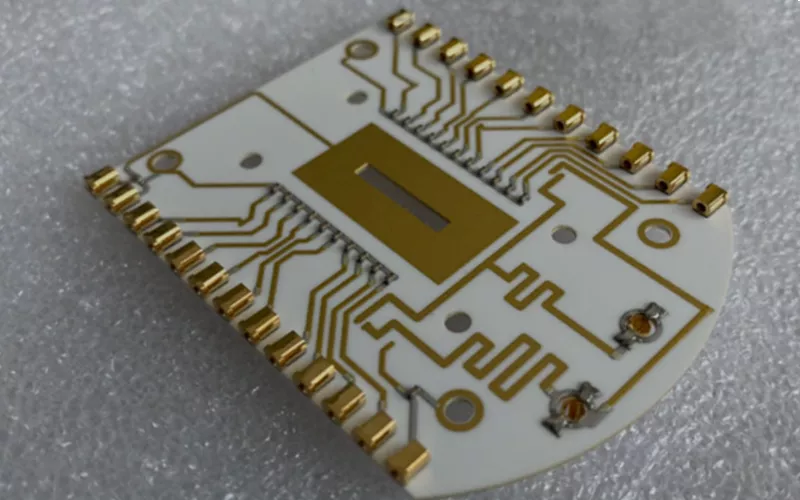
With high thermal conductivity and mechanical strength, your ceramic PCB is ideal for uses like power electronics and LED lights. Your PCB material matters as each offer unique properties, with nhôm oxit Và alumina nitride as common choices. Your ceramics PCB offer performance benefits but have cost limitations.
What Are Ceramic PCBs?
Your ceramic PCB is a Printed Circuit Board (PCB) with thermal conductivity >24 W/m·K ceramics substrates as base materials.
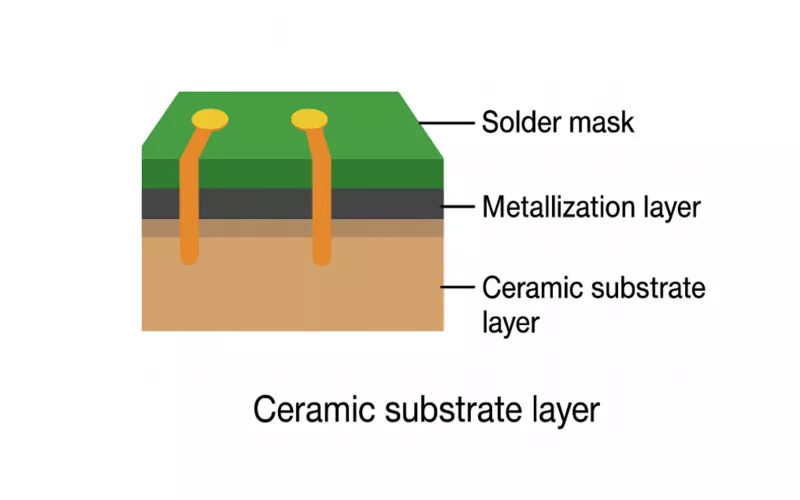
Difference Between Ceramic Core PCB and Ceramic PCB Substrate
Ceramic PCB substrate is that ceramic material, e.g, alumina, that is used as the foundation of your circuit board. Ceramic core PCB is where the entire core of your board is created with a ceramic material.
Why Ceramics PCBs Are Chosen in Your Application
When kim loại hoặc FR-4 PCBs are used, your operation risks low performance and inneficient heat tranfer.
Your ceramic PCB’s properties like heat dissipation, insulation, strength and stability improve efficiency and durability.
Your Ceramic PCB Materials
1. Alumina (Al2O3) Ceramic PCB
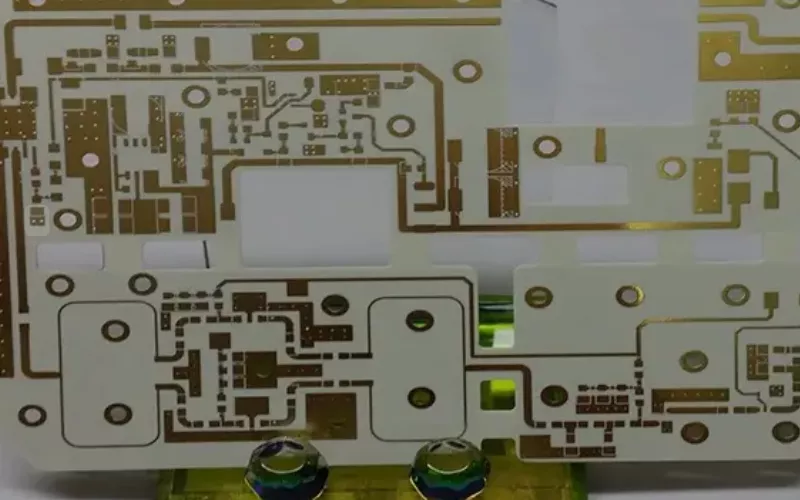
Your alumina substrate PCB is a cost effective material that offers a density of 3.99 g/cm³ and thermal conductivity of 24–27 W/m·K.
