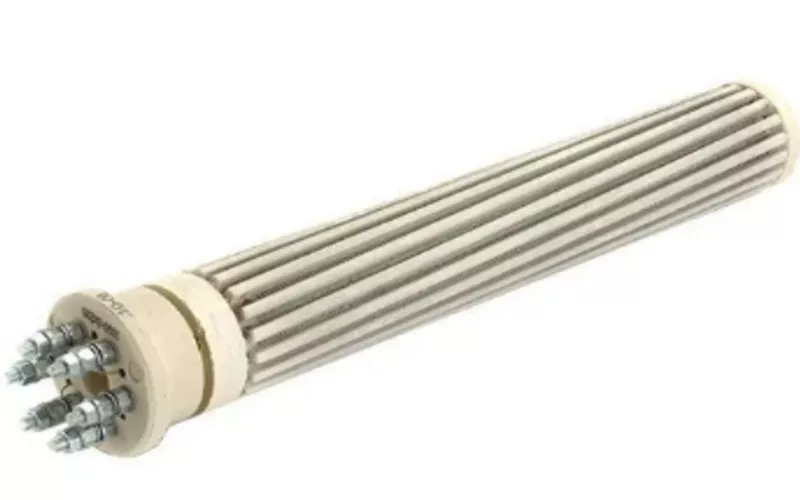
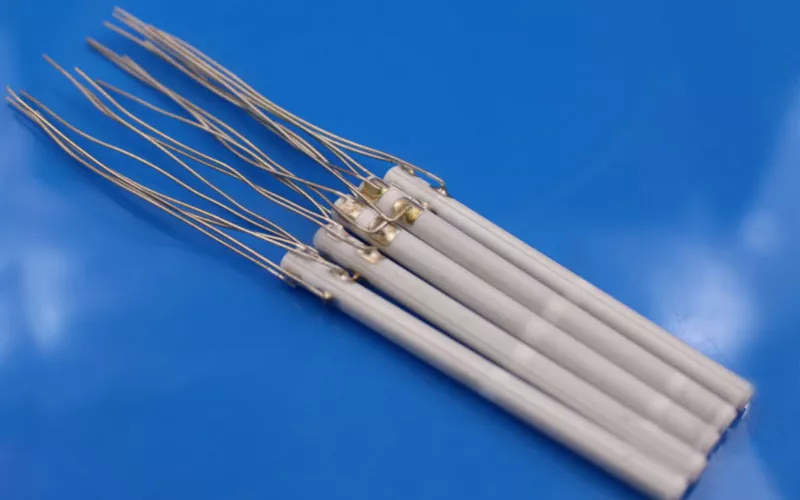
Your ceramic heating elements are the core component used in your electrical ceramic heaters. They’re preferred for your industrial furnaces and drying machinery due to their durability, temperature resistance, energy efficiency, and electrical properties.
2. What Is a Ceramic Heater
2.1 Definition of Ceramic Heater
-
你的 陶瓷加热器 is a complete device or appliance that uses the ceramic-based heating technology. Examples include space heaters, propane ceramic heaters, and electric heaters for rooms.
2.2 Definition of Ceramic Heating Element
-
Your ceramic 加热元件 is the core component that uses the electrical resistance of ceramic materials to convert electrical energy into heat. They’re made from materials such as alumina for PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) and metal ceramic composites for MCH (metal ceramic heaters).
3. How Does A Ceramic Heater Work?
3.1 Resistance Heating
-
你的 陶瓷制品 heater passes electricity through a ceramic heater plate, which resists current.
3.2 Generating Heat
-
Due to the electrical resistance, your ceramic heater plate heats up fast.
3.3 Circulating Air
-
Your ceramic heater fan pulls in air and makes it pass through the hot ceramic heating element.
3.4 Distributing Heat
-
Your ceramic room heater fan blows the newly heated air out. This heats your room.
4. Properties of Your Ceramic Heating Element
4.1 High Temperature Resistance
-
Your high temperature ceramic heating element withstands temperatures >1700°C. This resistance allows your ceramic heaters to operate under extreme heat that would degrade infrared and oil heaters.
4.2 Excellent Wear Resistance and Durability
-
Your ceramic heating element delivers 8.5-9.5 Mohs hardness and flexural strength 386-1000+ MPa. Your heaters resist abrasion, stress, and friction, making them durable and lasting longer.
