und hohem Druck hergestellt.
Die größte Spezialität von c-BN ist, dass es den Platz des zweithärtesten Materials der Welt einnimmt. Die mechanische Festigkeit von Kubisches Bornitrid ist beliebt und steht dem Diamanten in nichts nach. Es ist eines der beliebtesten Polymorphe von Bor Nitrid.
Struktur von Kubisches Bornitrid
Die Grundstruktur von Kubisches Bornitrid ist kristallin. Es hat eine Dichte von etwa 3,5 g/cm3 und erscheint in blassgelber oder transparenter Farbe. C-BN folgt einer abwechselnden Anordnung von Bor- und Stickstoffatomen. Hier ist die Bor-Stickstoff Atome gehen eine kovalente Bindung ein, die der Hauptgrund für ihre Härte und Stabilität ist.
Kubisches Bornitrid Formel wird als c-BN angegeben. Es gibt zwei gängige c-BN-Typen auf dem Markt. Einer ist dicht kubisches Bornitrid und das andere polykristalline kubische Bornitrid.
Eigenschaften von kubischem Bornitrid
C-BN ist ein brillanter Halbleiter, dessen Bandlücken empfindlich auf Änderungen des angelegten Drucks reagieren. Diese Änderungen der Bandlücke tragen dazu bei, dass sie sich als elektrische Isolatoren auszeichnen. Kubisches Bornitrid sind im Allgemeinen inert und besitzen eine niedrige Dielektrizitätskonstante. Ihre Wärmeleitfähigkeit liegt bei etwa 1300 KW/MK.
Wenn es um Reaktivität geht, c-BN bleibt auch gegenüber Eisenwerkstoffen unempfindlich. Der optische Bereich, der von kubisches Bornitrid variiert vom Ultraviolett- bis zum sichtbaren Spektrum.
Kubisches Bornitrid vs. Diamant

Obwohl nicht härter als Diamant, kubisches Bornitrid hat im Vergleich zu Diamanten seinen besonderen Stellenwert. Härte von kubischem Bornitrid beträgt 4500 kg/mm2, während Diamanten eine Härte von etwa 600 kg/mm2 aufweisen. Die Elastizitäts- und Volumenmodulwerte liegen ebenfalls in einem ähnlichen Bereich von 800 – 1000 und 370 – 450.
Darüber hinaus, wenn es um die Struktur geht, wie Diamant, c-BN hat zwei unterschiedliche Basisatome. Die Ähnlichkeit von Diamant und c-BN wird im Allgemeinen auf ihre ähnliche Struktur zurückgeführt.
Verwendung von kubischem Bornitrid
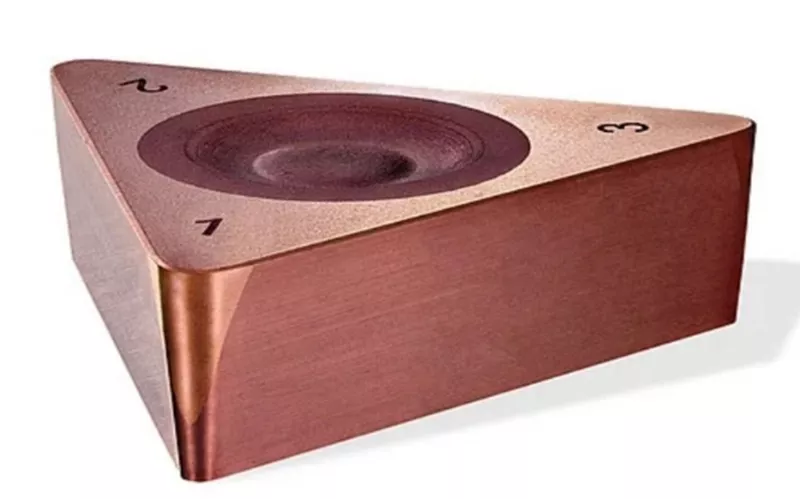

CBN-Schneidwerkzeugmaterial
Kubisches Bornitrid weist sowohl einen Elastizitäts- als auch einen Kompressionsmodul auf, der größer ist als bei Borcarbid und Siliziumkarbid. Genau dieser Grund trägt stark zur Härte von kubischem Bornitrid bei. Die Härte macht sie als Schleifmittel geeignet und hilft ihnen, als CBN-SchneidwerkzeugmaterialIm Allgemeinen wird dichtes c-Bn zum Schneiden und poröses c-Bn zum Schleifen verwendet.
