Ceramic igniters offer excellent insulation, high-temperature resistance, wear resistance, and durability. Alumina and silicon nitride ceramic igniters, in particular, ensure a long service life for your gas furnace systems, burners, and biomass applications.
2. What Is an Ignitor?
2.1 Definition
-
An ignitor is an electrical conductor device used to light or ignite fuel, charges, or fire.
-
Your ignition electrode generates a spark to initiate combustion in your fuel appliances, such as furnaces and burners.
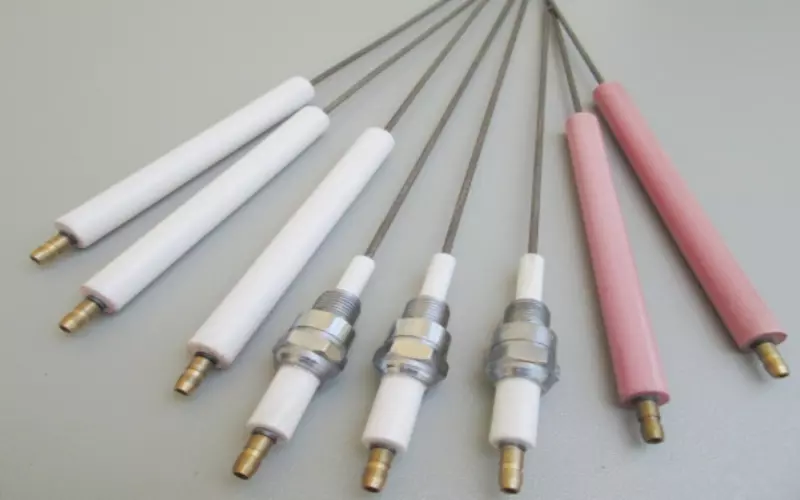

2.2 How Does a Piezo Igniter Work
-
لك piezo igniter consists of a piezoelectric crystal. When mechanical force is applied to the hammer, the crystal generates a high-voltage electrical charge in response to the deformation. The electric charge is transferred to your electrode, and it creates a spark that ignites your gas.
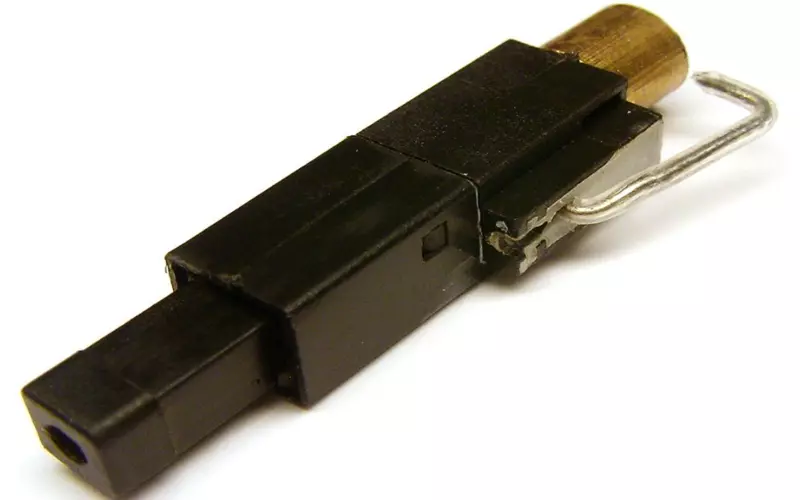
2.3 How Does a Spark Igniter Work
-
For your spark igniter, a high-voltage discharge is created in a small space between two الأقطاب الكهربائية. When power is applied to your module, it creates a spark. The spark ignites your fuel and air mixture. Your flame rod is used to confirm the establishment of the flame.
2.4 How a Furnace Hot Surface Ignitor Works
-
لك thermostat calls for heat, and the inducer motor starts for safe exhaust. The furnace board sends power to the igniter, which converts the electrical energy to heat, and it glows. The gas valves open, releasing gas to the burners. The gas reaches the heated igniter, causing it to ignite.
3. Your Ceramic Ignition Electrode
3.1 How Does a Ceramic Igniter Work?
-
لك سيراميك igniter uses silicon nitride’s 10^14 - 10^15 Ω·cm resistance to generate heat >1000°C. When this heat mixes with air, it heats up to a point where it can ignite your biomass or burners.
