Nitruro di boro cbn è una ceramica avanzata nota per le sue proprietà superiori. Chimica BN ha Azoto di boro legami che danno origine a diverse strutture. Tra le strutture del BN una di queste strutture di interesse è Nitruro di boro cubico cbnCerchiamo di comprendere c-bn e i suoi aspetti relativi.
Sommario
Nitruro di boro: una panoramica
Nitruro di boro esagonale (h-BN)
- Struttura del nitruro di boro esagonale
- Proprietà del nitruro di boro esagonale
- Applicazioni del nitruro di boro esagonale
- Che cos'è il nitruro di boro cubico?
- Struttura del nitruro di boro cubico
- Proprietà del nitruro di boro cubico
- Nitruro di boro cubico contro diamante
- Usi del nitruro di boro cubico
- Mole super abrasive – o mole diamantate c-BN
Nitruro di boro: Una panoramica
Nitruro di boro è indicato dalla formula chimica "BN". Come accennato in precedenza, Nitruro di boro esistono in diverse forme. Generalmente, è la posizione del boro e dell'azoto nel reticolo che crea vari Strutture del nitruro di boro. Alcune di esse sono piuttosto famose, come la pietra amorfa, quella esagonale, quella cubica e la wurtzite.
Quando si tratta di funzionalità, Ceramica di nitruro di boro è altamente lavorabile. Una volta lavorato, non richiede alcuna sinterizzazione termica o trattamento per la stabilizzazione. Inoltre, Nitruro di boro ha una maggiore capacità termica ed è anche un buon isolante elettrico.
Per ora, cerchiamo di capire le derivate di BN, Nitruro di boro esagonale (h-BN) e un altro Nitruro di boro cubico (c-BN)
Nitruro di boro esagonale (h-BN)
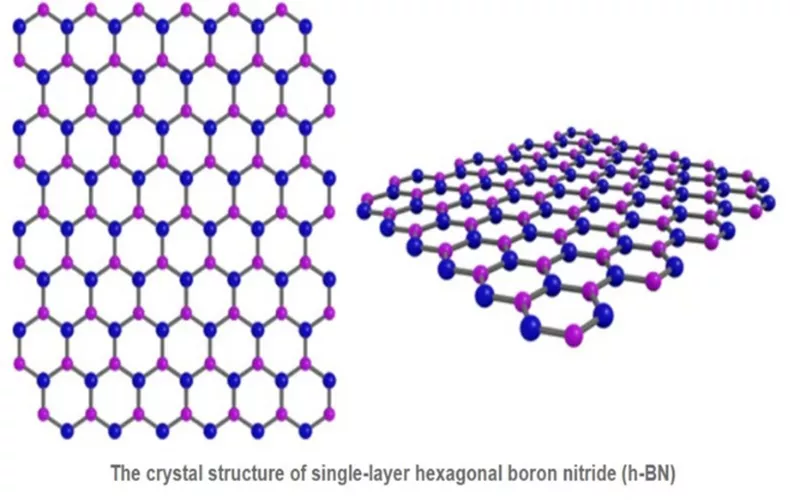
Struttura del nitruro di boro esagonale
Nitruro di boro esagonale è un costituente di molti prodotti industriali come i cosmetici. L'HBN ha una struttura controllata da legami covalenti. Tuttavia, gli strati in HBN obbediscono forze vaganti di Waals. La geometria a piastra dell'HBN è il motivo per cui è ideale per la lubrificazione.
Nitruro di boro esagonale ha elementi di boro e azoto fissati al suo reticolo. La disposizione prevede tre atomi di azoto legati a un atomo di boro. La somiglianza nella struttura a nido d'ape è la ragione della sua analogia con il carbonio. Inoltre, le proprietà di resistenza meccanica, chimica e isolamento elettrico sono dovute ai legami triangolari planari.
Proprietà del nitruro di boro esagonale
Nitruro di boro esagonale viene comunemente prodotto tramite nitrurazione di ossido borico a temperature elevate. Poiché la sua stabilità è più vicina a quella del grafene, Nitruro di boro esagonale è spesso acclamato come la ceramica tecnica più avanzata. Alcune proprietà superiori di Nitruro di boro esagonale sono la sua conduttività termica e il basso coefficiente di attrito.
