導入
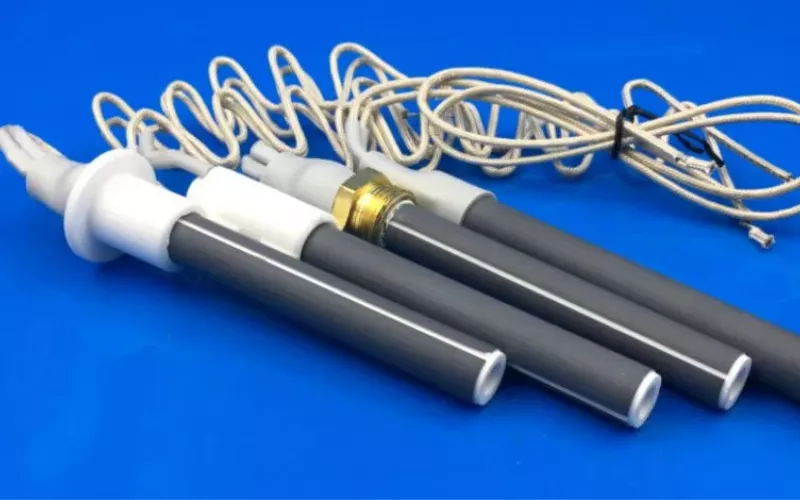
A quartz igniter is a device that transforms mechanical energy into electrical sparks with the help of a piezoelectric crystal. Its mission is to give it reliable ignition without any external power.
In this guide, you will learn the definition, working process, core parameters, advantages, disadvantages, industrial use, and other technical information.
What Is a Quartz Infrared Igniter?
Want to know “what is a quartz infrared heater?” So, a quartz igniter is an ignition device that produces high voltage using a piezoelectric crystal. Simply, it is a kind of igniter that can be used to start gas burners or heating systems. The machine uses the piezoelectric effect to change mechanical force into an electrical spark.
Contextually, “what is a igniter” refers to any device that triggers combustion in gas appliances, lighters, or heaters. Quartz igniters are used in applications where low price and small size are needed.
In commercial kitchen operations, the problem of a gas oven ignition may result in a delay in workflow. The solution was the replacement of the igniter with a quartz one, which improved safety and the functionality of the igniter.
What Are the Core Parameters of a Quartz Igniter?
The main parameters define the performance, durability, and reliability of a quartz ceramic igniter. These quantifiable measurements are fundamental in industrial, commercial, and household applications.
By understanding these parameters, you are able to choose the right ceramic igniter to suit your needs and be able to have a uniform performance.
|
パラメータ |
Typical Value / Notes |
|
材料 |
PZT, quartz, piezoelectric crystals |
|
Common Piezoelectric Types |
Lead Zirconate Titanate (PZT), Quartz |
|
Output Voltage Range |
10 kV – 20 kV |
|
Force Required |
25–50 N (verify) |
|
Temperature Tolerance |
-40°C to 250°C |
|
Durability Cycles |
50,000 – 100,000 |
|
Ignition Reliability Percent |
95% – 99% |
The combination of these parameters ensures that quartz igniters can be used in different conditions. With the right choice of material, type of crystal, and force tolerance, you can maintain steady ignition performance and a longer service life for the セラミック部品.
In the case of laboratory furnaces, a PZT-based igniter was picked based on the need to have a dependable behavior under repeated cycles of high-temperature operation. It shows the value of material in relation to durability.
How Does a Quartz Igniter Work?
So, as we have already talked about, “What is a quartz infrared heater?” Now, you may be thinking, “How does a piezoelectric igniter work?”
