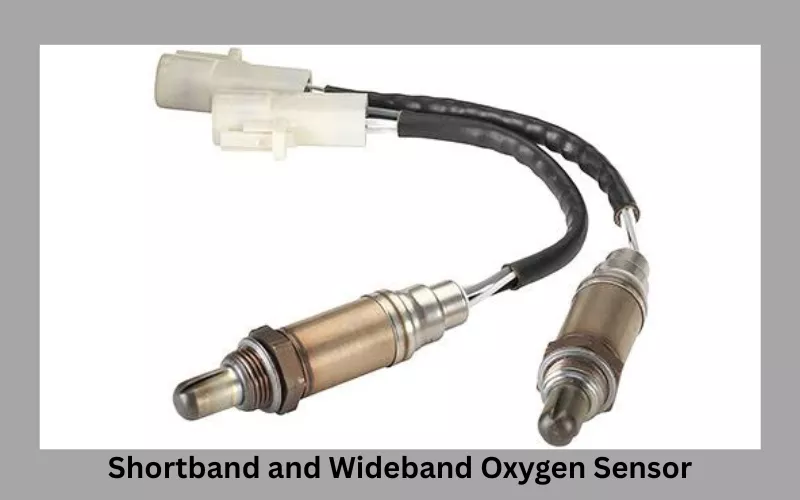
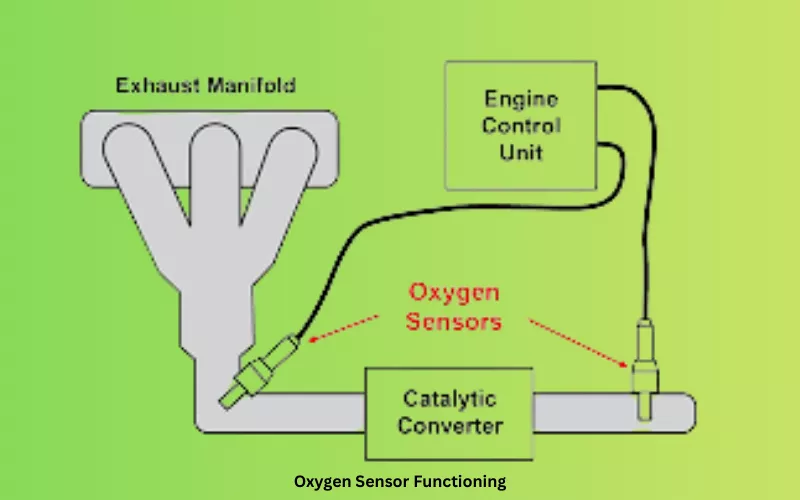
A lambda sensor is an electronic device that monitors the oxygen level in the exhaust gas of an IC engine. It then adjusts the air-fuel mixture ratio of the engine through the ECU and completes proper combustion within. It maintains the efficient operation of your car.

Let’s explore the lambda sensor.
What is a Lambda Sensor?
A lambda sensor, or oxygen sensor, is a sensing device used to monitor and measure the volume of oxygen in the exhaust gas of an IC engine. The sensor is set up in the exhaust line of your car or vehicle.
The O₂ sensor identifies the best air-fuel ratio(AFR) for the engine and maintains proper emissions. A Maximum of four oxygen sensors may be used in a vehicle, depending on its type and manufacturing. The lambda sensors identify the oxygen gas levels of the exhaust and send real-time data to the ECU.

Then the ECU calculates the air-fuel mixture ratio for the engine, which ensures proper combustion in the combustion chambers and reduces harmful gas emissions in the environment. The Lambda sensor maintains the air-fuel mixture ratio at around 14.7 stoichiometric for the gasoline engine.
This ratio of air and fuel is called the stoichiometric air-fuel ratio (AFR). Engines burn all fuels completely without any excess air or fuel if run in this ratio.
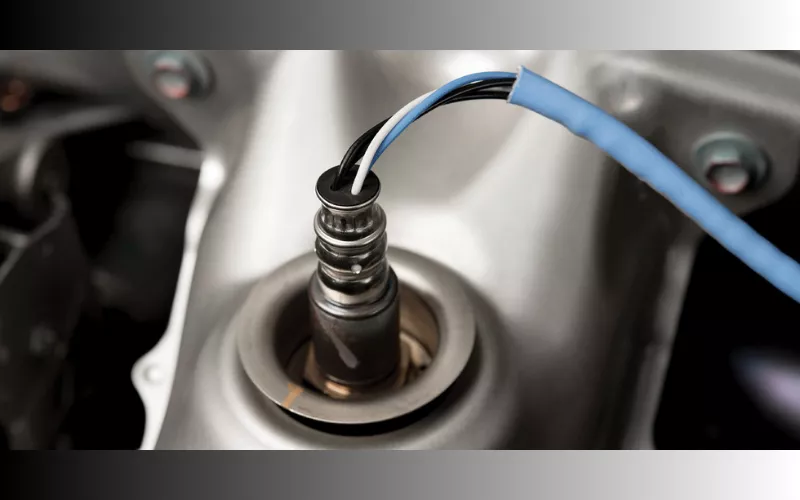

