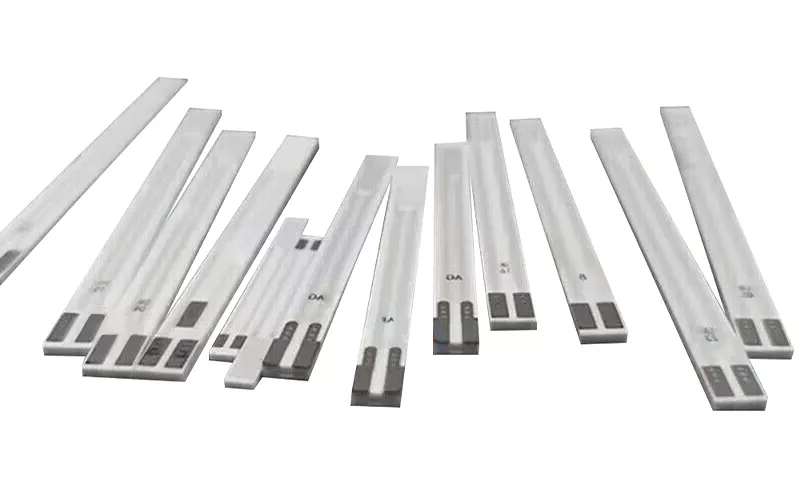
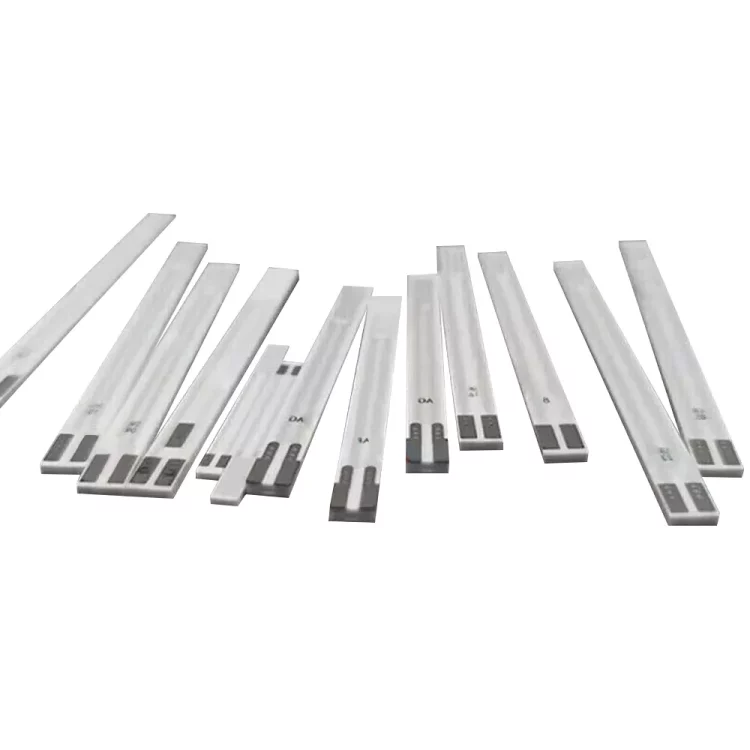
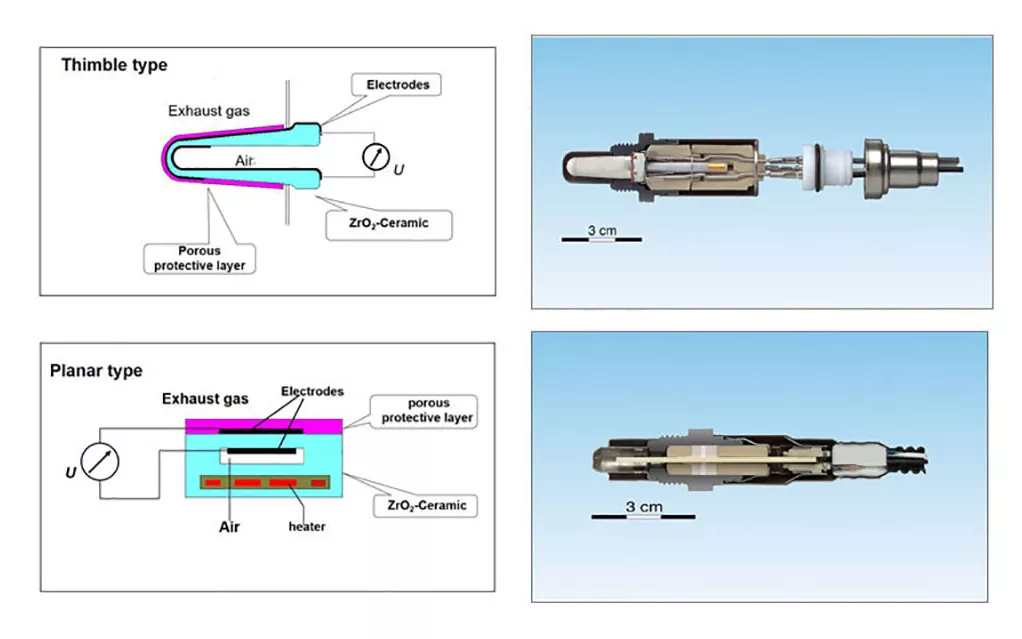
Oxygen sensors are used to monitor the oxygen content in vehicle exhaust in real time, and the ceramic heater plays a crucial role in the normal operation of the oxygen sensor.
When the sensor is working, the heating element heats the zirconia ceramic to its operating temperature, giving it excellent oxygen ion conductivity.