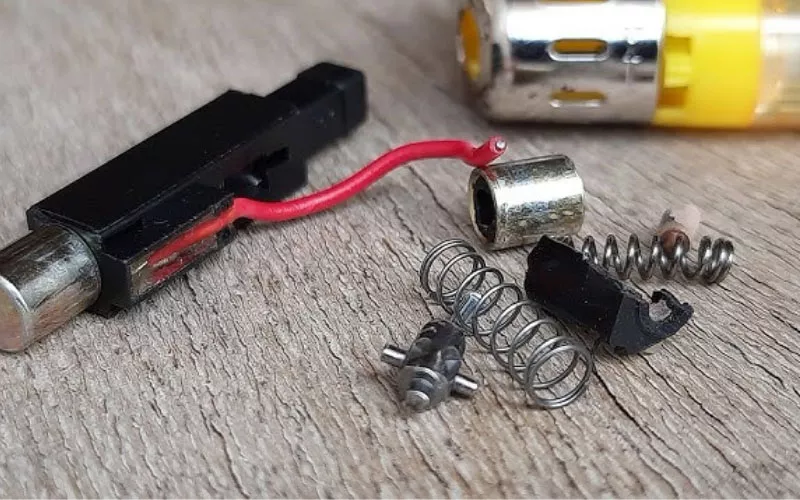
A quartz igniter works by producing a spark using the piezoelectric effect. An electric charge is generated when mechanical pressure on the crystal is applied when you press the actuator. In some designs, the converse piezoelectric effect can be used to make a crystal slightly deform. It can also help in improving efficiency.
In a school laboratory, students could not start burning burners because of the faulty igniter in the lighter. As a replacement, using a quartz igniter was necessary, so every student could safely use the burners for the first time.
The following step-by-step process is a direct response to questions like “how does a piezoelectric igniter work” and “how do piezoelectric igniters work.”
1: Press the Igniter Button
On button press, a mechanical force of around 25-50 N is put on the internal spring mechanism. This force is also meant to compress the piezoelectric crystal but not break it. This process that creates the electrical charge is triggered by the pressure.
2: Mechanical Force Compresses the Piezoelectric Crystal
The piezoelectric crystal within the igniter is forced by the applied force. As a result of the piezoelectric effect, the crystal creates an electric charge due to such pressure. This is the main concept of the working of the quartz igniter.
3: Crystal Generates a High-Voltage Pulse
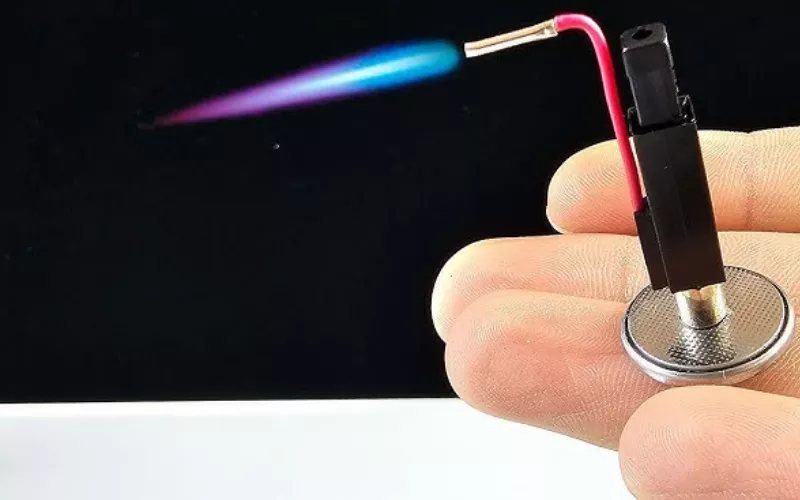
The crystal, as it is compressed, gives out a high voltage pulse, typically of 10 kV to 20 kV. This pulse is sent to the electrodes, where it is ready to jump across the spark gap. It is a very powerful voltage that can easily cause gas or fuel to ignite.
4: Voltage Jumps Across the Electrode Gap
Then, the high voltage pulse induces a spark by skipping the small distance between electrodes, which is typically 1-3 mm. This is a spark that is sudden and powerful and can set fire to inflammable material. The distance between electrodes is set to a safe and efficient distance.
5: Spark Ignites Gas or Heating Elements
The high-voltage pulse generates a spark, which generates the heating element or gas. In the industrial systems, the igniter guarantees ignition reliability of 95-99%. In domestic appliances, it is used to power grills, lighters, or quartz infrared heaters safely.
Quartz igniters work through this simple as well as effective mechanism. They offer reliable and long-lasting ignition using piezoelectric crystals, the piezoelectric effect, and in some cases, PZT materials.

What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages?
Quartz igniters are unique in a number of ways that make them safe and convenient in both industrial and domestic applications. Meanwhile, they possess some limitations that you should know before choosing an igniter for your application.
利点
-
Generates High Voltage Without External Power: The piezoelectric effect is used to generate sparks, which should not require a battery or electricity. Best suited for gas burners, lighters, and quartz infrared heaters.