With a dielectric constant of 9.8, it provides insulation and have less electrical loss.
“Even under 1780 °C, alumina PCB gave us LED performance…” —Michael Z., Engineer, Sledco
2. Aluminium Nitride (ALN) Ceramic PCB
Your aluminium nitride ceramic circuit board has a density of 3.26 g/cm³, thermal conductivity of 170–200 W/m·K, and CTE (coefficient of sự giãn nở vì nhiệt) 4.5 ×10⁻⁶/K. These features makes your AlN ceramic PCB more stable.
“After switching to AlN board, overheating reduced by 44% in our electronics.” —Shin J., Engineer, Nepow Electronics
3. Silicon Carbide (SiC) Ceramic PCB

Due to density 3.2 g/cm³, conductivity ~120 W/m·K and CTE of 4.0 ×10⁻⁶/K, your SiC ceramic PCB material maintains stability in your turbines.
4. Silicon Nitride Substrate PCB
Your Si3N4 ceramic PCB substrate features a density 3.2 g/cm³, flexural strength of 800–1000 MPa. This improves your automotive system reliability and offers fracture toughness.
5. Beryllium Oxide Ceramic PCB
Your beryllium oxide ceramics PCB have a density of 2.85 g/cm³ and thermal conductivity up to 230 W/m·K. Its dielectric constant of 6.5-7 reduces signal loss.
Note: Strict handling compliance is required due to BeO’s toxicity during processing. Your industry must adhere to OSHA Và RoHS and always ensure ISO-certified supplies.
Key Ceramic PCB Materials Summary Table
|
Vật liệu |
Mật độ (g/cm³) |
Độ dẫn nhiệt (W/m·K) |
Hằng số điện môi |
CTE (×10⁻⁶ /K ) |
Temperature Resistance (°C) |
Độ bền uốn (MPa) |
Trị giá |
|
Nhôm oxit |
3.99 |
24-27 |
9.8 |
7-8 |
>1750 |
386 ±12 |
Thấp |
|
AlN |
3.26 |
170-200 |
8.8 |
4.5 |
>1800 |
386 ±12 |
Cao |
|
Si₃N₄ |
3.2 |
70 |
8.0 |
4.0 |
>1750 |
800-1000 |
Cao |
|
SiC |
3.2 |
120 |
9.7 |
4.0 |
1750 |
450 ± 15 |
Trung bình |
|
BeO |
2.85 |
Up to 230 |
6.5-7 |
1.2 |
1800 |
280 ± 10 |
Cao |
Data source: Mater. Sci. Eng. 2025; 109(2): 021004; IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol., vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 21004–21012, Feb. 2025
Types of Ceramic PCBs
There are 4 key types of your ceramic PCBs by fabrication process:
4.1 Single-Layer Ceramic PCB
Your ceramic substrate with a layer of one conductive material. This is a basic structure applied for your simple circuits.
4.2 Ceramic Multilayer PCB
Consists of multiple layers of integrated ceramic and conductive material.
4.3 Thick Film Ceramic PCB
Screen-printing is used to apply conductive and resistive layers on your ceramic substrate
4.4 Direct Bonded Copper (DBC) Ceramic PCB
Heat and pressure are used to bond a layer of copper onto your ceramic substrate, enhancing reliability in your power modules.
Ceramic PCB Manufacturing Process
To maintain integrity of material and ensure circuit precision, your ceramic PCB manufacturing process involves these steps:
Substrate Preparation
Your >99% purity ceramic powders are blended with binders. The mixture is pressed into green sheets, forming your ceramic PCB substrate.
Thiêu kết
Your substrate is thiêu kết at temperatures >1750 °C to get all density and mechanical strength.
Kim loại hóa
Thi conductive layers like tungsten or copper are added to your substrate surface for insulation.
Circuit Patterning
Your circuit design is formed via photolithography with high-density in multilayer ceramic PCB structures.
