Your metal heating elements keep failing above 1300°C. You are wasting money on constant replacements. This guide helps you pick the right ceramic material, silicon carbide, aluminum nitride, alumina, or silicon nitride based on your temperature, budget, and application. You’ll learn specifications, real costs, and selection strategies that save you downtime.
What Is an Industrial Heating Element?

Precision ceramic coil spacing.
Su elementos calefactores industriales convert power to heat by electrical resistance. They power your furnaces, kilns and processing facilities from 600°C to 1850°C. You need advanced ceramics for anything above 1300°C. Metal can’t survive those temperatures.
What Materials Are Advanced Ceramic Heating Elements?
Advanced Ceramic Materials:
-
carburo de silicio (SiC): 1600°C max, 120 W/m·K conductivity
-
Nitruro de aluminio (AlN): 1800°C max, 170 W/m·K conductivity
-
Alúmina (Al₂O₃): 1800°C max, 25-30 W/m·K conductivity
-
Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄): 1400°C max, superior thermal shock resistance
Metal Alloys (Reference): FeCrAl and NiCr alloys max at 1300°C with 12-24 month lifespan.
We are covering ceramics here because metal can’t survive above 1300°C in your industrial applications.
What Are Core Performance Parameters?
|
Factor |
Metal Elements |
Ceramic Elements |
What It Means for Your Operation |
|
Temperatura máxima |
1300°C limit |
Up to 1850°C |
Ceramics let you run processes metal can’t handle |
|
Distribución de calor |
15-25 W/m·K |
25-170 W/m·K |
Higher conductivity means more uniform heating |
|
Esperanza de vida |
12-24 months |
3-6 years |
You’ll replace metal 3-4 times before ceramics fail |
|
Initial Cost |
$200-800 |
$600-4,000 |
Ceramics cost more upfront, less over 5 years |
Why Choose Advanced Ceramics?
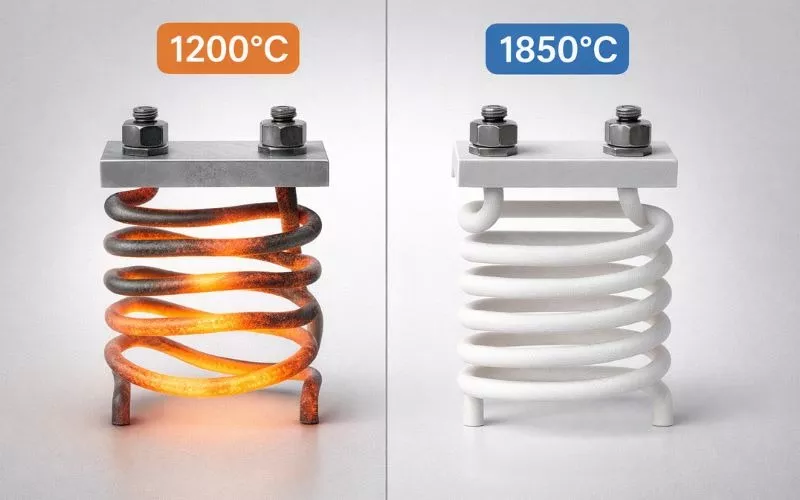
Metal fails at 1200°C. Ceramics thrive at 1850°C.
-
Temperature Capability: Your metal elements sag at 1200°C. Ceramic heating elements remain in perfect condition up to 1850 °C.
-
Resistencia química: Ceramics form protective oxide layers. Silicon carbide produces a self-repairing silica film.
-
Stable Performance: The electrical resistance is constant. Your metal’s resistance increases as oxidation reduces power output.
-
Manufacturing Flexibility: Precisión moldura y Mecanizado CNC enable formation of complex shapes that are impossible with metals.
What Are Ceramic Element Disadvantages?
Higher Cost: Advanced ceramics cost between $600 and $4,000, while metals range from $200 to $800.
Fragilidad: You will crack ceramics if you drop them. You need to handle them carefully.