“We’ve been using ceramic elements in our space heaters for over ten years now. Wear rate has consistently been below 0.001%.” — Brighton W., Engineer, SP Heats
4.3 High Electrical Resistivity and Dielectric Strength
-
Your electric ceramic heaters offer electrical insulation, which ensures safety.
-
Your ceramic element’s high dielectric strength allows it to withstand electric fields without breaking.
4.4 High Energy Efficiency
-
Your ceramic element has higher resistance than metal elements and converts a higher percentage of electrical energy. This lowers the energy consumed and minimizes energy lost to the surroundings.
“After switching to ceramic heating element in our kilns, energy loss reduced by 45%” — Meilin W., Design Engineer, Nutric Kilns
4.5 High Thermal Stability
-
Your high ceramic heating element maintains its shape, chemical properties, and performance at high temperatures with <0.001% deformation. This is due to their high 熔点 resulting from the ceramic stable crystal structure.
4.6 Corrosion Resistance
-
Metal elements are susceptible to corrosion and would degrade in such environments.
-
Your ceramic heating element is inert and resistant to corrosion and chemicals, providing superior performance and longevity.
5. Ceramic Heater Working Principles
5.1 Resistive Heating
-
Electricity flows through your ceramic heating element or ceramic heater plate with a high electrical resistance. Since the electrical resistance opposes flow of current, your ceramic heating element heats up.
5.2 Heat Transfer
-
Your heated ceramic heating element in your room heater transfers heat to surrounding air.
5.3 Thermostat Control
-
一个 thermostat monitors your room and controls your ceramic heating element.
5.4 Ceramic Heating Element Self-Regulation (PTC Behavior)
-
Most ceramic heaters use your Positive Temperature Coefficient ceramic element because regulates itself. Your PTC element gets more efficient as it continues to heat up.
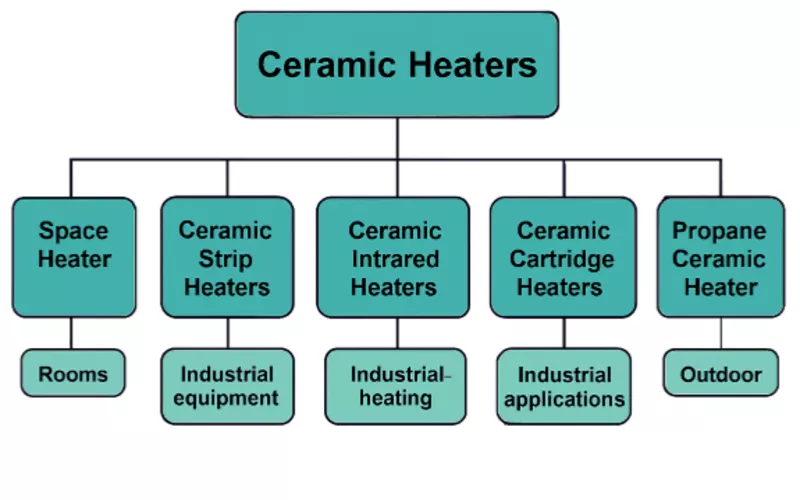
6. Types of Ceramic Heaters
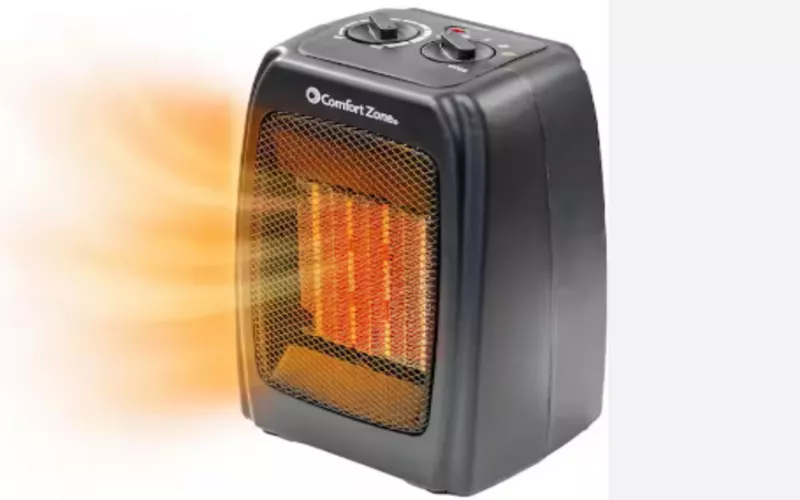
6.1 Space Heater

-
Your ceramic space heater uses a compact ceramic heating element and a fan to warm your room fast. It is safe, has a thermostat, and is and portable, making it ideal for heating your room.