Applicazioni del nitruro di boro esagonale

- L'HBN viene utilizzato nei dispositivi nanoelettronici come sostituto del substrato di grafene
- Nitruro di boro esagonale nella sua forma sottile viene utilizzato come rivestimento resistente alla corrosione
- L'HBN è spesso utilizzato nella produzione di materiali per sensori. Viene anche utilizzato nell'effetto tunnel degli elettroni grazie al suo basso valore di costante dielettrica.
Nitruro di boro cubico
Che cos'è il nitruro di boro cubico?
c-BN è un derivato di Nitruro di boro esagonale (h-BN) prodotto ad alta temperatura e pressione.
La più grande specialità di c-BN è che detiene il posto di secondo materiale più duro al mondo. La resistenza meccanica di Nitruro di boro cubico è popolare ed è alla pari con il diamante. È uno dei polimorfi del boro più popolari. Nitruro.
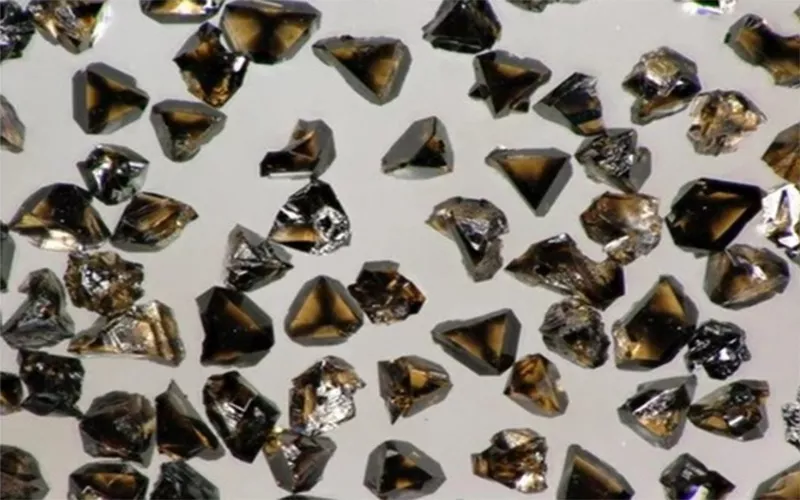
Struttura di Nitruro di boro cubico
La struttura di base di Nitruro di boro cubico è cristallino. Ha una densità di circa 3,5 g/cm3 e appare di colore giallo pallido o trasparente. Il C-BN segue una disposizione alternata di atomi di boro e azoto. Qui, il Azoto di boro gli atomi seguono legami covalenti che sono la ragione fondamentale della sua durezza e stabilità.
Formula del nitruro di boro cubico è indicato come c-BN. Esistono due tipi popolari di c-Bn disponibili oggi sul mercato. Uno è denso nitruro di boro cubico e l'altro nitruro di boro cubico policristallino.
Proprietà del nitruro di boro cubico
C-BN è un brillante semiconduttore le cui bande proibite sono sensibili alle variazioni della pressione applicata. Queste variazioni di bande proibite li rendono eccellenti come isolanti elettrici. Nitruro di boro cubico sono generalmente inerti e possiedono un basso valore di costante dielettrica. La loro conduttività termica è di circa 1300 KW/MK.
Quando si tratta di reattività, c-BN rimane non rispondente anche ai materiali ferrosi. La gamma ottica trattata da nitruro di boro cubico varia dallo spettro ultravioletto a quello visibile.