Lead Times: Custom elements take 3-4 weeks for sinterización at 2000°C or higher. Above 1400°C, you have no choice ceramics are your only option.
What Is Silicon Carbide?
Raw SiC crystalline structure.
carburo de silicio (SiC) is the most widely used advanced ceramic for industrial heating elements.
Specifications:
-
Operating range: 600-1600°C
-
Thermal conductivity: 120 W/m·K
-
Expansión térmica: 4.5 × 10⁻⁶/°C
-
Flexural strength: 400-550 MPa
Low expansion minimizes thermal stress. Elementos calefactores de carburo de silicio form a silicon dioxide layer for protection in an oxidative atmosphere.
Where Is Silicon Carbide Used?
Silicon carbide can be used for
-
Glass manufacturing at 1500-1550°C.
-
Ceramic sintering kilns for bisque and glaze firing.
-
Laboratory furnaces needing stable temperature control.
-
Non-ferrous metal heat treatment.
SiC should be your first choice, when operating at 1400°C to 1600°C.
What Makes Aluminum Nitride Special?
Alumina: Your cost-effective workhorse for everyday heating.
nitruro de aluminio (AlN) combines excellent thermal conductivity with electrical insulation.
Specifications:
-
Maximum temperature: 1800°C
-
Thermal conductivity: 170 W/m·K
-
Electrical resistivity: >10¹⁴ Ω·cm
-
Thermal response: <1 second
AlN is your only option for clean room compatibility in semiconductor manufacturing. Virtually no particles are generated.
Where Does Aluminum Nitride Make Sense?
AlN justifies its high cost in four professional applications:
-
Semiconductor wafer processing: If a batch of $50,000 is discarded due to contamination, a clean element of $3,000 is reasonable
-
LED manufacturing: High thermal conductivity eliminates hot spots that reduce performance
-
Ultra-high vacuum laboratory: Zero particulate material prevents the ruin of experimental work spanning several months
-
Medical device production: Your implantable devices can’t tolerate contamination due to component degradation
Other than these applications, SiC and alumina are 2-3 times cheaper and work well.
What Is Alumina?

Alumina elements: Cost-effective for applications under 1600°C.
Alúmina (Al₂O₃) offers reliable high-temperature performance at moderate cost.
Properties:
-
Operating temperature: 1800°C
-
Thermal conductivity: 25-30 W/m·K
-
Cost: 1.5x metal pricing
With electrical insulation, alumina is widely used in situations where both heating and insulation are important. You will find it in automotive applications, gas appliances, and water heaters.
How Does Silicon Nitride Handle Thermal Shock?
Nitruro de silicio (Si₃N₄) can withstand sudden temperature changes that crush other ceramics.
Actuación:
-
Flexural strength: 800-1000 MPa
-
Thermal shock: Survives 1000°C to room temperature
-
Operating temperature: 1400°C
Interconnected crystal structures deflect cracks. Automotive oxygen sensors use silicon nitride heating elements to repeat the temperature cycle from cold start to 800 °C or higher dozens of times daily.
How Do Materials Compare?
|
Material |
Max Temp |
Conductivity |
Best Use |
|
Metal |
1300°C |
15-25 W/m·K |
Low-temp only |
|
Alúmina |
1800°C |
25-30 W/m·K |
General purpose |
|
carburo de silicio |
1600°C |
120 W/m·K |
Glass, continuous |
|
Nitruro de silicio |
1400°C |
28 W/m·K |
Thermal cycling |
|
Nitruro de aluminio |
1800°C |
170 W/m·K |
Semiconductores |
Knowing these options helps you choose smarter.
How Do You Select Materials?