“We always use ceramic heaters in our control rooms during winter. None of them overheats and they usually give consistent warmth.” —Eric M., Facility Supervisor, KenKom
6.2 Ceramic Strip Heaters
-
A ceramic strip heater offers surface heating for your industrial equipment. It’s usually mounted on flat surfaces.
-
With an aluminium housing, your ceramic strip heaters ensures strength and uniform distribution of heat.
6.3 Ceramic Infrared Heaters
-
Your ceramic infrared heater’s emissivity allows it to blow out infrared thermal radiation at low wattage. It’s ideal for your drying and curing process because it heats objects directly.
6.4 Ceramic Band Heaters
-
Ceramic band heaters are cylindrical, and they wrap around your cylindrical pipes, molding machinery, and barrels. It provides consistent heating, with a ceramic insulation layer that improve energy efficiency by up to 40%.
6.5 Ceramic Cartridge Heaters
-
As a compact, high-density heater, your ceramic cartridge heaters locolize heating in molds and dies. They are used in your 3D printers, plastic molding, and lab equipment for precise and intense heating.
6.6 Propane Ceramic Heater
-
Your propane ceramic heater combine combustion and ceramic radiant heating. It’s used in your outdoor heating and construction sites.
6.7 Radiant Ceramic Heater
-
Most ceramic heaters transfer heat though convection. Your radiant ceramic heater uses radiation intead. They pprovide silent, draft free heating, making them ideal for delicate coating and laboratory use.
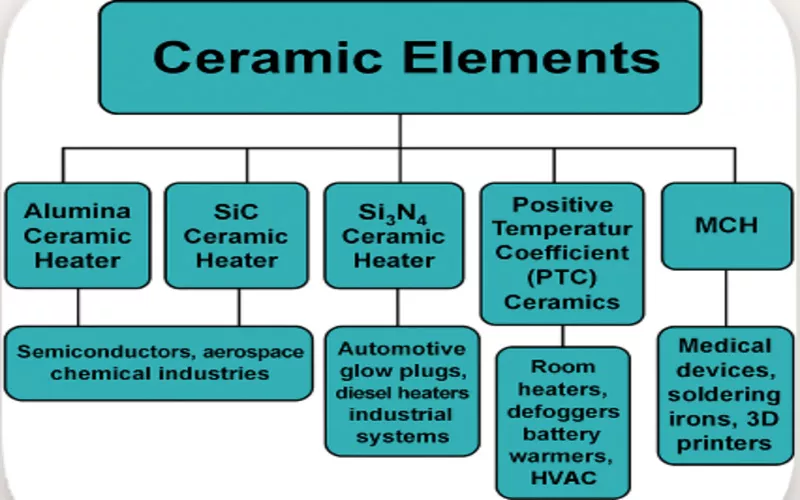
7. Types of Ceramic Heating Elements
7.1 Alumina Ceramic Heater
-
你的 氧化铝陶瓷加热器 uses 氧化铝 (Al₂O₃) due to its thermal conductivity of 24-27 W/(m·K) and excellent insulation. With compressive strength >2000 MPa, alumina elements work reliably at 1750+°C without deformation.
选择 GGSCERAMIC® for ISO-certified alumina ceramic heating elements that guarantee high-precision heating.
7.2 Silicon Carbide Ceramic Heater
-
For both semiconductor behavior and resistance to 1750+°C, your silicon carbide (SiC) ceramic heating element is an excellent choice. As heating increases, it’s resistance increases, offering your electric heater self regulation.
7.3 Silicon Nitride Ceramic Heater
-
你的 silicon nitride (Si₃N₄) heating element delivers flexural strength of 800-1000MPa and exceptional thermal shock resistance. With its superior endurance, this element is ideal for your semiconductor wafer heating and automotive applications.