Nitruro di boro cubico contro diamante
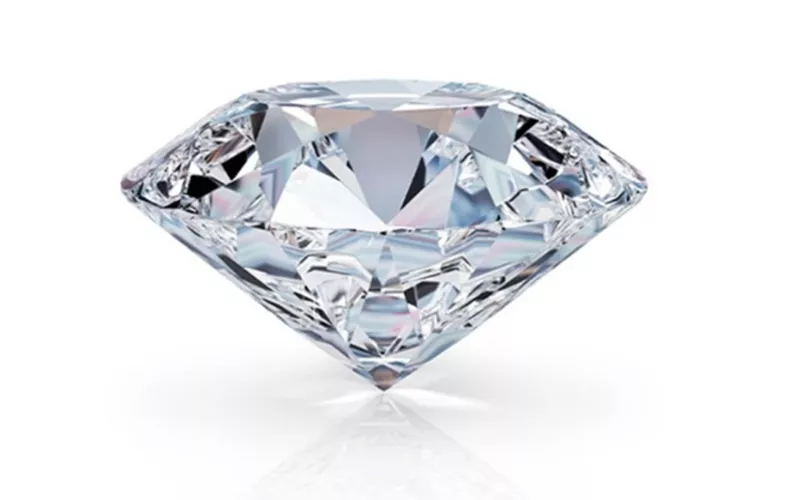

Sebbene non sia più duro del diamante, nitruro di boro cubico ha un posto speciale se paragonato al diamante. Durezza del nitruro di boro cubico è di 4500 Kg/mm2 mentre il diamante ha una durezza di circa 600 Kg/mm2. Anche i valori del modulo sia di Young che di massa rientrano in un intervallo simile di 800-1000 e 370-450.
Inoltre, quando si tratta di struttura, come il diamante, c-BN ha due atomi di base diversi. La somiglianza tra il diamante e il c-BN è generalmente attribuita alla struttura simile che possiedono.
Usi del nitruro di boro cubico
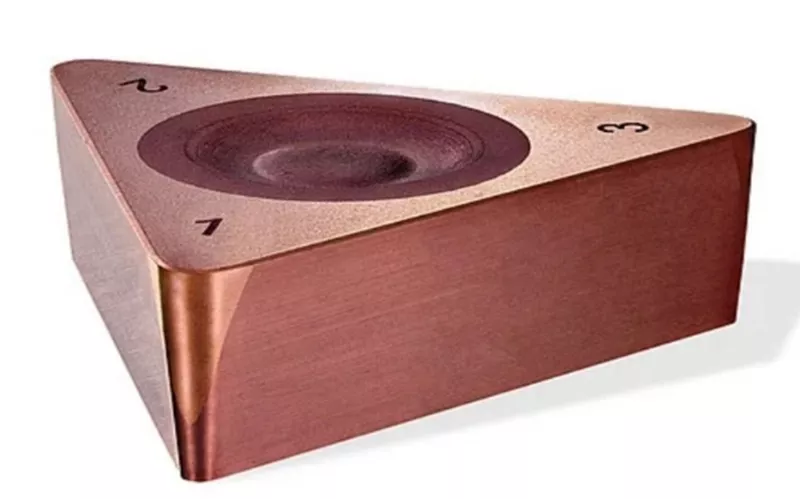

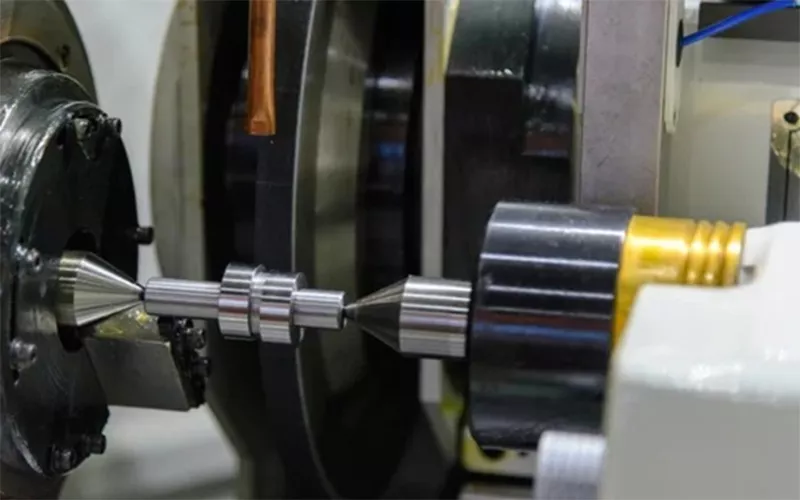
materiale per utensili da taglio cbn
Nitruro di boro cubico presenta sia il modulo di Young che quello di massa maggiori rispetto al carburo di boro e al carburo di silicio. Questo stesso motivo contribuisce notevolmente alla durezza del nitruro di boro cubico. La durezza li rende adatti come abrasivi e li aiuta a funzionare come materiale per utensili da taglio cbnGeneralmente il c-Bn denso viene utilizzato per applicazioni di taglio, mentre il tipo poroso viene utilizzato per esigenze di rettifica.