Firing, Drilling, & Plating
Conductors are bonded by firing metallized layers
Laser drilling is used to creat via holes
Copper thickness is added through platting, which ensures durability in your power applications
Hoàn thiện
Final coatings such as ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold) or silver protect your circuit.
Surface finishing enhances extends your ceramic PCB lifespan to 50-70+ years.
Ceramic PCB vs FR4

Your ceramic PCB has a conductivity of 24 W/m·K- 200+ W/m·K, while that of FR4 is 0.3 W/m·K.
FR4 is cheaper and more flexible, but lacks stability in temperatures >1700. Your ceramic PCBs cost more, but perform dependably.
Ceramic Antenna vs PCB Antenna
Your ceramic antenna vs PCB antenna choice is determined by RF performance. Your ceramic antennas provide higher efficiency in small designs, providing stability in your telecommunication systems. PCB antennas offer lower cost and easier integration.
Drawbacks and Limitations of Ceramics PCB
Your ceramic PCB costs high, $50-$200, while FR4 costs only <$10 per square foot. The brittle nature of your ceramic substrates makes mechanical shock resistance lower. Also, your ceramic PCB manufacturing process demands precision.
Ceramic PCB Applications
9.1 Automotive Systems
With a temperature resistance >=1750°C, your ceramic multilayer PCB supports control units and powertrain electronics.
9.2 Power Electronics
Due to ceramic PCB material thermal conductivity of >24W/m·K, your converters and inverters are durable.
9.3 Aerospace
Your radar and satellite communication systems must use materials that don’t fail under radiation.
Your ceramic substrate PCB CTE of 1-8 ×10⁻⁶ /K and thermal conductivity >24W/m·K ensures reliabilility under vibration and temperatures >1750 °C.
9.4 LED Lighting
Ceramic core PCB efficient heat dissipation ensures your LED modules and lighting systems lasts and performs reliably.
9.5 High-Frequency Electronics
Since your ceramic PCB has low signal loss and dielectric constant 6.5-9.8, it supports your RF devices, microwave circuits, and telecommunication các thành phần.
Choosing the Right Ceramic PCB and Ceramic PCB Manufacturer
What to Consider When Choosing Your PCB Ceramic Material
Consider the thermal conductivity, dielectric strength, and mechanical stability of your ceramic PCB custom design. Match your application requirements with ceramic PCB material features and budget.
Ceramic PCB Suppliers and Manufacturers
Choose ceramic PCB manufacturers with technical expertise and consistency.
Check that your supplier offers quality certifications (ISO 9001, ISO 14001, IATF 16949, and RoHS) to ensure compliance. Select GGSCERAMIC® for ISO-certified ceramic PCB custom designs.
Ceramic PCB Cost Factors
Material type, layer count, and complexity determine your ceramic PCB cost.
Manufacturing location matters, with ceramic PCB China often offering lower labor costs. Specialized materials like aluminium nitride increase cost but enhance performance. Select GGSCERAMIC® for ISO-certified solutions.
Phần kết luận
Your ceramic PCB offers high thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and electrical insulation, ensuring the reliability of your process. While your ceramic PCB material costs more than FR4 and may be brittle, its properties and benefits outweigh limitations.
LỘNG LẪY is a leading international supplier of advanced ceramics, offering and customizing ceramic substrates and PCBs in various materials. If you encounter any technical challenges, please contact us, and we will provide you with the best ceramic PCB solutions.
FAQs About Ceramic PCB Material
Q1: What are the ceramic PCB advantages?
A: Your ceramic PCB offers thermal conductivity >24 W/m·K, high electrical insulation, and flexural strength >280 MPa, ensuring reliability in your application.
Q2: What is the difference between a ceramic PCB vs FR4?
A: Your ceramic PCB provides thermal >24 W/m·K and mechanical properties. FR4 is cheaper but has only a heat resistance of 140-150°C.
Q3: What base materials are used for ceramic PCB substrates?
A: Alumina, aluminium nitride, silicon carbide, silicon nitride, and beryllium oxide are your main ceramic PCB materials.
Q4: What are the types of ceramic PCBs?
A: Single-layer, multilayer ceramic PCB, thick film ceramic PCB, and direct bonded copper ceramic PCB.
Q5: What are the ceramic PCB applications?
A: Your ceramic PCB board is used in automotive, aerospace, LED lighting, defense, RF electronics, and power modules.
Q6: How is ceramic PCB manufactured?
A: Your ceramic PCB manufacturing process involves sintering ceramic powders, applying metallization, and bonding copper.