Introducción

Diagram 1: Modern heating appliance
In today’s world, where warmth, comfort, and heating consumption are non-negotiable, modern systems like electric heating tubes have taken center stage. You’ll literally find them in every corner. What really makes them so efficient, and how can you make the best use of these powerhouses? Let’s quickly run through it together!
What Are Electric Heating Tubes
Electric heating tubes are heating systems made up of a tubular structure that converts electrical energy into heat (thermal energy). These electrical heating tubes play a heating role in many homes, firms, and industries.
They mostly come as metal tubes manufactured from stainless steel or copper, with a heating wire sealed inside. This wire, known as a resistance coil, turns electrical energy into heat when you power these appliances. Once the heat is generated by these electric heating tubes, it travels through the tube’s body and spreads evenly.
Also, inside this tube is a magnesium oxide powder, which acts as both a heat conductor and an electrical insulator.
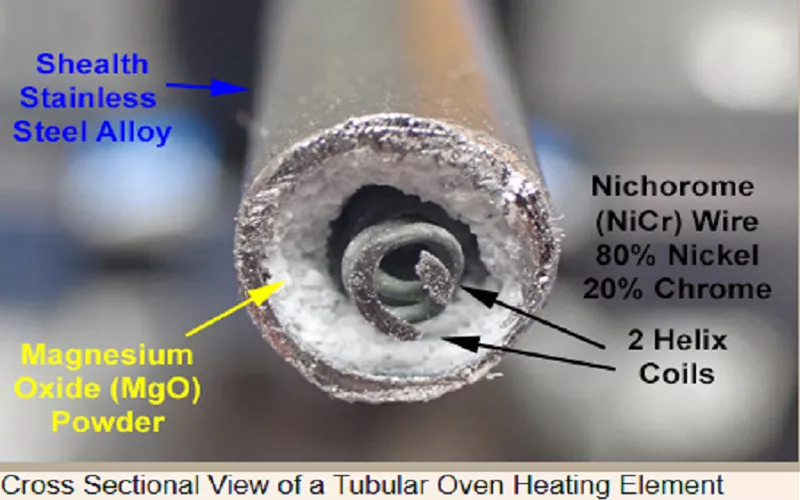
Diagram 2: Magnesium Oxide powder in a tube
What does it do? It keeps the wire safe while ensuring maximum heat transfer. These tubular heating elements are strong and can withstand very high temperatures. It is designed to take a long, cylindrical shape, that makes it ideal to heat spaces like bathrooms, offices, warehouses, cupboards, etc.
Let’s see a few of their properties:
-
They have an operating temperature of about 200°C - 900°C.
-
They have a voltage rating ranging between 110V - 240V AC. Although industrial heater elements are slightly higher.
-
They usually have a power rating of about 100W - 5000W.
-
Their sheath material is usually stainless steel or copper to maintain durability and heat resistance.
-
They have an Insulation resistance of about 100 MΩ at 500V DC.
-
They have a thermal conductivity of about 15 - 25 W/m·K, allowing efficient heat transfer.
-
They have a diameter range of 6mm - 20mm.
Types of Electric Heating Tubes
Just as you have different tools for different jobs, there are also different types of electrical heating elements for various heating needs.
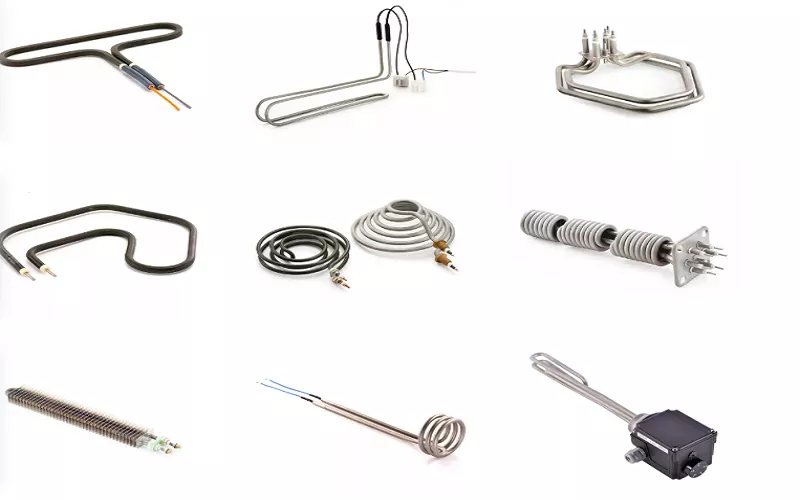

Diagram 3: Various heating elements
These are five of the most common types:
1. Immersion Heaters: These types of tubular heating elements are designed to heat liquids like water and oil by direct immersion. You’ll see them mostly in ring boilers, water heaters, and laboratory baths.
2. Finned Tubular Heaters: They are fast heaters that convert electrical energy to thermal energy. They have metal fins that increase surface area. This makes them ideal for heating air in ovens or large drying chambers. Fin heating tubes offer the advantage of fast heating, low cost, and high thermal efficiency.