-
Compact Design: Compact in size, lightweight, and can be used in industrial burners, grills, and portable devices.
-
Long Operational Life: May take tens of thousands of cycles, which guarantees the consistency of performance and fewer replacements.
デメリット
-
Limited Continuous Output: Not applicable in applications requiring a constant spark.
-
Mechanical Wear: Mechanical wear can be experienced by springs and actuators, which makes them less reliable.
-
Not Ideal for High-Power Systems: Electronic igniters can be used in very high-energy or sustained sparks.
Where Are Quartz Igniters Used?
Quartz igniters have found many applications in industries and households as they produce dependable sparks without any external source of power.
-
Gas Grills: They offer safe and instant ignition. Thus, grilling is fast and convenient.
-
Lighters: They produce a high-voltage spark in portable devices, lasting thousands of cycles.
-
Burners: Make sure gas ignition is reliable for both industrial and lab use.
-
Heating Devices: Found in quartz infrared heaters, providing regulated and reliable ignition.
In the commercial baking business, irregular ignition of the oven may interfere with production. The use of quartz igniters guaranteed a quick start of the burners. It minimizes the workflow and downtime.
Additional Technical Details
PZT or quartz crystals are used as igniters in quartz igniters, producing voltages of 10-20 kV with the ability to withstand -40°C to 250°C. This gives good sparks both in the house and in the industry.
Design Variations
-
Handheld Units: Lighters and portable burners, up to 50,000 cycles.
-
Integrated Burners: Grills and small industrial systems, 12-15 kV output.
-
Industrial Modules: High-power systems, forces of up to 50N and 100,000+ cycles.
Material Durability
Ceramics hold the crystals, which are resistant to wear, high temperatures, and moisture, to provide an extended ignition duration.
Troubleshooting
-
Electrode Gap: This should not exceed 1-3 mm to achieve the best spark.
-
Crystal Integrity: Replace any cracked or chipped crystals.
-
Springs: Change ineffective actuators.
-
Contacts: Make sure that electrodes are clean to ensure 95%+ reliability.
Why Choose GORGEOUS For Quartz Crystal Igniter?
GORGEOUS offers accuracy, high-quality industrial and domestic ceramic quartz igniters. Our experience can help you find high-quality, durable, and reliable solutions to ignition.
-
Precision Manufacturing: CNC machining makes sure the crystal housing and electrodes are placed just right. This helps keep the spark performance consistent.
-
PZT and Ceramic Materials: We use PZT and ceramic materials of high quality for their high durability, temperature, and long-term reliability.
-
品質保証: All parts are checked using automated inspection systems and high-temperature resistant furnaces to ensure that no defects are present.
-
Advanced Production Facilities: We have 3 smart manufacturing plants and more than 56 CNC machines, which deal with complicated designs.
-
Custom Solutions: You can provide drawings or specifications. Then, we can supply tailor-made quartz igniter components to any industrial or household use.
-
Industry Expertise: Our products serve a variety of industries, such as エレクトロニクス, 自動車, 航空宇宙, and heating systems. This will make sure you get parts that meet rigorous standards.
結論
A piezoelectric igniter is a reliable, compact kind of ignition device that makes use of piezoelectric crystals. Now, you know its working principle, parameters, applications, and advantages of its usage.
If you need precision ceramic components for quartz igniter systems, you can contact our team. Check out our other blogs and product pages about advanced ceramics, PZT materials, and industrial ignition solutions for more information.
よくある質問
How long does a quartz igniter last?
The average life of a quartz igniter is 50,000 to 100,000 cycles. Its life can be increased with regular maintenance.
How does a piezoelectric igniter work?
You press the igniter, making the crystal compress, which produces a high-voltage spark for ignition.
Why do quartz igniters fail?
They do not work because of mechanical wear, problems with electrode gaps, or crystal damage with time.
Can you replace a quartz igniter yourself?
Yes, you can safely replace it by disconnecting the old unit and the installation of a compatible quartz igniter.
Is a quartz igniter safe for home use?
It is safe, however, when used within the guidelines of appliances. It should not be exposed to sparks directly.
What is the difference between a quartz igniter and an electronic igniter?
Quartz igniters use mechanical pressure on crystals, while electronic igniters rely on electricity and circuits.