How Does a Lambda Sensor Work?
Sensors operate on the principle of taking an input and comparing it with the standard value, then sending the related output.
When the probe of the lambda sensor senses temperature around 350 degrees, the extra amount of oxygen in the exhaust gas generates a voltage change in the probe.
This indicates the sensing function depends on the oxygen content in the exhaust gas.
Then the lambda pin of the oxygen sensor counts the O2 gas in the exhaust (which is near 0.3 to 3%) compared to the oxygen in the natural air (around 20.8-21%).
-
If the surplus oxygen amount in the exhaust is less than 3%, the air-fuel mixture of the engine is indicated as a rich burn state, which means it takes excess fuel. At this state, up to 0.9 V is recorded in the sensor probe.
-
On the other hand, if the surplus oxygen in the exhaust is equal to 3%, it is identified as a lean burn engine, which means it takes more air than the standard and causes inefficient burning. In a lean burn state, the probe senses 0.1V.
As mentioned above, the lambda oxygen sensor calculates the surplus oxygen in the exhaust gas of the engine.
When the calculation is done, the lambda O₂ sensor sends an electrical voltage signal to the engine control unit circuit. ECU then identifies whether the engine is in a lean-burn or rich-burn condition based on the voltage transmitted to it.
Types of Oxygen Sensors:
The Zirconia and Titania are two popular oxygen sensor types used in modern exhaust systems. Among them, the zirconia oxygen or lambda sensor is the most used one.
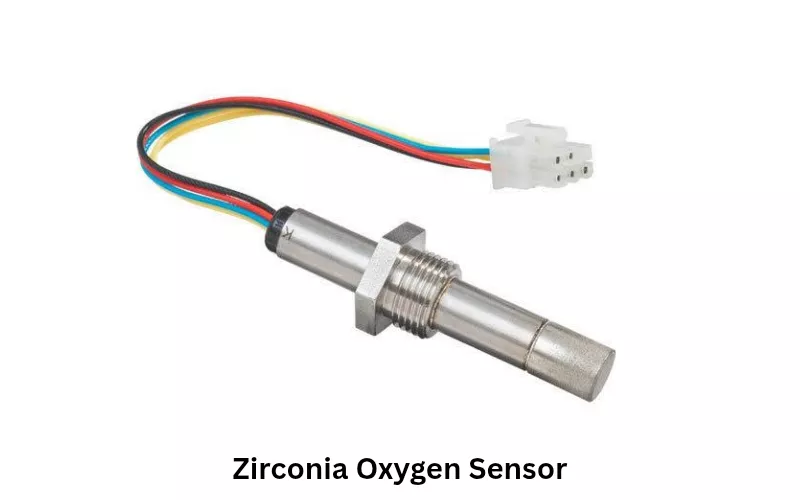

The zirconia oxygen sensor works on the voltage signal generated for the O2 emission change with the exhaust gas.
When the volume of oxygen in the exhaust of an engine is higher than the standard value, it is a lean mixture, and the O2 sensor receives low voltage.
And when the amount of oxygen in the exhaust is low, it is defined as a rich mixture of air and fuel. The sensor senses high voltage.
Conversely, the Titania sensor functions based on the electrical resistance changes that occur due to the volume of oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas. Then the engine control unit (ECU) interprets these fluctuations in the sensor resistance to fix the air-fuel ratio.
There are two other oxygen sensor types:
-
jump probes
-
and broadband probes
Jump Probe: The jump probe oxygen sensor is also known as a narrowband or switching type sensor. This type of sensor does not provide continuous data like the broadband sensor. It detects any sudden jump in voltage and sends the jump signal data to the ECU.
This means that the jump probe oxygen sensor can sense and send the data when it identifies the mixture as being at lean or rich conditions.
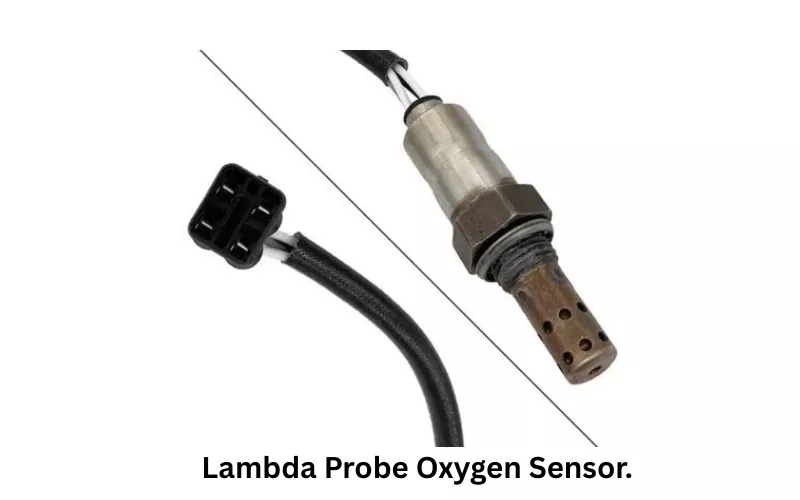