7.4 Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) Ceramics
-
Your PTC heating element increases resistance as temperature rises. This ability to regulate itself eliminates overheating and boosts safety. PTC heaters like the 24V 200W PTC heater are ideal for your compact electric devices and climate systems.
7.5 Metal Ceramic Heaters (MCH)
-
Your MCH element uses a metallic heating circuit in a ceramic substrate. This element is ideal for your automotive sensors and household appliances, as it provides uniform temperature distribution.
8. Applications of Ceramic Heating Elements
8.1 Space Heaters
-
Your space heaters uses compact ceramic elements to convert electrical energy into radiant or convective heat. Their design is energy efficient, reducing consumption.
8.2 Water Heaters and Cooking Appliances
-
Your ceramic heating coils are used in consumer appliances like ovens, toasters, and hot plates because they deliver consistent heat.
-
Your electric ceramic heaters provide efficient, long-lasting heating required in your electric water heaters and boilers.
8.3 Industrial Furnaces and Kilns
-
Your high temperature ceramic heating element supports temperatures >1700°C for your sintering and melting operations. Due to hardness >1500 HV, wear resistance increases by 40% in grinding and furnace environments.
8.4 Industrial Packaging
-
Your automatic packaging lines would be unreliable without proper sealing. Ceramic strip heaters provide consistent sealing temperatures and withstand continuous cycles. This reduces downtime in your industry.
8.5 Drying and Curing
-
Your ceramic infrared heater speeds up paint and coating curing processes. Because of its uniform radiant heat, drying times gets shortened by up to 50%.
8.6 Medical and Laboratory Equipment
Your sterilizers, analyzers, and DNA amplification equipment demands precision heating. Your Si₃N₄ and alumina heating elements offer purity >99% and stable performance. This ensures accuracy and eliminates contamination in your processes.
9. Ceramic Heaters Vs Other Electric Heaters For Rooms
9.1 Ceramic Heater Vs Infrared Heater
-
When comparing your ceramic heater vs infrared heater, difference lies in heat transformation. Your ceramic heaters warm the air and are preferred for enclosed spaces, while infrared heats objects directly.
9.2 Ceramic Heater Vs Oil Heater
-
The difference between ceramic heaters vs oil heater is in their response times. Your ceramic heaters offer faster heating while oil heaters require longer preheating. However, oil heaters retain heat longer after switching off.
9.3 Ceramic Heater Vs Fan Heater
-
Your ceramic heater consumes less power than a fan heater. Fan heaters are cheaper, but they are noisier and distribute heat more unevenly compared to ceramics.
10. How to Select the Right Ceramic Heating Element
10.1 Choosing the Right Ceramic Heater Decision Flowchart
10.2 Choosing the Right Ceramic Heating Element Flowchart
10.3 Factors To Consider
-
Ensure your ceramic heating element meets temperature and power requirements, size, and shape. Your ideal ceramic wall heater also balances cost and efficiency.
10.4 Certification Checks For Quality
-
Your electric ceramic heaters must adhere to the ISO AND ASTM standards. Verify your supplier certification when selecting a ceramic heating element manufacturer for your application.
选择 GGSCERAMIC® for ISO-certified 陶瓷加热元件 that ensure consistency and performance.
结论
Your ceramic heaters use a ceramic heating element to convert electricity to heat energy. Your ceramic heating elements are preferred over oil, infrared, and fan heaters due to their exceptional properties. Your SiC, Si3N4, and alumina heaters provide resistance to both temperatures >1700°C and corrosion and longevity.
FAQs About Ceramic Heating Elements
Q: What is the difference between a ceramic heating element and a ceramic heater?
A: Your ceramic heater is the core component that generates heat. Your ceramic heater is the entire device that delivers heat using the element.
Q: What are the benefits of ceramic heaters?
A: Your electric ceramic heaters provide energy efficiency, safety, portability, and durability under harsh temperatures or corrosive environments.
Q: Are ceramic heaters energy efficient?
A: Yes. Your ceramic heaters heat up faster, store, and retain heat well, which minimizes energy waste.
Q: Which are the top examples of ceramic heating elements?
A: Examples include ceramic band heaters, PTC heaters like the 24v 200w PTC heater, and space heaters.
Q: How long does a ceramic heating element last?
A: Your ceramic heating element lasts 7-15 years because it withstands high temperatures, resists rust and corrosion, and is durable.