Die inerte Natur von Kubisches Bornitrid auch ermöglicht ihnen die Funktion als Schneid- und Bearbeitungsmaterial. Im Gegensatz zu Diamant reagiert es nicht mit Eisen. Herkömmliches c-Bn muss jedoch für die Schneidanwendung bearbeitet werden. Dies geschieht in der Regel während der Umwandlung von h-Bn in c-Bn beim Sintern.
CBN als elektrische Isolatoren
Abgesehen von der Härte Kubisches Bornitrid eignet sich auch hervorragend als elektrischer Isolator. Dies ist auf die große Bandlücke zurückzuführen.
CBN in Halbleiteranwendungen
Durch die Beschichtung von Aluminium und Metallen der Gruppe 8 C-BN Die Funktion, als Senke zu fungieren, ist in der Elektronikindustrie beliebt. C-BN wird als Kühlkörper in Lasern, mikroelektronischen Geräten und LEDs verwendet.
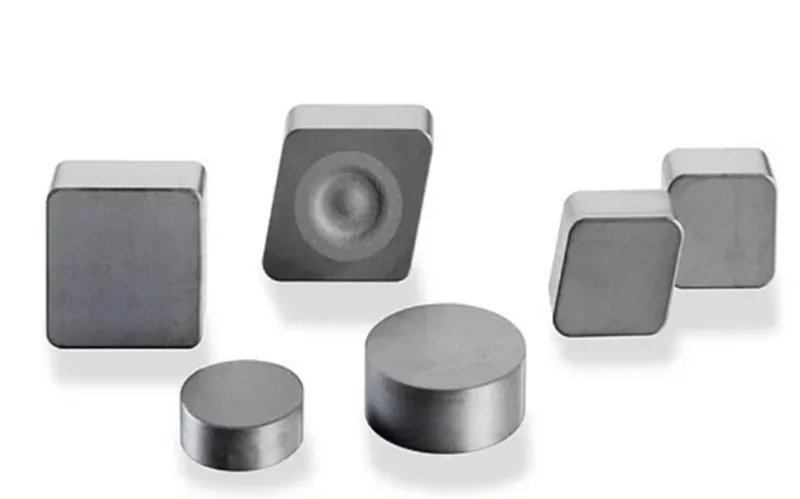

Kubisches Bornitrid Auch bei der Halbleitersynthese bietet sich durch geeignete Dotierung ein Mehrwert, da p- und n-Typen erhalten werden können. Übliche Dotierungsmaterialien sind Silizium oder Beryllium. Diese Halbleiter arbeiten bei hohen Temperaturen und werden in UV-Sensoren eingesetzt.