The jump probe sensor is not usually used in modern vehicles due to some limitations. However, some jump probe sensors have a faster response time of four seconds, and they don’t require any reference gas value. It is connected with the 5V supply from the engine control unit.
Broadband Probe: The broadband probe lambda sensor is renowned for its measurement accuracy. It is also known as the wideband oxygen sensor, which can maintain a wide range of air-fuel ratios compared to the old narrow-band sensor. It can measure both rich burn and lean burn mixtures, which is not possible with the normal jump probe sensor.
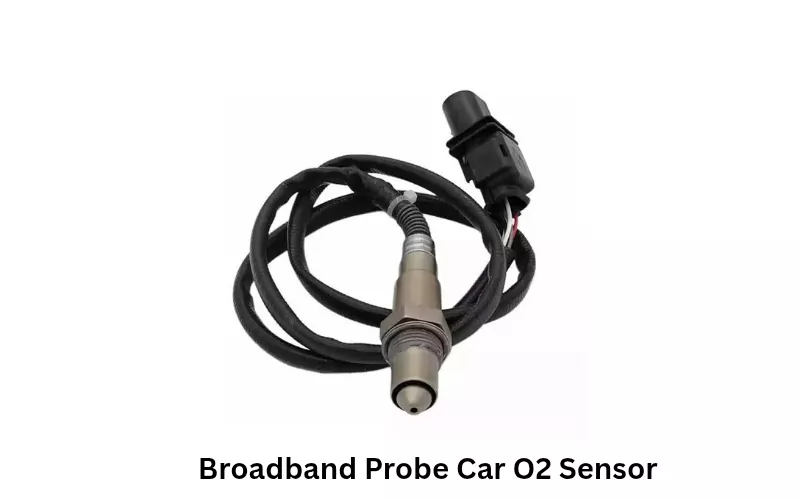

The other name of this wideband sensor is the linear probe oxygen sensor. Most modern engines have wideband oxygen lambda sensors for different advantages. This probe has all the facilities for modern exhaust system monitoring.
It has improved fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, faster response time, accurate measurement, and enhanced engine performance.
It has applications in performance tuning of the engine and in the research and development of new technology.
Veelgestelde vragen
What Does a Lambda Sensor Do?
The lambda sensor examines the volume of O2 gas in the exhaust of an IC engine. Then it sends back a signal to the engine control unit to adjust the AFR accordingly.
What Happens if the Lambda Sensor Is Faulty?
A faulty lambda sensor leads to deviation in the air-fuel mixture and can increase fuel consumption and excessive CO₂ emissions in the exhaust gas. It may also affect the engine performance.
As the sensor sends a real-time signal of the oxygen amount in the exhaust, it may send the wrong message to the ECU when it malfunctions. As a result, your vehicle engine may consume too much fuel(rich burn state) or may take too little fuel (lean burn state).
How long do lambda sensors last?
Lambda sensors may last between 50000 and 100000 miles at an average driving speed of 50 mph. If we convert it to running hours, it will be between 2000 and 4000 hours.
However, this lifetime calculation is just an estimate and can vary significantly depending on the vehicle conditions and other situations.
What happens if I remove the lambda sensor?
Some users may remove the lambda sensor from their vehicles to reduce maintenance costs and troubleshooting. Yet it is not good practice and may cause some problems, such as engine performance lag, fuel consumption increase, and an increase in exhaust emissions.
This may result in environmental regulation violations and unwanted fines from the authorities.
What kills lambda sensors?
The oxygen sensor may fail due to age, mileage, internal contamination, or electrical faults.
So, regular checks and replacement every 30000 miles might be necessary.
Conclusie: The lambda O₂ sensor is a small but crucial device for diesel, petrol, and gas engines. It identifies and calculates the volume of oxygen in the exhaust and sends real-time data to the ECU.
The ECU then fixes the air-fuel mixture ratios and ensures efficient fuel burning. Hence, you need to take care of the oxygen sensor for efficient operation of your vehicle.