3. Cartridge Heaters: They have very compact rods inserted into holes of metal blocks. They have a very simple structure, high mechanical strength, reliability, high thermal efficiency, and safety. You can also install them easily and be guaranteed of long service life, little or no pollution, and a low price. Also, their lightweight means you can disassemble, assemble, and bend them into any shape you want.
4. Radiant Heaters: These types are used in commercial electric radiant heaters. They’re specifically built to warm open spaces like warehouses or workshops. Radiant heating tubes are enclosed in a protective covering that is energized and heated. The casing indirectly radiates heat to the furnace lining and workpiece to be processed. They make heating furnaces very efficient especially in the heat treatment industry.
5. Quartz heating tube: Quartz heating tubes are devices that use quartz glass tubes as the major component for infrared radiation. They consist of milky white quartz glass tubes with high temperature resistance that have been specially processed. Not only that, they’re also combined with resistive materials as heating elements. While using them, you’ll enjoy their strong high-heat capacity, large power margin, adjustable power settings and durability.
You can get any of these electrical heating tube elements from us at GGSCeramics. We have various equipment suitable for any heating application.
How does an Electric Heating Tube work?
An electric heating tube works on the simple principle of resistance heating. How? Inside the tube is a wire coil, made of a strong alloy like Nichrome. Once electricity passes through it, the wire resists the flow of current and becomes very hot. This heat is then transferred safely by an insulator (magnesium oxide powder) to the outer metal tube.
Diagram 4: Heating cycle
The metal sheath (copper or steel) then releases the heat into the surroundings (water, air, or oil). It’s that simple - power goes in, the coil heats up, and the tube smoothly transfers that heat equally. This straightforward design by tubular heater manufacturers makes electric heating tubes powerful and reliable. With that, they can comfortably handle different environments.
Some industrial heater elements are best for air heating, while others work well for immersion. This same principle of resistance heating applies to electric radiant heaters for warehouse systems, where the tubes emit warmth that feels natural and very consistent. Simply put, these electrical heating tubes convert electrical energy to thermal energy and proceed to spreading the heat.
How To Use Electric Heating Tubes
Knowing how to use electric heating tubes properly is one sure way to enjoy their best performance and even prolong their lifespan.
Here are some simple steps on how to use them:
-
You must first of all check the specifications and ensure the tube matches your voltage and wattage needs (e.g., 220V, 2kW).
-
Install it properly and firmly - Any loose installation can spoil things for you. So ensure you fit the tube into the machine or the mounting hole. Then check to see that it’s tightly secured to ensure good heat transfer.
-
Connect the terminals: Join the wire connections properly. If it’s your first time handling such parts, call a technician or watch clips on how to use electrical heat shrink tubing to insulate and protect connections.
-
Ensure grounding and safety: Remember, it’s safety first, so always ground the unit before you switch it on. This is the same as earthing/ ensuring that electricity flowing into the heating tube also has a safe path to flow into the ground instead of passing through you or anything that could get damaged.
-
Switch on gradually: Don’t be in a hurry to power up and use this equipment. After you’ve switched it on, allow it to heat slowly before anything else.
-
Avoid dry heating: Never put on the electric tube heater without the medium around it or else it’ll burn out fast.
-
Ensure you maintain it regularly by cleaning off any scale, residue, or dust. Just like commercial electric radiant heaters, a clean surface ensures a better performance.
Follow these few simple steps, and your heater will last longer and perform well while doing its job quietly.
Applications of Electric Heating Tubes
There are several ways to use tubular heating elements, and you can find them almost everywhere. They have various industrial and commercial applications because they provide efficient and reliable heat. The fun fact is that many don’t know how to use electrical heat shrink tubing. Now, let’s see some common applications for these tube heaters:
-
Laboratory water baths and incubators use electric heating tubes to provide steady and uniform heating.
-
Electric kettles and ring boilers use electrical heating elements to efficiently heat water to boiling temperature within seconds.
-
Ovens and dryers also use electrical heating elements to maintain a stable temperature while heating.
-
Offices, rooms, open spaces, and warehouse heating are all made possible through electric radiant heaters for warehouse systems. They help you spread gentle heat across very wide areas.
-
Industrial machines like plastic sealers or molding equipment also use industrial heater elements to function properly.
-
Your home appliances, such as washing machines, toasters, and dishwashers, are all powered by these tubular heating elements.
Preguntas frecuentes
How long should electric heating tubes last?
It depends on how well you handle them. Although with proper use and maintenance, they should last many years.
Can I use an electric heating tube without any liquid or air flow?
No, unless it’s specifically designed for air heating.
What’s the difference between commercial electric radiant heaters and tubular heaters?
Commercial electric radiant heaters emit heat as infrared energy to warm up a room, warehouse, or open space. A tubular heater transfers heat directly through contact (like heating water or air inside a machine).
Conclusión
Despite their simplicity, tubular heating elements are an entirely different breed of modern heating systems. Knowing how tube heaters work will help you make the best use of them. They have amazing properties to suit large applications, ranging from your bathing water to industrial heaters and lab baths. With proper care and maintenance, trust them to keep providing you with reliable and efficient heat. Now is the best time to watch out and invest in them!