3.2 Materials Used for Your Ceramic Igniter
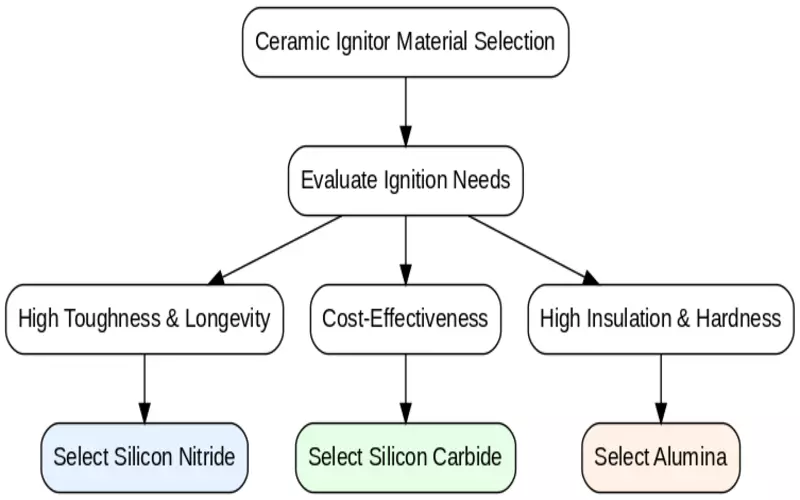
3.2.1 Alumina Ceramic Igniter

-
Your alumina ceramic igniter offers a hardness of 9 on the Mohs scale, ensuring resistance to wear and erosion.
-
With a temperature resistance >1750°C, it ensures your operation stability and excellent insulation.
3.2.2 Silicon Nitride Igniter
-
لك مشعل نتريد السيليكون offers fracture toughness 5.6 to 7.6 MPa·√m, ensuring superior durability and service longevity in your furnace systems.
-
Its fast ignition ensures efficiency, and it also provides temperature and oxidation resistance >1750°C.
3.2.3 Silicon Carbide Igniter

-
Your silicon carbide igniter is a cost-effective option that resists temperatures up to 1750°C.
Note: Silicon carbide is brittle. Careful handling during installation is crucial to prevent cracking and breaking. ISO-certified supply and ongoing maintenance are also required to minimize failures.
3.3 The Ceramic Firing Process
-
In your ceramic firing process, ceramic materials are shaped, dried, and fired at temperatures >1740°F (1000°C). Your grain boundaries get densified, which boosts strength, thermal conductivity, and insulation. Precision in the process is key to your igniter’s reliability and longevity.
4. Benefits of a Ceramic Ignition Electrode
4.1 Durability and Long Life
-
Your ceramic igniter’s thermal stability, wear resistance, and strength result in an extended life span. This ensures reliability in your industry as there are fewer replacement cycles and downtimes.
“We’ve been using ceramic igniters for over 7 years now and haven’t seen a single failure in our pellet stoves.” — Yu S., Procurement Manager, Pellceras Solutions
4.2 Fast & Reliable Ignition
-
Your ceramic igniter heats up fast to reach ignition temperatures 1000°C+. This means less startup time, less wasted fuel, and increased efficiency in your furnaces and pellet grills.
4.3 Energy Efficiency
-
Since your ceramic ignition electrode converts electrical energy to heat in seconds, it reduces energy waste. This efficiency translates to cost savings in your operations.
4.4 High Operating Temperature
-
Traditional igniters would degrade under 1000°C, but your ceramic ignitor withstands up to 1750°C. This ensures performance and consistency in your biomass systems.
4.5 Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance
-
Metal igniters get oxidized at high temperatures, reducing their lifespan.
-
Your ceramic igniter resists oxidation and chemical attack, ensuring reliability in combustion and corrosive environments.
“Switching from metals to alumina igniters reduced our maintenance costs by 46%” — Alexa W., Design Technician, Funsh Systems
4.6 Versatility
-
Your ceramic ignition electrode works for applications such as pellet stoves, boilers, biomass burners, and fuel cells. Due to the ceramic materials’ exceptional properties, your igniter is flexible. Their formatibility and design flexibility make your ceramic igniter customizable.
5. Applications of a Ceramic Igniter
5.1 Gas Furnace Systems and HVAC
-
Your ceramic igniter offers stability under temperatures >1000°C. This ensures reliable ignition for residential and commercial heating in your gas stoves, ovens, water heaters, and boilers.
-
Select GGSCERAMIC® for ISO-certified solutions for your HVAC uses.
5.2 Biomass Heating Systems
-
Traditional ignitors would fail under the ash and dust conditions of your biomass fuels. Your ceramic pellet igniter performs reliably despite the challenging conditions. It’s also durable, minimizing replacements.