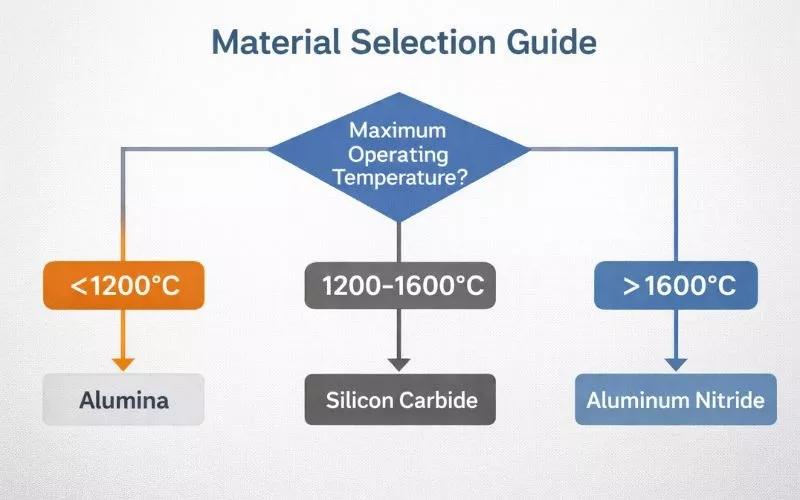
Temperature-based material selection flowchart.
Start with the maximum operating temperature. That immediately eliminates incompatible materials.
Temperature-Based Selection:
-
Below 1200°C: Alumina works well
-
1200-1600°C: Silicon carbide becomes optimal
-
Above 1600°C: Aluminum nitride or zirconia
Procurement Checklist:
-
Temperatura máxima de funcionamiento
-
Continuous versus intermittent operation
-
Furnace atmosphere composition
-
Physical space constraints
-
Power supply specifications
-
Purchase and Exchange Budget
Supplier Qualification: Evaluate manufacturing capacity, material certification, customization services, technical support, and industry certifications. Industrial heating elements suppliers should show that they possess in-house research and development expertise in materials science.
What Maintenance Extends Life?
Temperature Monitoring: Install thermocouples at multiple points to avoid exceeding the maximum rated heating element temperature. The deterioration rate doubles every time the specification value exceeds 50 °C.
-
Power Control: Use SCR controllers and not on-off relays.
-
Physical Protection: Prevent impact during loading.
-
Connection Inspection: Check the oxidation of terminals quarterly.
Advanced ceramics require specific handling procedures. Always refer to the material guidelines from your ceramic manufacturer.
Replace at 80% of expected life, rather than using until failure.
Preguntas frecuentes
What determines ceramic element pricing?
You will pay based on material purity, manufacturing complexity, and customization level. Silicon carbide costs you less than aluminum nitride. If you need custom shapes, expect to pay 20-40% extra.
How do I transition from metal to ceramics?
You need to check electrical compatibility and your installation setup. Work with application engineers who can help you pick the right material based on your temperature and conditions.
What causes ceramic failures?
You will damage ceramics by running them above their rated temperature, hitting them with thermal shock, or physically breaking them during handling.
How hot can silicon carbide operate?
You can run your silicon carbide elements at 1600°C all the time. You can push to 1650°C for short periods, but this will shorten how long they last.
Which ceramic resists thermal shock best?
You’ll get the best thermal shock resistance with silicon nitride. It works great if you have common ceramic heating element needs.
Do ceramics need special controls?
You should use SCR controllers they will make your elements last much longer compared to simple on-off switching.
What industries use advanced ceramics?
You will see them in glass, semiconductor, ceramics, aeroespacial, automotive, lab equipment, and powder metallurgy anywhere you are working above 1300°C.
Can coils be customized?
Yes. You can get custom heating element coil designs that work better for your needs. They take 3-4 weeks to make.
Conclusión
Su metal elements can’t survive above 1300°C. You need ceramics, silicon carbide, aluminum nitride, alumina, or silicon nitride. Pick based on your temperature, atmosphere, and budget. Proper material selection saves you money long-term.
Need help choosing? GGS Ceramic has built heating elements since 2006. Our engineers understand your challenges. Contact us to discuss your specific furnace requirements.