c-BN Schleifscheiben
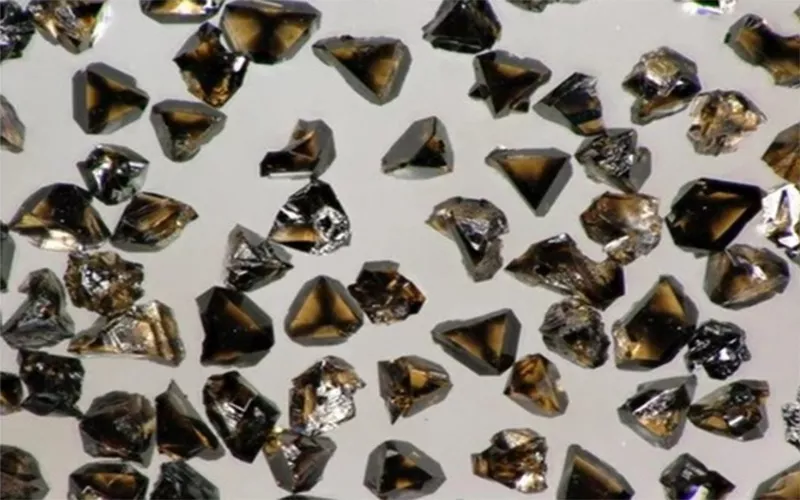
Die Erfindung von c-BN Schleifscheiben Aufgrund der erhöhten Effizienz wurde eine Präzisionsfertigung erforderlich. Räder aus c-BN wurden in Branchen wie der Luft- und Raumfahrt, dem Maschinenbau, der Werkzeugproduktion und der Automobilindustrie eingesetzt. c-BN Schleifscheiben Sie bieten außerdem eine hohe Härte und eine gute Leistung im Vergleich zu SiC und Aluminiumoxid. Sie gewährleisten die strukturelle Integrität bei höheren Temperaturen und unterliegen keiner Degradation.
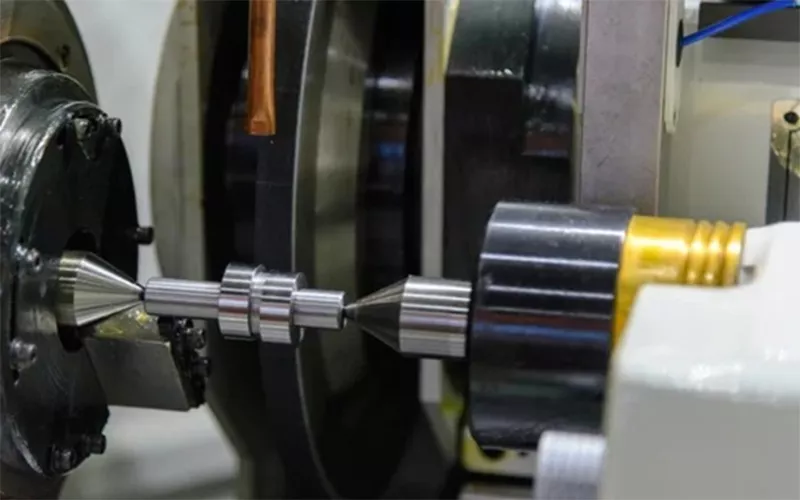
Die Räder von c-BN hält hohen Temperaturen stand und bewältigt die während des Prozesses entstehende Wärmemenge. Die Verschleißfestigkeit ist auch wirtschaftlich vorteilhaft, wenn c-BN-Schleifscheiben in Betracht gezogen werden. c-BN Schleifscheiben bieten hervorragende Oberflächengüte und vermeidet Werkstückabfall. Es sorgt auch für kürzere Zykluszeiten, da die Aufgaben schnell und präzise erledigt werden.
Super-Schleifscheiben – oder Diamant-C-BN-Scheibe
Die Super-Schleifscheiben unterscheiden sich von herkömmlichen Scheiben aus SiC und Aluminiumoxid. Sie bestehen aus einer Kombination aus C-Bn und Diamant. Die Super-Schleifscheibe bietet eine bessere Wärmeleitfähigkeit und begrenzt so den Temperaturanstieg des Werkstücks. Die Diamant-C-Bn-Rad bieten außerdem hohe Genauigkeit und Präzisionsschnitte, die zu einer längeren Lebensdauer beitragen.
Abschluss
Kubisches Bornitrid ist in der modernen Wissenschaft und Materialherstellung gefragt. Sie sind im Vergleich zu Materialien wie Diamant konkurrenzfähig. Sie zeichnen sich durch Eigenschaften wie Härte, Festigkeit und elektrische Isolierung aus. Die große Bandlücke, die inerte Natur, die niedrige Dielektrizitätskonstante und optische Besonderheiten sind weitere Vorteile.