In this state, oxygen ions migrate from the side with high oxygen concentration (air side) to the side with low oxygen concentration (exhaust side), thus forming a measurable electrical signal.

As an important component working in conjunction with the three-way catalytic converter to reduce exhaust emissions, the oxygen sensor detects the oxygen potential in the exhaust pipe through its ceramic sensing element, helping the engine control system to precisely adjust the air-fuel ratio.
Based on the sensing material used, oxygen sensors can be divided into two categories: zirconia oxygen sensors and titanium dioxide oxygen sensors.
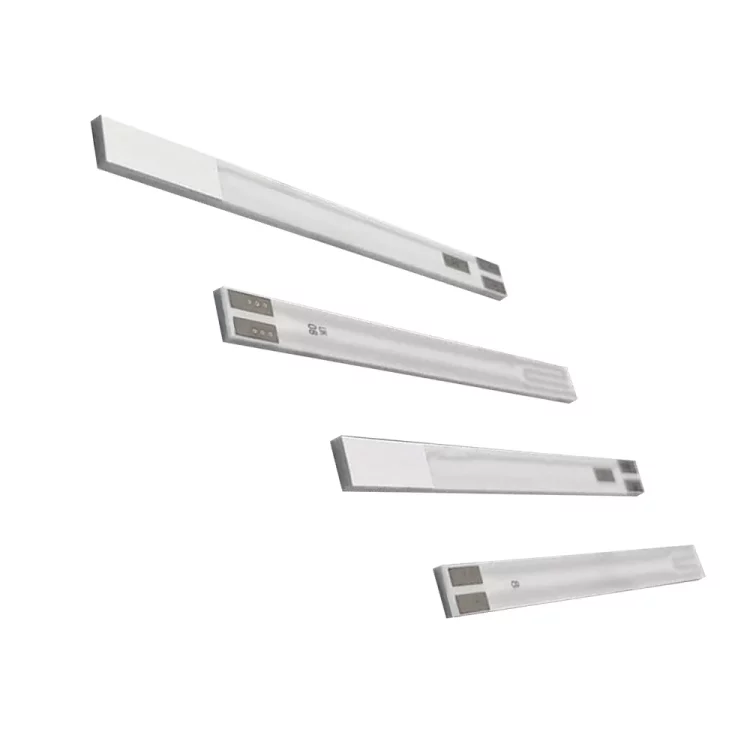
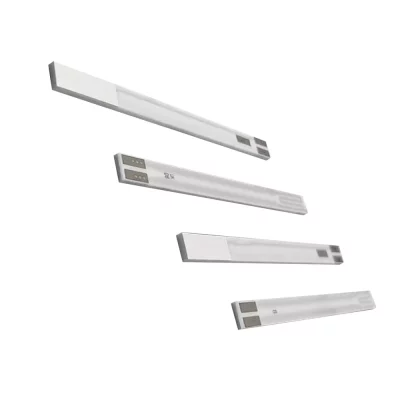
Characteristics of Planar Ceramic Heating Rods in Chip Oxygen Sensors
- The product has a fast ignition time.
- It possesses better insulation properties.
- It has higher temperature resistance and stronger resistance to poisoning.
- It has a long service life and is available in pump current switching type, conventional switching type, air-fuel ratio type, and wide range type.
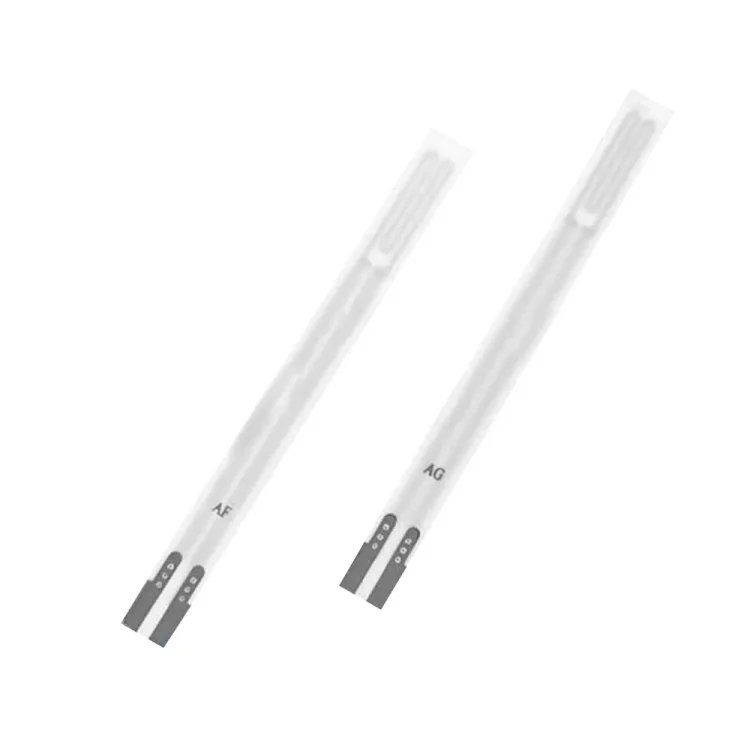
Examples of DENSO’s Zirconia Chip Automotive Oxygen Sensor Specifications
- Dimensions: 46.2*4.0*1.45mm
- Resistance: 2.1Ω (@24℃+/-3℃)
- Material: Zirconia
- Operating Voltage: 13V+/-1V
- Current: 0.5+/-0.1A@13.5V
- Insulation Resistance: >100MΩ
- Normal Operating Temperature: 350-850℃
- Maximum Continuous Operating Temperature (250h): 1000℃