“After switching to ceramic pellet igniters in our boilers 3 years ago, we saw a 30% reduction in failures, and they actually light up very quickly” — Lars M., Operations Engineer, Biofaction Systems
5.3 Industrial and Commercial Tools
-
Your Alumina and silicon nitride ceramic igniter withstands repeated thermal cycles without a single crack. Together with its performance and reliability, it’s ideal for your commercial ovens, industrial kilns, and burners.
5.4 Water and Exhaust Systems
-
Due to your ceramic ignition electrode’s stability, it supports your exhaust after-treatment and water heating processes.
-
Your ceramic igniter maintains controlled combustion and cleanliness, ensuring compliance with emissions standards.
5.5 Solid Oxide Fuel Cells
-
Your ceramic ignitor maintains performance under temperatures >1750°C. This ensures renewable energy development and efficient electricity generation when used to initiate reactions in your solid oxide fuel cells.
6. Maintaining and Troubleshooting Your Ceramic Ignition Electrode
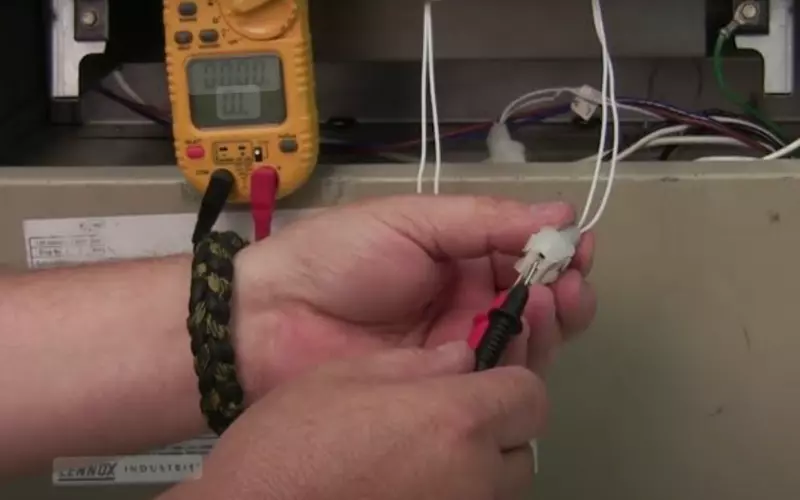
6.1 How to Test Your Hot Surface Ignitor
-
Disconnect the power and then remove your ignitor.
-
Check the resistance using a multimeter. The normal range is between 40 and 200 ohms, but infinite resistance indicates failure.

6.2 How Do You Know If a Furnace Ignitor Is Bad?
-
Signs include visible cracks or white residue, delayed ignition, or repeated startup failures.
-
Non-glowing ignitor and overload resistance also suggest failure.
6.3 Replacement Cycles & How Long Does a Furnace Ignitor Last
-
Your furnace hot surface ignitor lasts 3 to 10 years. Operating conditions and material quality impact service life.
-
Regularly inspect your ceramic ignition electrode to prevent unexpected downtime.
7. What to Look For When Buying Your Ceramic Igniter
7.1 Specifications to Check
-
Review critical parameters such as voltage, material, ignition time, and temperature rating.
-
Match specifications to your application’s demands to ensure safety and efficiency.
7.2 Ceramic Ignitor Material Selection Flowchart
7.3 What to Look For in a Ceramic Igniter Supplier or Manufacturer
-
Look for suppliers who guarantee ISO-certified quality and technical support. China ceramic igniter suppliers offer large-scale production at competitive prices. Select GGSCERAMIC® for tested, reliable ISO-certified ceramic igniters.
8. Frequently Asked Questions About Ceramic Ignition Electrode
Q: What are the applications of a ceramic igniter?
A: Your ceramic ignitor is used in gas furnaces, pellet grills, boilers, biomass heaters, kilns, and fuel cells.
Q: How long does a furnace ignitor last?
A: Your furnace ignitor typically lasts 3 to 10 years. Service life is influenced by operating conditions and material quality.
Q: What are the benefits of a ceramic ignition electrode?
A: Your ceramic ignition electrode offers long life, fast ignition, energy efficiency, corrosion resistance, and versatility.
Q: How does a piezo igniter work?
A: Your piezo igniter uses mechanical force on a piezoelectric crystal to generate a spark.
Q: How does a spark igniter work?
A: Your spark igniter produces a high-voltage discharge between electrodes to ignite fuel.
خاتمة
Your ceramic ignition electrode combines science, durability, and efficiency. By selecting the right material and supplier, your industry benefits from reliable performance in heating and combustion systems.
GORGEOUS is a leading international ceramics supplier, offering a wide range of ceramic heaters/igniters. Please feel free to اتصل بنا with any technical questions.