La natura inerte di Nitruro di boro cubico anche Li rende adatti come materiale da taglio e lavorazione meccanica. A differenza del diamante, non reagisce al ferro. Tuttavia, il c-Bn convenzionale richiede una manipolazione per essere utilizzato in applicazioni di taglio. Questa operazione avviene generalmente durante la conversione di h-Bn in c-Bn durante la sinterizzazione.
cbn come isolanti elettrici
A parte la durezza Nitruro di boro cubico eccelle anche negli isolanti elettrici. Ciò è dovuto al loro ampio bandgap.
cbn nelle applicazioni dei semiconduttori
Rivestendo l'alluminio e i metalli del Gruppo 8, C-BN La funzionalità di trasformarsi in un lavandino è diffusa nell'industria elettronica. C-BN viene utilizzato come dissipatore di calore nei laser, nei dispositivi microelettronici e nei LED.
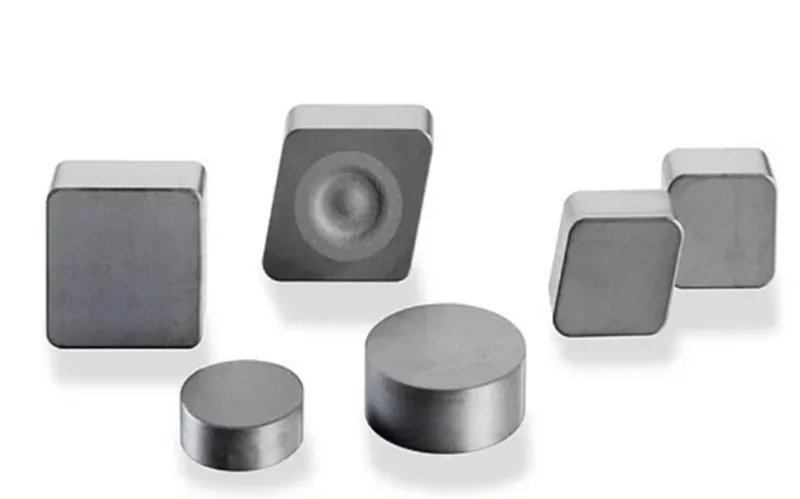

Nitruro di boro cubico Aggiunge valore anche durante la sintesi dei semiconduttori per ottenere i tipi p e N mediante un drogaggio appropriato. I materiali comunemente utilizzati per il drogaggio sono il silicio o il berillio. Questi semiconduttori lavorano ad alta temperatura e sono utilizzati nei sensori UV.
mole abrasive c-BN
L'invenzione di mole abrasive c-BN meritava una produzione di precisione grazie alla maggiore efficienza. Le ruote realizzate in c-BN hanno contribuito a settori quali l'aerospaziale, la meccanica, la produzione di utensili e l'automobile. mole abrasive c-BN Offrono inoltre elevata durezza e buone prestazioni rispetto a SiC e allumina. Garantiscono l'integrità strutturale anche a temperature più elevate e non subiscono degradazione.
Le ruote di c-BN Possono resistere ad alte temperature e gestire la quantità di calore generata durante il processo. La resistenza all'usura è anche economicamente vantaggiosa quando si prendono in considerazione le mole abrasive c-BN. Le mole c-BN offrono eccellenti finitura superficiale ed elimina gli sprechi di materiale. Garantisce inoltre tempi di ciclo ridotti, poiché le attività vengono eseguite in modo rapido e preciso.
Mole super abrasive – o mole diamantate c-BN
Le mole super abrasive si differenziano dalle mole convenzionali in SiC e Allumina. Sono realizzate combinando C-Bn e diamante. La mola super abrasiva offre una migliore conduttività termica, limitando l'aumento di temperatura del pezzo in lavorazione. mola diamantata c-Bn offrono inoltre un'elevata accuratezza e precisione di taglio che contribuiscono a una maggiore durata.
Conclusione
Nitruro di boro cubico Sono desiderabili nella scienza moderna e nella produzione di materiali. Sono competitivi rispetto a materiali come il diamante. Eccellono in proprietà come durezza, resistenza e isolamento elettrico. L'ampio band gap, la natura inerte, la bassa costante dielettrica e le proprietà ottiche sono altri fattori di merito.
